Al-Ándalus: Muslim Art in Spain

The muslim art or also known as Islamic art is the set of artistic manifestations that occurred in the different religious areas of Islam. Within the regional focuses we have to highlight Al Ándalus, the peninsular territory conquered by the Muslims in the year 711 and which ended in 1492 after the conquest of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada by the Kings Catholics. Next, in this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to discover the Muslim art in Spain so that you better know the legacy that the invasion of the Arabs left us.
We start this summary of Muslim art in Spain focusing on architecture.
Islamic architecture is a mixture of elements taken from other artistic styles such as Visigothic art, from which they took the horseshoe arch or Roman art from which they copied the use of bicolor voussoirs, columns and semicircular arches, with the difference of employing great technical-constructive innovations that would make them stand out from the rest, and They are:
- The buildings will be of dimensions regular Y horizontal, that is to say, of a plant.
- The materials used for its construction will be mainly the lbrick and the wood and the cast.
- The closing system for these buildings will be the vaults and domes, among which we could highlight the ribbed vaults, the muqarnas vaults and the gallon domes.
- The pillars Y columns will be the supporting elements, generally thin since the roof was not usually very heavy.
- We will also see the use of arches, the most notably used being the Horseshoe arch, although we will also see the presence of Round arches, the pointed arches and the lobed arches or polylobulated.
- The decoration exterior is austere, however, in the inside it is the opposite, since we will see a varied and rich ornamentation based on tiles, plasterwork, wood, marble... to hide their poverty.
- In decoration, the theme can be of three types; vegetable or also known as ataurique; from geometric motifs, based on lacerias or stars; epigraphic, which is what the writing captures.
There are two types of constructions in Muslim architecture, one of a religious typology whose building is more representative is the mosque, and a civil typology that are the alcazabas, castles, palaces and baths public.
In this other lesson from a TEACHER we will discover a summary history of Al Andalus.

We continue with this summary talking about the different stages. We are going to discover the five periods or stages in which you can classify Islamic art in Spain depending on the different reigns there were:
Cordoba or Caliphate period (8th - 11th century)
It receives many influences from Visigothic art, especially due to the use of horseshoe arches and Hispano-Roman art due to the way of placing rope and brand rigging. It is also very characteristic to see in the constructions the alternation of voussoirs in color and texture, the alfiz that is It is a molding subordinate to architecture, specifically to frame well the arches or the openings of windows or doors.
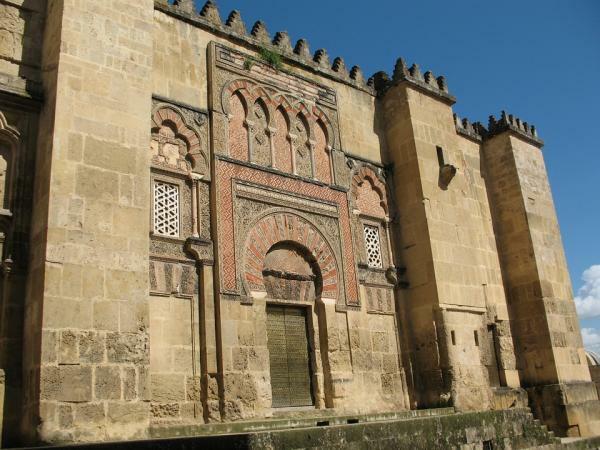
The great work of this period is the Mosque of Córdoba, a work built on an old Visigothic basilica from which its columns and capitals were used, as this It is another of the characteristics of this period to take advantage of many of the construction materials of buildings previous.
Period of the Taifa kingdoms (11th century)
The art of these kingdoms was characterized by emulating the splendor that occurred in the previous stage and by what has been called popular baroque, that is to say, an excessive overload in the ornamentation constructions. The materials were characterized by being low cost (plasterwork), but despite performing their function The main thing that was to decorate, being a very poor material, very few buildings have been able to keep.
Among them we could highlight the Aljafería Palace in Zaragoza, which is a palace-fortress, very austere on the outside but very decorated on the inside.
Almoravid period (12th century)
His artistic manifestations were characterized by the use of the mocárabe, a decorative element that is, let's say, a kind of stalactite that hangs from the arches and domes and is made of plaster, often polychrome.
It is an art owed to the Taifa kingdoms, however, there are hardly any remains and samples significant of this period, being the best conserved those that are in the north of Africa.
Almohad period (12th century)
This civilization came to the Peninsula and brought with it one of the most original elements that had not occurred so far, it is what is known as sebka, a type of geometric decoration in the form of a network of superimposed rhombuses that masks the construction systems.
To cite some example we have to say that the most important mosque of this period was that of Seville, of which the patio of the orange trees and part of the minaret, today known as the Giralda, where you can see the sebka cloths externally.
Period of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada (14th - 15th centuries)
Granada was characterized by being a very rich, independent and powerful town and in this way it will be reflected in the monument par excellence of this period, the Palatine complex of the Alhambra in Granada. It is a return to the sumptuous art that we saw at first and a reaction against the austerity of the Almohad period from which it takes, however, some elements.
Regarding the materials, they will be poor but covered with plasterwork, marble, sebka cloth and tiles. As for the most used construction elements, they will be the banded semi-circular arches and the columns of white marble with very thin shafts and Corinthian capitals.

Unfortunately there are very few sculptures and paintings referring to this period of Islamic art, although we do know that the Muslim decorative arts were very varied, ranging from ceramics, through carpets, fabrics, goldsmithing…. Among the few sculptural works that have been preserved, it is worth highlighting the bronze fawn from Medina Azahara, dated around the second half of the 10th century.
One of the most important industries in Caliphate Córdoba was the manufacture of carved caskets in ivory or jars whose function was to store valuables or perfumes, so we highlight the boat of the cathedral of Zamora, cylindrical in shape and conical top.
In painting deserves mention the fresco on treasure painted in the vault of the hall of the Kings of the Alhambra of courtly themes and hunting.
If you want to expand your historical knowledge, in this other lesson you will learn a summary on the Muslim invasion in Spain.