Discover the COMPOSITION of human BONES

Bone is a rigid organ due to the mineralization of bone tissue, its main component. However, despite its inert appearance, it is a very active organ thanks to the fact that it also contains living tissues with cells of various types that are in constant activity.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will explore the composition of bones at different levels. We will see what is the chemical composition of bones, what tissues make up bones, what are the cells that are part of their tissues and what chemical composition has the extracellular matrix.
Index
- The chemical composition of bone
- Bone tissue and structure
- The tissues of the outer covering of the bone: the periosteum and cartilage
- The majority of bone tissue: bone tissue
- Types of bone tissue
- The soft tissue in the innermost part of the bone: the bone marrow
The chemical composition of the bone.
The bone it is a mineralized organ. The large amount of minerals it contains makes its water content much lower than in other tissues. The bone only contains 25% water, the remainder being 75% dry matter.
The dry matter that bone contains, has an approximate chemical composition of a 65% inorganic matter (calcium and phosphorus salts) and a 35% organic matter (which includes biomolecules like collagen and specialized cells like osteocytes).
The proportion of the cellular fraction of bone is only 2% of its total volume. However, the role of the different cell types is fundamental. Because these cells are responsible for the formation, maintenance and remodeling of bone and for regulating the levels of Calcium and Phosphorus that circulate in the blood.
Bone tissue and structure.
The bones that make up the skeleton they are very diverse, both in their structure and in their composition. However, all of them are mainly composed of woven bone which is responsible for the mineral appearance of the bones.
Some bones also contain soft tissue inside called bone marrow that performs essential functions for life such as hematopoiesis or mineral homeostasis.
In addition to bone tissue and bone marrow, there are other tissues that are part of the composition of bones such as cartilaginous tissuearticulate or the periosteum.
Structure of bone and its tissues
If we consider the bone structure from the outermost part to the innermost, we find different fabrics:
- External covering of the bone: the periosteum and articular cartilage.
- The main tissue of bones: bone tissue.
- The soft tissue that is housed in the innermost part of the bones: the bone marrow.
In the following sections we will see in more detail the composition and structure of the different tissues that make up the bone.

The tissues of the outer covering of the bone: the periosteum and cartilage.
In the superficial area of the bone, above the bone tissue, there are two different types of tissue. In general, the bone is covered by the periosteum; But in the areas where the bones come into contact with each other (joints), the surface of the bone is covered by articular cartilage.
The periosteum
- It is a thin fibrous layer that covers almost the entire surface of the bone, except in the areas of the joints.
- It is made up of collagen fibers.
- The periosteum contains nerve endings that provide sensitivity to the bone; and blood vessels that are responsible for supplying nutrients to the cells that make up the different tissues of the bone.
Articular cartilage
- Covers the surface of the joints, where there is no periosteum. It is a tissue that does not have blood vessels.
- Joint cartilage (also called hyaline cartilage) is a very flexible fabric and its function is to cushion impacts and lubricate the joints.
- Its characteristics are determined by a high concentration of water (65%) collagen fibers (15%) and the presence of glycoproteins (15%) that act as lubricants.
- The cells of the cartilage tissue are the chondrocytes that represent 5% of the cartilage. Chondrocytes are responsible for the synthesis of collagen and other components of the extracellular matrix.
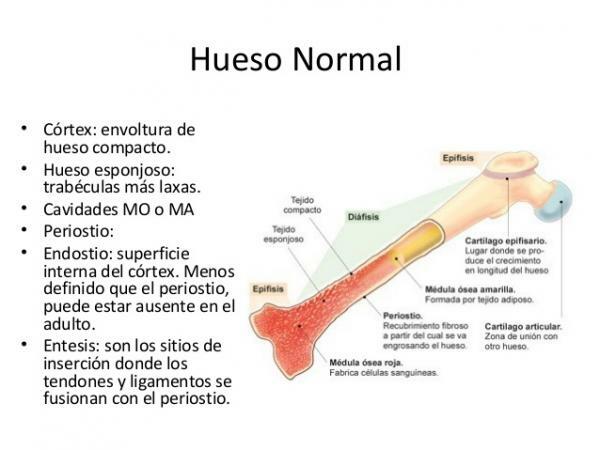
Image: Slideshare
The majority tissue of bones: bone tissue.
We continue to analyze the composition of bones talking about bone tissue, which is the main tissue of all bones. The general chemical composition of bones is very similar to that of this tissue.
From a structural point of view, bone tissue is made up of two components: the matrix mineralized extracellular (the bone matrix) and three types of cells (osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts).
The bone tissue that makes up bones is made up of two components, the mineralized extracellular matrix (the bone matrix) and three types of cells (osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts).
Cell types of bone tissue
- Osteoblasts: They are cells specialized in the synthesis of bone matrix matrix and those responsible for the growth and remodeling of bone. They are found in the growth areas of the bone that are not yet mineralized (osteoid), and they form deposits of calcium salts at the extracellular level during the maturation process of the bone. When the mineral deposits completely surround the osteocytes, they are enclosed within the mineralized matrix of the bone in cavities that are called bone lagoons. Inside the bone lagoons, the osteoblasts differentiate, giving rise to a new cell type typical of mature bones: osteocytes.
- Osteocytes: They are the most abundant type of cells in mature bones. They are inactive osteoblasts trapped in mineralized bone tissue. They are responsible for the maintenance of the bone matrix and are also involved in the metabolism of calcium.
- Osteoclasts: They are the cells in charge of bone resorption. Eliminating bone tissue.
The bone matrix
- The bone matrix is a mineralized extracellular matrix 65% composed of a mineral compound: crystallized calcium phosphate, which is called hydroxyapatite.
- In addition to this mineral compound, the bone matrix contains organic molecules. The most abundant organic molecule in the bone matrix is collagen fibers.
- This composition is responsible for the characteristics of the bone tissue (consistency, hardness, resistance to compression and a certain flexibility)
There are two types of bone tissue that differ in their structure, although both contain the same basic elements (mineralized matrix and cells).
Types of bone tissue.
exist two types of bone tissue that we must take into account. They are as follows.
Compact bone tissue
It is the one that forms the outermost part of the bone. It is formed by concentric sheets or rings around central channels (Harvers canals) that extend along the bone, connected to these, are other horizontal channels (Volkmann canals) that pierce the periosteum.
The network formed by the connection of these two types of channels allows the passage of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerve endings to the interior of the bone. Osteocytes are housed one by one in small holes in the laminae (bone gaps).
The structural unit formed by the central canal, the concentric laminae and the osteocytes is called osteon or Harvers system. Interspersed with the osteons are sheets of bone tissue that are called interstitial sheets.
Spongy bone tissue
It is found inside the bones and at the end of the long bones (Epiphysis). This bone tissue is made up of a series of irregularly arranged laminae called trabeculae.
The trabeculae form a septum that separates large empty spaces where the bone marrow is located. Spongy bone tissue contains a large number of blood vessels.
The soft tissue in the innermost part of the bone: the bone marrow.
We finished this lesson on the composition of bones to talk about the bone marrow, a soft tissue that occupies the internal area of some bones, filling the cavities of the spongy bone tissue. They have bone marrow long bones that form the limbs, the irregular bones like vertebrae and flat bones such as the ribs, sternum, and the bones of the hip and scapula.
The bone marrow is a tissue with a great abundance of cells and that has a large number of blood vessels and nerves.
Types of bone marrow
According to its composition, different types of bone marrow are defined:
Red bone marrow: Contains mother cells. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can give rise to any type of cell. Red marrow stem cells are the ones that make up all three types of blood cells. Its proportion is very important in newborns and in adulthood it is gradually replaced by yellow bone marrow.
Yellow bone marrow: It is made up of adipose tissue, it occupies the interior of long bones. It is made up of two types of cells:
- Adipocytes: cells responsible for synthesizing and storing fat. They are the ones that are found in the highest proportion.
- Red blood cells: blood cells responsible for the transport of oxygen. In small numbers, they are scattered among the adipocytes.
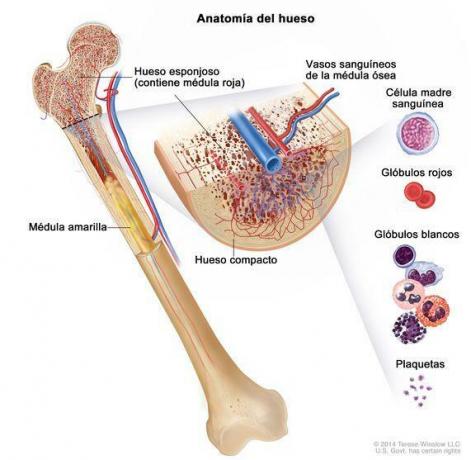
Image: National Cancer Institute
If you want to read more articles similar to Composition of bones, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
Ulrich Welsch. (2009) Histology. Madrid [etc.]: Panamerican Medical



