PARTS of the EXCRETOR appliance with their functions
The human body is made up of nine systems: locomotor, nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, immune, endocrine, reproductive and excretory systems. Normally, the excretory system is overlooked, and it is considered to have a "secondary" role. Everything is further from reality, since the excretory system is responsible for eliminating substances and maintaining composition, volume, etc. of our blood in perfect condition.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will study all the parts of the excretory system that make it possible for it to perform its functions: the urinary system (made up of kidneys, ureters and urethra), skin, lungs and liver.
Index
- What is the function of the excretory system?
- The urinary system, one of the parts of the excretory system
- The lungs as part of the excretory system
- The skin as an excretory organ
- The liver in the excretory system
What is the function of the excretory system?
It may not be as popular as other appliances, systems, or organs, but the
excretory system has a primary function in the human body. This set of organs is responsible for the disposal of waste substances through different mechanisms such as urination or production of urine, sweat or respiration.This system plays a fundamental role in excreting the substances that the body does not need, since the accumulation of these substances can lead to serious health problems, such as poisonings, infections or organ failure.
The failure of organs of the excretory system is quite common in our society due to the aging of the population, but also to unhealthy behaviors such as overeating or obesity, the consumption of alcohol or drugs, etc.
Parts of the excretory system
As we will see below, the excretory system is not only made up of the kidneys, organs that produce urine, but it is made up of:
- The urinary system. Formed by the kidneys, the excretory tract (ureters and urethra) and the bladder.
- Lungs
- The skin
- The liver

Image: Slideshare
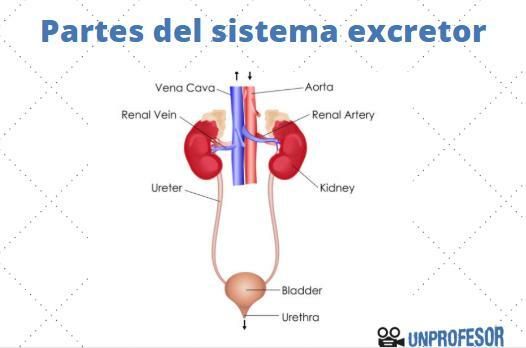
The urinary system, one of the parts of the excretory system.
The urinary system is a set of organs in charge of produce and eliminate urine. Urine is largely made up of water, in which other substances are dissolved, such as example urea (a toxic substance when it accumulates in the body), but it also has a lot of you go out.
Urine is synthesized in kidneys, where the nephrons are responsible for filtering the compounds that reach it through the blood. Once produced, the urine passes into tubes called ureters (there are two, one for each kidney), until the bladder. Once in the bladder, urine builds up.
When the bladder is full enough, the person feels the need to urinate. This need is controlled by a series of nerve impulses, which originate in the cells that form the lining of the bladder. Although the bladder has a storage capacity up to one liter, the need to urinate begins to be felt when about 400 or 500 cubic centimeters of urine accumulate. In this way, the body ensures that our bladder does not suffer long-term damage from excessive stretching, but also takes care of possible urinary tract infections, etc.
When our body receives the necessary stimulus for urination, we open the valves that allow the emptying of the bladder. There are two types of valves or sphincters: there are voluntary sphincters and involuntary sphincters. Voluntary sphincters allow us to control urination, while involuntary sphincters allow us to urinate when the bladder is too full.
When the valves or sphincters relax, urine is released into the urethra, a single tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside. The urethra and the ereters are often confused: while the ureters are paired tubes, which carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, the urethra is a single tube, which is responsible for transporting urine from the bladder to the Exterior.
In men, the urethra, in addition to fulfilling an excretory function, also has a reproductive function since the excretory and reproductive systems are united in their last portion.
The lungs as part of the excretory system.
The lungs are one of the most overlooked parts of the excretory system. The lungs reach the lungs through the blood cellular waste that the body needs to eliminate, and that they have not been able to be eliminated by both the kidneys or the skin.
Through the process of respiration, water is released from the body, and the body, in turn, gets oxygen.
The skin as an excretory organ.
The skin is the largest organ in the world and, together with other functions, it allows the elimination of toxins, water, organic substances and salts. Specifically, the skin eliminates waste substances thanks to sweat.
Sweat is generated in the sweat glands and is expelled through the pores. Sweat is a clear liquid made up of water, minerals, urea, and lactic acid.
Thus, sweating is the process that allows, in addition to expel toxins, regulate our body temperature. We sweat continuously and normally, but sweat production increases when we do physical exercise, when we are nervous, when we are very hot, when we are overweight or when we eat food spicy
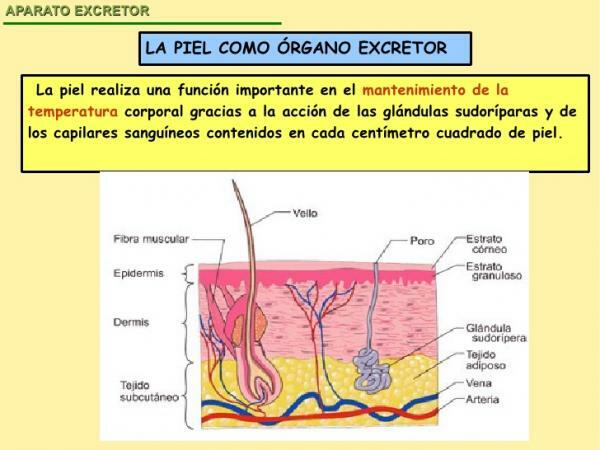
Image: Slideshare
The liver in the excretory system.
The liver is an organ that is located in the upper right part of the abdomen, and is responsible for eliminating large amounts of toxins, drugs, medicines, fats and all those organic substances insoluble in water.
One of the main substances that the liver is responsible for is the ammonia. Ammonia is a highly toxic substance for our body, so the liver transforms it into urea, which is less toxic. Urea passes into the blood and is excreted in the kidneys.
Another of the substances eliminated by the liver is hemoglobin of red blood cells. Red blood cells are the blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen; these are cells that are constantly replenishing. The liver is responsible for taking the dead red blood cells and recycling the hemoglobin to be able to use it again, since it is a highly complex and expensive molecule to manufacture.
Image: Slideshare
If you want to read more articles similar to Parts of the excretory system, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Torres Ruiz, A (s.f). Human excretory system: what it is, parts and functions. Recovered from: https://azsalud.com/
- Montagud Rubio, N (s.f) Excretory system: characteristics, parts and operation. Psychology and mind. Recovered from: https://psicologiaymente.com/



