The parts of the nervous system
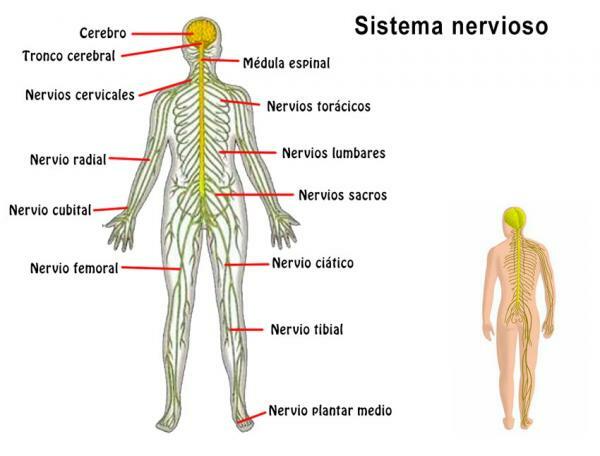
Image: Paxala
The nervous system It is composed of a huge and complex network that completely controls all aspects of human life, whose structural unit is the neuron. Regulates bodily activities, detecting changes in the internal and external environments, interpreting changes and reacting to stimuli, to carry out all the work that the body needs human.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to study what are the parts of the nervous system, that make up one of the most complex and important structures of the human body.
Before talking about the parts of the nervous system let's find out what are the basic functions of the same:
- Establish the relationship between subject and environment where it is.
- Regulate the functional mechanism of the various devices and systems that comprise it.
For the first function, count on the central nervous system (CNS), whose operation is voluntary and conscious; for the second, with the peripheral nervous system (PNS), involuntary and unconscious action, which is called relationship life because it allows the individual his relationship with the environment.
In this other lesson we will discover the nervous system functions.
To know which are the parts of the nervous system we have to know that it comprises two major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), formed by the cranial and spinal nerves, which originate in the CNS.
The central nervous system (CNS)
It is made up of the brain, cerebellum, isthmus of the brain and bulb, which together are called brain, and for the spinal cord or rachis. The brain is housed within the cranial cavity and the spinal cord, in the spinal column. The role of the CNS has to do mainly with sensations and voluntary movements. The messages that go to and from the CNS travel through the branches of the fibers of the peripheral nervous system, reaching all the extremities of the body.
The peripheral nervous system
The peripheral zone of nervous system comprises two sectors: peripheral and the autonomous.
The peripheral sector is known as peripheral nervous system (PNS) and it is made up of nerves that originate from the brain and spinal cord. Those that are born from the brain exit through the holes in the skull and are called cranial nerves. Its job is to connect the central nervous system with the organs, limbs, and skin.
The autonomous sector, called autonomic nervous system (ANS), It is called as the vegetative life, since it controls and regulates the physiological mechanisms in which there is normally no conscious attitude, such as breathing or the heartbeat. It is made up of two nerve cords and a set of ganglia. It therefore intervenes in the involuntary actions of the human body and decomposes into sympathetic nervous system, that stimulates activities that are accompanied by an energy expenditure, and parasympathetic, for activities that facilitate energy storage or saving.
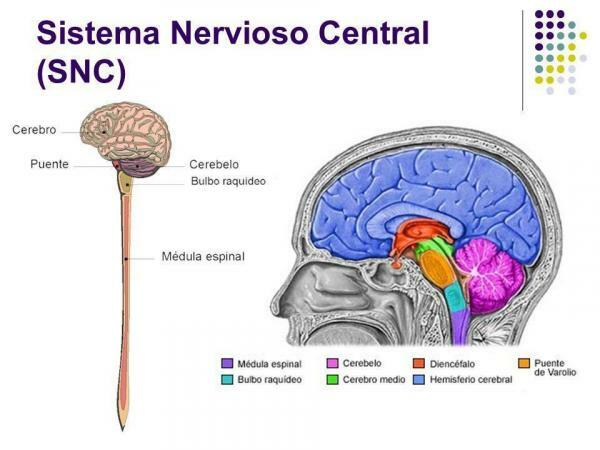
Image: Slideplayer
The neurons or nerve cells are the basic functional unit of the nervous system, specialized in the transmission of information in the form of nerve impulses.
Each neuron is divided into the following parts:
- Body or soma: where the nucleus and some corpuscles (Nissi granules) are located. Branches for all areas grow from the body.
- Dendrites: extensions made up of thick, short and highly branched fibers, the number of which varies according to their function. They pick up the messages from other cells.
- Axon: single fiber, long and branched, at its terminal end. An axon can extend from the CNS to the fingers or toes to actuate the muscles with which it works.
Axons and dendrites are nerve fibers that make up nerves. The point in the cell body from which each fiber emerges is called the pole.

