Differences between the central and peripheral nervous system
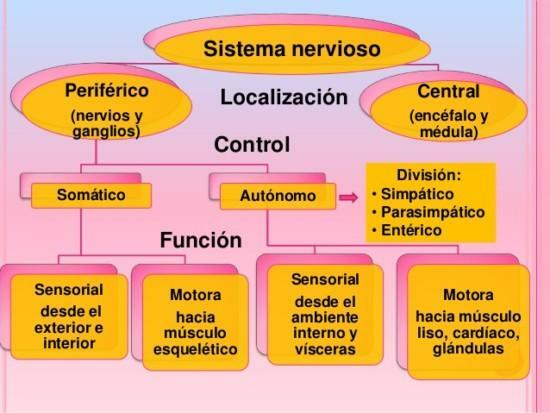
Image: Information | A Universe of Information
The nervous system It is a huge and complex network that regulates all aspects of human life and activity: from breathing to running, eating, and so on. It extends throughout the body and captures, interprets and acts on the basis of the data that is collected both from outside and inside the body. Next, in this lesson from unPROFESOR.com we are going to study the differences between the central and peripheral nervous systems so that you know our human anatomy better.
Before focusing on the differences between the central and peripheral nervous systems, we will discuss each of these systems in detail.
The central nervous system is made up of a huge and complex structure that collects millions of stimuli per second, which it memorizes and processes continuously, adapting the body responses to all conditions. It is the mechanism that regulates the entire structure of the nervous system and its main parts are the brain, cerebellum, isthmus of the brain and bulb, which together are called brain, and the spinal cord or rachis.
The CNS receives and processes the information collected by the nerve endings, giving concrete answers. It is surrounded by three membranes of connective tissue, which are called meninges. Between these there are spaces through which the cerebrospinal fluid, that nourishes these organs and prevents them from hitting the cranial box and the cerebral canal.
The messages that pass to and from the CNS they navigate through the ramifications of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), that reaches all the extremities of the body.
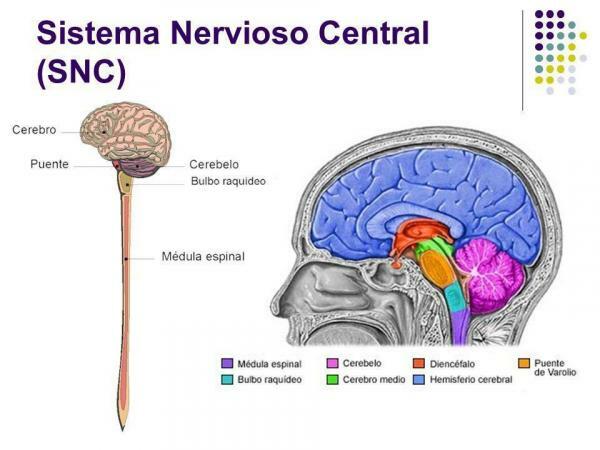
Image: Slideplayer
The nerves are made up of nerve fibers that are extensions of neurons. Neurons are the basic functional unit of the nervous system, transmitting information in the form of nerve impulses. The nerves meet in bundles, surrounded by connective tissue.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) it is formed by a series of nerves Y ganglia nervous The former are bundles of nerve fibers that are located outside the neuraxis that form the spinal cord and brain. Ganglia are junctions of nerve cells interspersed along the path of the nerves or at their roots.
The SNP it communicates with the CNS through twelve pairs of cranial nerves and thirty-one pairs of dorsal nerves, which leave the brain and spinal cord, reaching all the extremities of the body.
You have to distinguish between afferent neurons, responsible for transporting signals to the CNS, and efferent, that do the same from the SNC. The groups of afferent fibers reach the back of the spinal cord, forming the dorsal roots, and the efferent fibers exit the front of the cord through the ventral roots.
Efferent fibers are divided into somatic nervous system (SNS) Y autonomic nervous system (ANS). Somatic fibers activate skeletal muscles while autonomic fibers activate smooth or involuntary muscles, such as the heart, internal organs, etc.
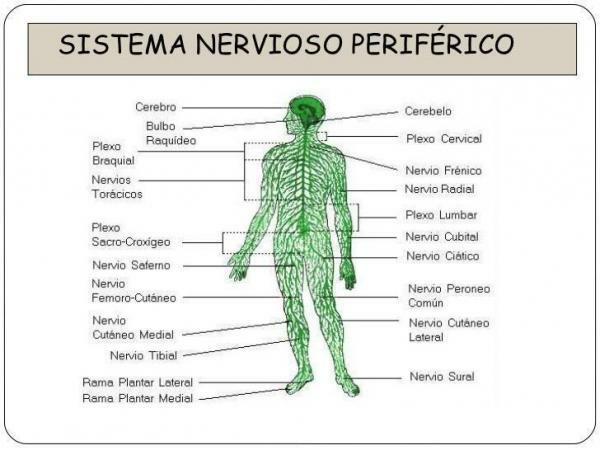
Image: Partsdel.com
Let's focus on the differences between the central and peripheral nervous system. Although both CNS and SNP have the neuron as the main structural and functional basis, there are basic differences between the two.
The main one is that the SNC is protected by bone structures, membranes and the blood-brain barrier, not being the case of the PNS, which is more exposed to mechanical damage or toxins.
On the other hand, another important difference is in their functions, Since the SNC processes and stores information, preparing responses that are executed, and the SNP transmits information from various areas, both the collection in the middle and that of internal organs, which goes to the CNS, as well as the opposite, that is, the orders that go from the CNS to the organs.
The differences between the central and peripheral nervous systems are clear in the case of injuries, since those that occur in the SNP are localized and easier to treat, quite the opposite of those that occur in the CNS, which give rise to global problems and in large areas. We have an example in the consequences that occur in an accident if we suffer an injury to a nerve branch, for example an arm, which would be located in this limb. Quite the opposite of an injury to the brain or spinal cord, which can leave problems throughout the body with various paralyzes.
Finally, point out the different neurotransmitters that intervene in these two parts of the nervous system, since in the CNS they are numerous, such as serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, glutamate, acetylcholine, GABA, etc., and in the SNP there are only two, norepinephrine and acetylcholine.
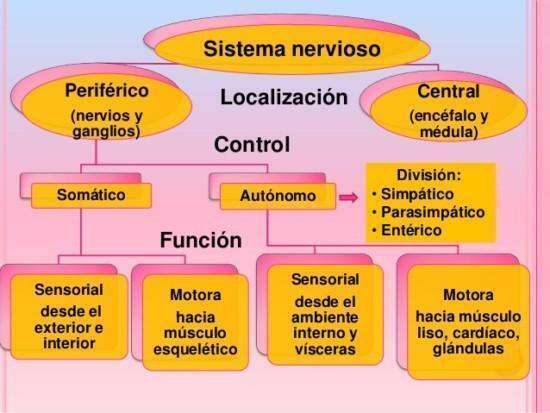
Image: Information | A Universe of Information
If you want to read more articles similar to Differences between the central and peripheral nervous system, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.



