Frog metamorphosis

Image: Slideshare
Frogs are a class of amphibians very curious and are the oldest terrestrial vertebrates living today. In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will see one of the processes that most attract the attention of this striking amphibian, we will review the metamorphosis of the frog step by step so that you know better how this animal goes from being an egg to an adult frog. Here you can see in detail everything that happens in each step and, thus, learn more about this natural process.
Index
- What is the metamorphosis of animals?
- First step of the frog's metamorphosis: the egg
- Larva or tadpole, the second step
- Metamorphosis is the third step
- Adult frog, the final step of metamorphosis
What is the metamorphosis of animals?
Metamorphosis it is a biological process, that is, a series of changes, by which an animal develops from birth to maturity by means of large structural and physiological changes.
During metamorphosis there are not only changes in size and an increase in the number of cells, but there are changes in
Cell differentiation. That is: cells that had decided to form a certain tissue are eliminated to be replaced by others or simply for that structure to disappear.Metamorphosis is typical of many insects (like the butterflies), amphibians (salamanders, frogs, toads), mollusks (oysters), crustaceans (crabs, prawns), etc. but in each animal group, changes in habitat, behavior and different body structures can be observed. In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to review the step by step of the frog metamorphosis.
Image: Answers.tips
First step of the frog's metamorphosis: the egg.
The steps of the frog's development are as follows: egg, tadpole and adult. The metamorphosis occurs during the transition from tadpole to adult and involves not only changes in the outer structures of the animal such as legs if not changes in its internal organs, in its behavior and in the place where they live.
The first stage of development of frogs is that of egg. Remember that frogs are oviparous with external fertilization, so the female lays the eggs, usually in sweet waters, and the male fertilizes them. These eggs are transparent and are joined by a gelatinous substance that protects them while allowing the passage of oxygen from the outside to the eggs and the elimination of the waste substances produced. After fertilization, the gelatin becomes more liquid to allow free movement of the developing embryo.
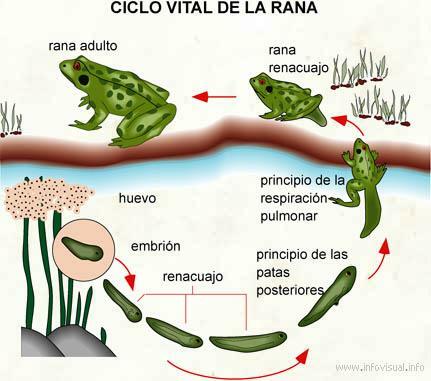
Image: Life Cycle
Larva or tadpole, the second step.
When they have spent about a couple of weeks in the water (it depends on the species), the eggs will The larvae, which in the case of frogs are known by the name of tadpole, break open and come out into the middle. Remember, saying tadpole or frog larva is the same. The tadpole remains in the water, so it has tail to facilitate movement in the water and gills for breathing. The lungs they soon begin to develop and are used as an accessory breathing organ.
Tadpoles are normally herbivores and feed mainly on algae by filtering the water through the gills by means of a oral disc. Some species are carnivorous in the tadpole stage, eating insects, smaller tadpoles, and fish. These have several rows of teeth called keradontes, which are not bones like ours, but rather structures covered with a hard substance (keratinized).
Tadpoles are very vulnerable to attacks from other animals, so in some species they cover themselves with a poisonous substance to avoid being eaten.

Image: Google Sites
Metamorphosis is the third step.
At three to four weeks, the tadpole begins to undergo a series of step-by-step changes called metamorphosis. During metamorphosis the tadpole has to make many external physical changes, but also its internal organs to adapt to the change from the aquatic ecosystem to the terrestrial one. While these changes are taking place, the tadpole is unprotected against predators as it cannot move or defend itself well in the new environment. These changes have to be made Quick. So fast that some tadpoles can make them in one day!
The first significant change is going to be in breathing. The gills disappear and the lungs They become its main organ for respiration. In addition, changes also occur in your circulatory system.
The second significant change is the change in the method of movement (locomotion): they go from swimming to jumping. For it tail disappears and the legs rear; the front legs had been formed in the egg, but were hidden by a structure of the gills that, as they disappear, come out. Before the tail disappears, the legs are formed, so we can see frogs in the final stages of metamorphosis that have legs and a tail.
The third significant change is the transition from a humid environment (water) to a dry one (terrestrial). The skin it becomes thicker and harder and glands in the skin develop that form the mucus that covers it.
Other changes during the frog's metamorphosis
Finally, there are also other changes which are also important:
- the oral disc, which served to filter the water in search of food, begins to form the tongue and also shortens the intestinal tract to adapt to the carnivorous diet
- the tympanic membrane is formed, a structure that allows frogs to hear
- eyelids are formed and vision becomes three-dimensional (stereoscopic)
- reorganization of the nervous system occurs to adapt to the changes undergone
All these changes (and some others that we have not seen) give rise to young frogs, which are not yet adults since they cannot reproduce.

Image: Google Sites
Adult frog, the final step of metamorphosis.
After metamorphosis, the young frogs they can disperse in terrestrial habitats, although still occasionally living in water. Almost all species of frogs are carnivorous and have different methods of hunting (sticky tongues, use their front legs, etc.). In addition, they need to shed their skin as they grow.
Young frogs take between 1 and 4 years to reach sexual maturity and therefore the stage of adult frog. Little is known about the longevity of frogs and toads in the wild, but some can live for many years - up to 14 years in some cases!
If you have any questions, concerns, contributions or comments, do not hesitate to tell us in our comments section!
If you want to read more articles similar to Metamorphosis of the frog: step by step, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.