What is Cross POLLINATION

The pollination is a very important process, key to the plant reproduction and therefore for the maintenance of ecosystems and our planet. During pollination, the male gamete (the pollen grain) is transported to the female gamete (the oosphere) for fertilization and the formation of a new individual: the seed. This seed, if lucky, will germinate and give rise to a new adult individual - a plant.
One of the most widespread forms of pollination is cross pollination, a very interesting and complex pollen transmission process. If you want to know what is cross pollination, its characteristics and its importance in agriculture, keep reading this lesson from a TEACHER!
Index
- What is pollination?
- Cross pollination: simple definition
- The importance of cross pollination for artificial crops
What is pollination?
The pollinationIt is the process by which the pollen is transported from its place of production (the pollen sacs) to the oosphere, to produce the fertilization of this. Fertilization of the oosphere produces a
seed, a structure that, if environmental conditions are favorable to it, will grow into a new individual: a plant. Therefore, pollination is a process essential for the life cycle of plantsIf the pollination of a species were to fail, there would be no fertilization and therefore no new individuals would be generated.Mechanisms of pollination
Pollen transport is very important for plants, which is why they have developed different mechanisms to carry them out: it can occur between different parts of the same flower (self-pollination) or between different flowers, either from the same plant or from different plants (Cross pollination).
Self-pollination usually occurs in species in which the individuals grow widely dispersed, far from each other, or in which there are not a large number of them together. Sometimes, it is also a form of adaptation in species that, due to human action, no longer reproduce with so easily and plants have trouble finding other plants to pollinate crusade.
If you want to continue discovering things about pollination, you can take a look at the lesson in which we talk about the types of pollination or from how is the pollination of bees.
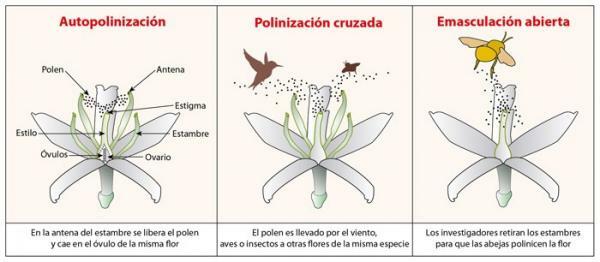
Image: Comparison Chart
Cross pollination: simple definition.
In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will focus on explaining what cross pollination is since it is the type of pollination they have most plant species of our planet. This is because cross pollination allows the creation of new genetic combinations.
In the case of self-pollination, the genes that are mixed are always those of the same flower, while in pollination crossed the genetic material of the oosphere comes from another flower or, in the best of cases, from a flower that is from another plant. An apparition of more genetic diversity makes plants better adapt to the environment or colonize new ecosystems, making it an important mechanism of plant evolution.
The transport of pollen that takes place during cross pollination must be done thanks to some tool, something that physically moves the pollen grains. These tools are called vector and they can be of two types.
Vectors biotic
They can be living beings (biotic vectors) or forces of nature, things that without being alive can move things (abiotic vectors). Examples of biotic vectors Those responsible for cross-pollination are insects (beetles, wasps, butterflies, etc.) or birds (such as hummingbirds).
These animals are normally attracted to the nectar, a sugary substance; when the animal goes to eat the nectar, the pollen grains remain attached to its body so that, when This visits the next plant, the pollen falls to the anthers, where the oospheres are waiting for the fertilization. The different species have different mechanisms to attract the attention of animals: some produce large amounts of rich nectar, others produce flowers very colorful and large although less nectar while others have colors that mimic the females of some insects ...
Vectors abiotic
In other species, pollen moves thanks to abiotic vectors like wind or water (rivers, streams, the surface of lakes and ponds, etc.). In these cases the pollen grains and anthers will also have some modifications: in plants pollinated by the wind (anemophiles), pollen grains are light and some have wing-like structures that allow them to fly; in the case of plants hydrophilicpollinated by the action of water, the pollen grains must float (so as not to fall to the bottom of the water) and the anthers also float on the water or rise during the flowering period, when they are ripe.

The importance of cross pollination for artificial crops.
Crops planted by humans are called artificial crops. To carry out an artificial cultivation that is productive and profitable for farmers, it is of great importance know what is cross pollination and how is carried out the pollination of the different species that it make up.
In cases where crops are made up of cross-pollinating species, one must first consider what type of cross pollination they have: Are flowers of the same plant pollinated, with different stages of maturation or flowering? Or, on the contrary, are we dealing with a species with male plants, which produce pollen, and female plants, whose flowers are fertilized by pollen created by other individuals?
If we are facing species with female and male plants, we will have to investigate and find out different things, what proportion of female plants do we have to put for each male plant so that our pollination (and therefore, our production) is the most efficient possible? What distance is sufficient for the plant to grow but the pollen can continue to travel and is not too far from the female plant? In the case of cross-pollination between flowers of the same plant, we should ask ourselves other questions.
At other times, cross pollination can help us increase crop production in species that do not initially cross-pollinate. As we saw in the first section, there are certain species that present self-pollination, that is, the same flower that produces pollen is pollinated by it. This type of pollination usually occurs in plants that do not have other individuals nearby, that are in small numbers in a ecosystem or that grow very far from each other but, when given the possibility, they do pollination crusade.
Faced with an artificial cultivation of these species, the farmer always favors cross pollination since it leads to higher fruit productivity, better quality of these, etc. Crops with cross pollination are, in general, much more productive and efficient than those in which there is self-pollination.
As you can see, cross pollination is a very important issue, both for the conservation of the environment, ecosystems and crop production. Do you have any additional input to make on the subject? Do you have any doubt? Leave a comment below!
If you want to read more articles similar to What is cross pollination, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Guadanatur (May 23, 2015). Cross pollination. Recovered from http://guadanatur.es/polinizacion-cruzada/
- Syngenta (s.f) Cross Pollination. Recovered from https://polinizadores.com/polinizacion/polinizacion-cruzada/
- Briceño V, G. Euston69 (s.f) Pollination. Recovered from https://www.euston96.com/polinizacion/
- FAO (s.f) Bees are the diligent pollinators of fruits and crops. Recovered from http://www.fao.org/3/y5110s/y5110s03.htm