What are ACCESSORY bones and their function
When they tell us about human skeleton, the first thing they tell us is that it is constituted approximately by 204-206 bones. Isn't the number of bones that make up the skeleton fixed? The answer is no. There is a type of bone that only some people have while others do not... In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will explain to you what Accessory bones and their function and thus you will discover the reason why the total number of bones of the skeleton can only be approximated.
The vast majority of bones that are part of the skeleton they are bones that appear in all individuals equally. However, there is a small set of bones, the so-called bones supranumeraries (“extra” bones or extra bones) than do not appear permanently in all individuals, for this reason they are also called fickle bones.
Supranumerary bones may or may not be present in a given person. However, within the general population they appear with a relatively high frequency among the population, so it is considered that their presence is significant. The cause for which they sometimes form (etiology) is unknown.
The supranumerary bones can be accessory or sutural (The latter also known as Wormians). The difference between these two types of supranumerary bones is that, while the accessory bones are independent bones, unlike suturals, they remain attached to the joint in which they were created. Wormian bones appear in the skull frequently. While accessory bones are common in the feet and hands, they can also appear in other parts of the skeleton.

As we have already discussed, accessory bones are a supernumerary bone variety, which represent relatively frequent anatomical variations. It is estimated that more than 50% of the population has at least one accessory bone.
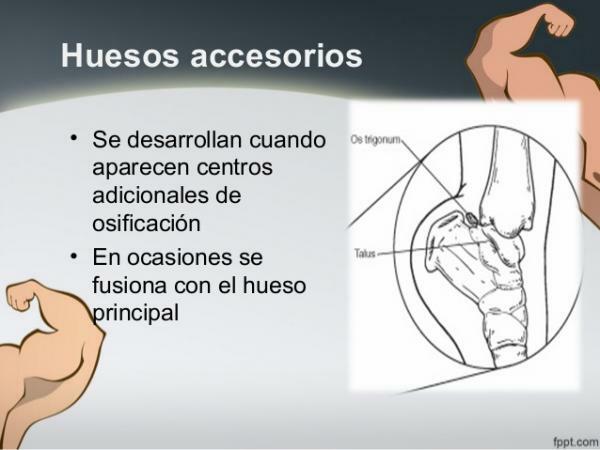
Accessory bones are formed when a center of ossification fragments and gives rise to several independent bones. Accessory bones are common in the hands and feet, although the spine and extremities may also have accessory bones.
Accessory bones do not develop a function in the body. These are bones that are asymptomatic, they do not suppose an advantage or a disadvantage for the individual who presents them. However, in some cases they can cause pain syndrome in response to overuse or trauma.

There is a great variety of accessory bones in the human skeleton, not being possible to study them in their entirety. Here we will see the most frequent examples.
Accessory bone of the Astragalus: the Trigonum or trine
The trigonum bone is an additional bone that sometimes forms at the back of the heel bone (talus) and is attached to it by a fibrous band. The presence of this bone in one or both feet is congenital (it occurs from birth). Only a small percentage of the population has this bone, between 1.7 and 7.7% of the population.
Some people with this accessory bone develop a painful condition called trigone syndrome, which is usually triggered by injury. The type of injury that causes this syndrome is called "Nutcracker injury" and occurs when, when pointing the toes down, the trigone is pressed between the bones of the heel and ankle and the fiber that attaches it to the talus is torn or pulled, producing inflammation.
Cervical rib
The cervical rib is an accessory bone that arises from the process of the seventh cervical vertebra and ends loosely in the neck tissue or articulates with the first rib. This accessory rib occurs more frequently in women, both in isolation and in association with other bone alterations. The cervical rib is the most frequent rib alteration and occurs in a percentage of between 0.2 and 1% of the population. It can be asymptomatic or cause supraclavicular pain or thoracic outlet syndrome.
Accessory scaphoid Tarsus
The accessory tarsal scaphoid is an accessory bone that some people have in the tendon that joins the tibia and the scaphoid of the tarsus posteriorly. This accessory bone can have different shapes, attached to the posterior tarsal tendon or even be fused to the tarsus after an ossification process that occurs in adolescence. The percentage of individuals with this accessory bone is between 10 and 14% of the population.
Fabella
It is a sesamoid accessory bone, that is, a small bone that attaches to the posterior tendon of the knee; in the same way that the patella attaches to the tendon in the anterior part of this joint. This small bone occurs between 12% and 23% of people and in most cases it is bilateral (it appears in both knees). It does not usually cause clinical problems.
Limbus vertebra
The limbus vertebra or limbus vertebra is an accessory bone that appears in the intervertebral space as a consequence of the separation of a part of the intervertebral disc during development and the appearance of a secondary ossification center that will give rise to this small ossicle Independent. This type of accessory bone most often forms in the lower back. It is not known what percentage of the population has this type of accessory bone.
Netter, Frank H. (2019). Atlas of Human Anatomy - 7th Edition Barcelona: Elsevier España, S.L.U.



