Main MUSCLES of the human body
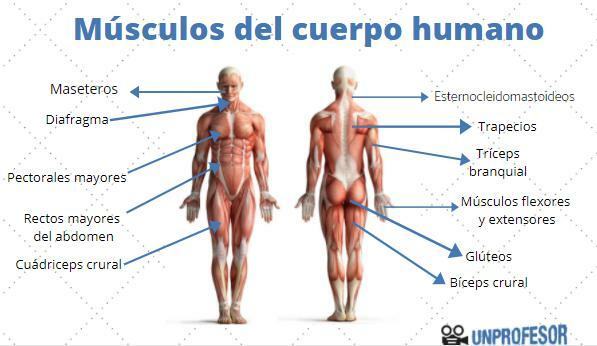
The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half the body weight of an average adult person. All of them perform an important function within their body environment, if not performing fundamental functions, helping others such as bones or some viscera, to carry out their mission.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review the main muscles of the human body, from the most important muscles of the head to the trunk, passing through the limbs. If you want to know more about the main muscles that make up your body, keep reading!
Index
- Types of muscles of the human body
- Muscles of the human body in the head and neck
- Main muscles of the trunk
- Major muscles in the arm and hand
- Major muscles of the leg and foot
Types of muscles of the human body.
To begin, we must make it clear that not all muscles in the human body are the same. Within our body we can find fundamentally three types of muscles or muscle tissue:
- Smooth or involuntary muscles. This is the name given to the muscles that are activated involuntarily in our body. Seen under the microscope, the fibers that make up these muscles are smooth, that is, they do not have stretch marks. Smooth muscles are automatically controlled by the nervous system and form the organs and viscera (the walls of the stomach and intestines), the walls of the blood vessels, etc. Smooth muscles take longer to contract than the rest, but they can remain in that position for longer as they do not tire as easily.
- Heart muscle. This type of muscle is only found in the heart and forms the walls of the heart chambers. Although the heart muscle is also an involuntary muscle, it has different characteristics and anatomy from other smooth muscles.
- Skeletal muscle. It is what people commonly call muscle and is primarily responsible for movement and displacement, although it also allows us to maintain the correct position of the body and its structures. Viewed under the microscope, the cells or fibers that make up skeletal muscle show horizontal stripes or striations. In addition, skeletal muscle, unlike smooth muscle, can be controlled at will, which is why it is also called striated or voluntary muscle. Striated muscle contractions are fast and energetic, but they tire easily and must rest between efforts.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review the main skeletal muscles of the human body, as they are the best known, but this does not mean that the others are not fundamental to the functioning of our Body. Without the heart muscle our heart would not be able to beat, and without the smooth muscle we would not be able to digest, for example.
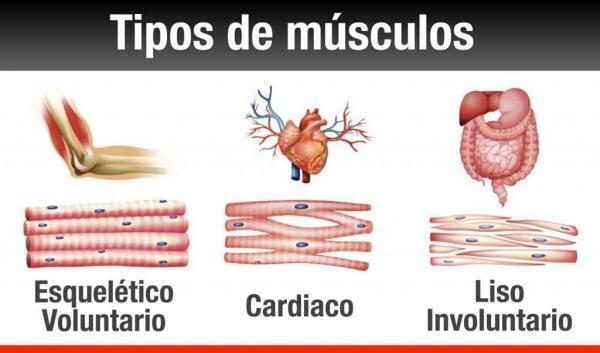
Image: Pinterest
Muscles of the human body in the head and neck.
Despite going somewhat unnoticed, some of the most important muscles in the human body are in the head and the neck. Some of them are:
- Masseters: these muscles are in the cheeks, and they are the muscles that we use to chew food.
- Orbicularis lips: these muscles are around the mouth and they allow the movement of the lips when we speak. Thanks to them we open and close our mouths, but we also speak and generate facial expressions.
- Orbicularis of the eyelids: They are located in the eyes and are responsible for opening and closing the eyelids.
- SternocleidomastoidThese neck muscles allow you to move your head sideways and forward.
- Splenium: this is the main muscle responsible for moving the head back.
- Buccinadores: They are located at the end of the corner of the mouth and allow blowing, hissing, chewing, etc.
Other main muscles of the head are: the frontal muscle (allows to raise the eyebrows and wrinkle the forehead), muscles nasal (which allow the nose to move slightly, as when we wrinkle the nose), laughing muscles (which stretch the lips), etc.
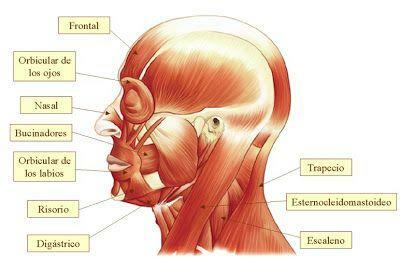
Image: Pinterest
Main muscles of the trunk.
Inside the trunk we can find various major muscles of the human body, such as:
- Intercostals: As its name suggests, the intercostals are muscles that are found between the ribs and are involved in breathing.
- Diaphragm: it is a single muscle, which is between the abdomen and the thorax and is involved in breathing, allowing the lungs to swell and deflate.
- Pectorals major: they are in the front part of the trunk and allow to move the arms.
- Rectus abdominis: they are in the midline of the trunk and allow flexion of the trunk.
- Trapezoids: behind the trunk, they raise the shoulder and keep their heads upright.
- Dorsal: allow the arm to move backwards.

Image: Pinterest
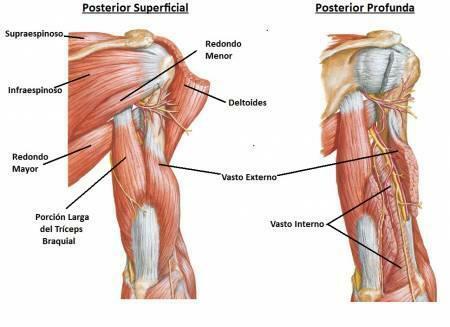
Major muscles in the arm and hand.
In the upper extremities, the arms and the hands, we can find a great variety of muscles. Some are:
- Deltoid: these muscles form the shoulder and therefore are responsible for raising the arm and moving it back and forth.
- Brachial biceps: flexes the forearm on the arm and allows these two parts to have mobility by separated.
- Triceps brachii: extends the forearm, separating it from the trunk.
- Pronators and supinators: rotate the wrist and hand with respect to the forearm.
- Flexor and extensor muscles fingers
Main muscles of the leg and foot.
Numerous major muscles of the human body are found in the lower portion of our body, in the legs Y the feet. Like the arms and hands, the legs have a great capacity for movement, much more than the head and trunk. In addition, they are responsible for moving the human body, so most people have more developed leg muscles than those of the upper part of their body.
Some important muscles of the human body located in the train or bottom They are:
- Buttocks: they form the buttocks and their function is to maintain the straight position of the body.
- Sartorius: this muscle allows us to cross the legs in a complex movement in which it must flex on the hip and move the femur outwards as well as rotate the femoral head outwards.
- Crural biceps: it is located behind the leg and is responsible for flexing the leg at the knee.
- Crural quadriceps: Unlike the previous one, it is in front of the leg and its function is to extend it.
- Twins: they form the calf and are used for walking.
- Flexors and extensors of the toes.
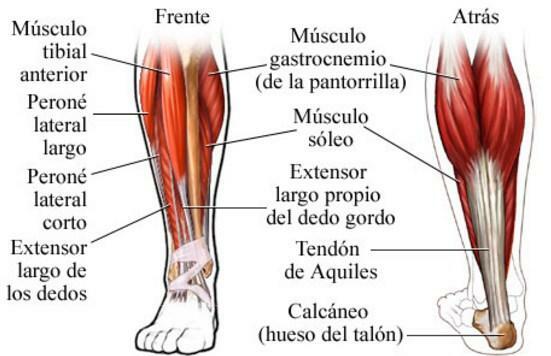
Image: What is it called
If you want to read more articles similar to Main muscles of the human body, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Dowshen, S (August 2009) Bones, muscles and joints. Rady Children's Hospital San Diego. Recovered from: https://www.rchsd.org/
- Biología-Geología.com (s.f) Muscles of the human body. Recovered from: https://biologia-geologia.com/