Classification of BIOELEMENTS
What atoms are living things made of? In this article by a PROFESSOR we will learn that, of all the chemical elements that exist in the universe, only a few are part of living matter: bioelements. But not all bioelements are the same and in this lesson we will see what is the classification of bioelements and what criteria it is based on.
Index
- What are bioelements? Principal functions
- Primary bioelements, the first group of the bioelements classification
- Secondary bioelements
- Trace elements
What are bioelements? Principal functions.
Bioelements, also called biogenic elements, are all those chemical elements that are part of living organisms. They are not presented in isolation, but rather form the molecules own of living beings called biomolecules, many of them large (macromolecules).
Bioelements are presented in very different proportions in the composition of living beings. While some bioelements are very abundant in the composition of living beings, others are found in less quantity and some are found in living organisms in very small quantities.
Although bioelements are also present in the inert medium (geosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere) the proportions in which they are found in living beings are very different from those in the environment. For example: carbon represents only 0.18% of the inert medium, while in the human body its proportion is much higher: 19.37%. Therefore, living beings accumulate relatively few elements in their bodies in the inert environment and this represents a significant consumption of energy.
Bioelements functions
Bioelements can also be defined as those elements that are essential for life because they participate in any of these biological processes:
- They participate in the construction of body tissues
- They are involved in the development processes of the organism
- They help regulate metabolism.
Of all the 92 natural elements that exist, only some are bioelements. The total number of bioelements differs considerably depending on whether they are considered to be bioelements or not elements found in the organism in very low proportions, since in these cases it can be difficult to demonstrate its role biological. We can consider that there are between 20 and 27 bioelements.

Image: Yumpu.com
Primary bioelements, the first group of the bioelements classification.
As we have already commented, the bioelements that are part of living beings can have very different proportions. While some are very abundant, others only appear in small quantities.
The classification criterion for bioelements it is based precisely in proportion in which these are forming part of living organisms. The classification of bioelements may be different depending on the author consulted, with regard to secondary bioelements and trace elements.
According to the proportion in which they are forming part of living matter, they are distinguished three groups within the classification of bioelements: primary, secondary and trace elements.
What are primary bioelements?
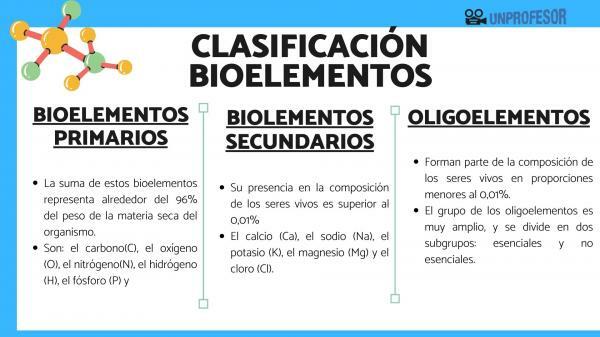
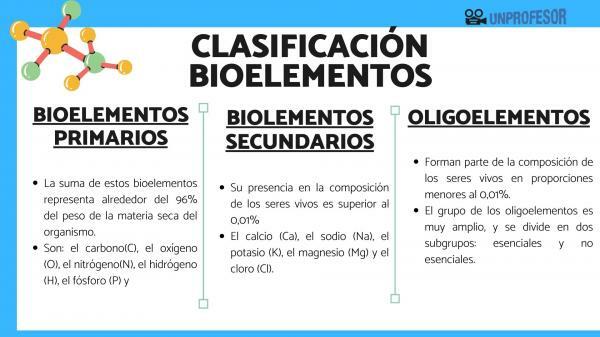
The primary bioelements are: carbon (C), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S).
They are the elements that are found in a higher proportion in the composition of living organisms. The sum of these bioelements represents around 96% of the body's dry matter weight.
The reason why they are found in such high proportions is that they are essential elements for the construction of biomolecules. This is so because all these atoms have a characteristic that makes them suitable to fulfill this function:
- They are small atoms. This allows them to form very stable covalent bonds that contain high energy.
- Except in the case of hydrogen, they have the ability to form single and multiple bonds, which makes possible a great diversity in the type of molecules they can build.
- The high electronegativity of elements such as nitrogen or oxygen gives rise to molecules that have a certain polarity (asymmetric distribution of charges) that allows the dissolution of many biomolecules in water (the medium where all the biological reactions).
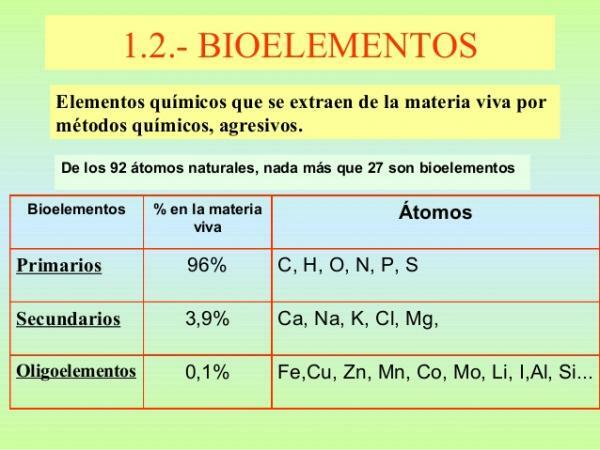
Image: Slideshare
Secondary bioelements.
Within the classification of bioelements we must also include the secondary ones, which are: andl calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg) and chlorine (Cl). Its presence in the composition of living beings is less than that of primary bioelements but greater than 0.01%. Together, these five bioelements represent around 3.9% of the weight of living organisms.
These elements are found in organisms as part of mineral salts or in ionic form.
In the form of salts
These bioelements have a structural function as constituents of bones, shells, shells, etc. An example is calcium, which is part of the salts that make up bones.
In its ionic form
They have a very important metabolic role as chemical messengers in the regulation of processes such as:
- The transmission of the nerve impulse in which calcium, sodium and potassium ions play a fundamental role.
- Muscle contraction where calcium ions are essential.
- Photosynthesis where magnesium is one of the components of chlorophyll (photosynthetic pigment)

Image: Youtube
Trace elements.
We finish the classification of bioelements to talk about trace elements, that is, those that are part of the composition of living beings in proportions less than 0.01%. Even if found in very small quantities, they perform vital functions. Trace elements are multifunctional and they act.
- Regulating metabolism as part of the active center of some enzymes.
- Stabilizing certain macromolecules or cellular structures such as plasma membranes.
The group of trace elements is very broad, and is divided into two subgroups: essential and non-essential. Essential trace elements are considered those whose deficiency causes alterations in growth or health. The elements are part of this group: Vanadium (V), molybdenum (Mo), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), zinc ( Zn), silicon (Si), iodine (I), (Se) and fluorine (F).
For example:
- Iron is part of the active center of hemoglobin that is responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood, its deficiency causes anemia.
- Zinc is essential for the development of plants and animals. This element in its ionic form catalyzes (regulates) more than one hundred enzymatic reactions and is a constituent of the plasma membranes where it performs an antioxidant role, helping to stabilize the bilayer structure lipid.
If you want to read more articles similar to Classification of bioelements, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Trudy McKee, James R. McKee (2020) Biochemistry: The Molecular Basis of Life (7th Edition), Mexico City: McGraw-Hill
- Javier Ramírez Hernández, María José Bonete and Rosa María Martínez-Espinosa Division of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Alicante. (2015). Proposal for a new classification of trace elements for their application in nutrition, oligotherapy, and other therapeutic strategies. Journal of Hospital Nutrition



