HIGH Middle Ages: main CHARACTERISTICS

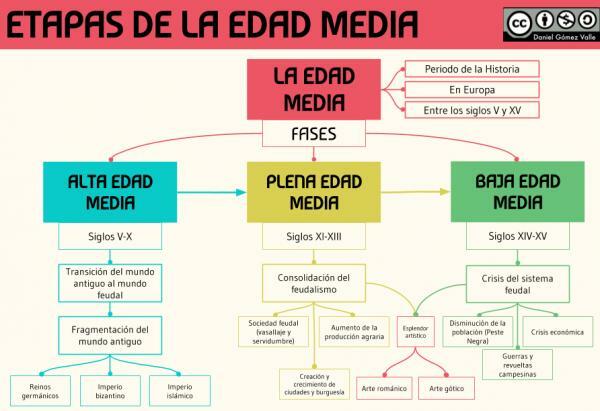
The great historical periods of our existence are usually divided into several phases in order to understand the evolution of some of its characteristics, such as the Middle Ages is divided into the High, the Full and the Middle. To know the beginning of the medieval period in this lesson from a Professor we must talk about the characteristics of the High Middle Ages.
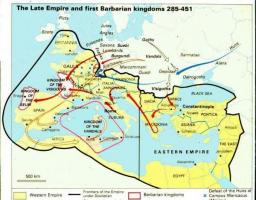
The High Middle Ages is he first of the periods into which the Middle Ages. The start date of the period is a matter of dispute, since some historians place its beginning in the reign of Charlemagne, although the most accepted is usually that starts at V and ends at X, being its beginning the the fall of the Roman empire of the West and its end in the Crusades.
We must bear in mind that the High Middle Ages used in Spanish historiography is not the same for German or British scholars, since for this first period of medieval history tend to use the concept of the early Middle Ages, using the term High Middle Ages for what we know as Full Age. Half. In the case of this lesson, when the Spanish sources are used, we must speak of the High Middle Ages as the period
between the 5th and 10th centuries.The High Middle Ages is one of the more complex historical periods, already because it signifies the change between two societies as different as the ancient and the medieval, if not also because it is a period of huge tension due to the existence of three cultures as powerful and different as they were Christian Europe, the growing Islam and the Byzantine Empire.
Image source. Professor Francisco
To understand the High Middle Ages it is necessary to talk about its main characteristics, to understand the reasoning that makes us divide the Ancient Ages and the Middle Ages as two very different elements between Yes. The main characteristics of the High Middle Ages are as follows:
- A new way of governing, at the beginning with monarchies strong dynastically such as the Carolingian Empire, and later with the rise of the social class of the nobility how much power he had.
- Birth of the feudalism, an economic and social system that replaced the slavery, based on an agreement between the lords and the servants.
- The rise of feudalism brought new social classes, forming the estates that divided the population into nobility, clergy and peasants.
- Much of this time was marked by the conflicts between the nobility and the monarchy, there were tensions and even wars over who was really the central power.
- Religion was the center of everything, being the confrontation between Christianity and Islam an absolute constant, and causing numerous wars for being the predominant belief in the known world.
- The Byzantine Empire it was trying to go back to what the Roman Empire once was, but was attacked and overtaken on numerous occasions by Muslims and Slavs.
- The Islam had a rapid and extensive evolution, Rarely seen in the history of humanity, forming three great caliphates that dominated much of the world.
- The economy during the High Middle Ages it was predominantly rural, being a subsistence system in which most of what was produced was to feed the population.
- The Catholic Church was almost more powerful than the kings themselves, who needed his permission to marry, make pacts or be crowned, forming an essential relationship between nobility, monarchy and clergy.
- The art essential is the Romanesque, being able to create numerous churches in a short time for fear of the arrival of the honey year that they considered the end of civilization.
- Culture focuses on monasteries, where texts from Latin are translated and almost all relevant texts exist.
- The invasions of foreign peoples become the predominant element of the High Middle Ages, first the Germanic peoples who took much of Europe after defeating the Romans, then the Muslims who took Africa and much of Spain in their expansion, and finally the vikings that began the looting and conquest of much of Europe.

To conclude this lesson on the characteristics of the High Middle Ages, we must make a brief summary about this period of the history and know the main events that took place and the relevance they had to create the characteristics that we have named.
The High Middle Ages as such starts in 476 with the fall of the Western Roman EmpireThis is the moment when the world map changes and two control events occur: first, with the survival of the Eastern Roman Empire and the formation of the Eastern Byzantine Empire; and on the other hand, the German invasions throughout southern Europe, forming numerous kingdoms that, although at first pagan, eventually became Christian. These German invaders, like the Goths or the Avalos, they were the fathers of the monarchies that we know today.
In another part of the world, the prophet Muhammad founds the religion known as Islam, which has a strong base of Holy war for its expansion. For this reason, after the death of Muhammad, a rapid military expansion of the Muslims began, reach the Iberian Peninsula, facing the Visigoths already Christianized for control of the region.
After defeating the peninsulares, the Muslims sought continue its expansion in Europe towards France, but were stopped and defeated at the Battle of Poitiers by the Franks, who years later would form the great kingdom of the High Middle Ages, known as Carolingian empire.
In this situation we already find the three great forces of the European medieval world, being Byzantium, the Muslim Empires, and the Carolingian Empire which, later, would be divided into the kingdoms of France and the Holy German Empire. The Carolingians were joined by the Papal States, forming what is known as medieval Christianity, forming one of the great forces.
Finally, the arrival of the Viking invasions and the end of the Muslim expansion led to the end of the High Middle Ages and to the passage known as Full Middle Ages.