The 7 types of BONES of the human body

The human body of an adult is formed by 206 bones. These bones are very varied, since they are found in very different parts of our body and perform varied functions. From the ossicles of the ear, which allow us to hear, to the knee bone, which allows us to flex our legs, they are all important.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see the different types of bones of the human body. There are seven kinds of bones, do you want to know more about them?
Index
- The 7 types of bones in the human body
- Long bones of the body
- Short bones of the body
- Irregular bones
- Flat bones of the human body
- Sesamoid bones
- Pneumatic bones
- Accessory bones
The 7 types of bones in the human body.
The bones of the human body are responsible for giving our body consistency, the ability to move and move and organ protection important like brain, heart or lungs. But in addition, they have the secondary function of serving as a reservoir or store of calcium and phosphorus.
To classify the 206 bones of the human body, scientists use their shape and main characteristics. The 7 types of bones in the human body are:
- Long bones
- Short bones
- Irregular bones
- Flat bones
- Sesamoid bones
- Pneumatic bones
- Accessory bones
Remember that some can be part of two or more types of bones in the human body. A bone like the fabela can be an accessory bone and a sesamoid bone.
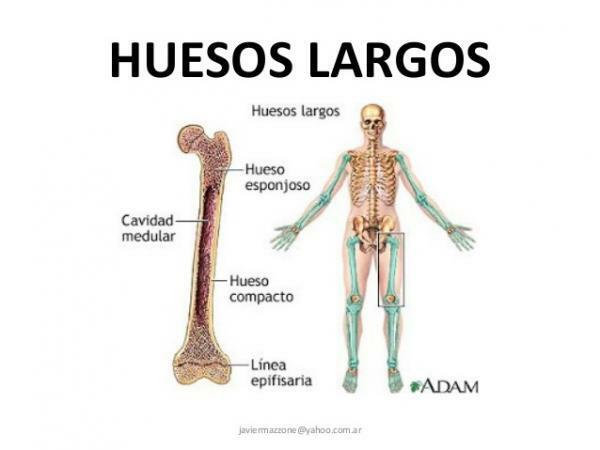
Long bones of the body.
The long bones that make up our body have cylindrical or tube shape, that is, they are longer than they are wide. Remember that long bones do not have to be large, there are relatively small bones, in the fingers of the hands, which are also long bones but they are not large.
The main function of long bones is support the weight of the body and facilitate movements. That is why they are normally found in the extremities, arms and legs. They are part of joints that bear great stresses, and are points of insertion of muscles that are usually small but powerful.
The main examples of long bones we can find them in:
- Leg, thigh, and foot bones: tibia, fibula, femur, metatarsals, and phalanges
- Bones of the arm, forearm, and hand: humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, and phalanges.
Short bones of the body.
The short bonesThey are one of the types of bones in the human body that usually go unnoticed, but they have very important functions within our locomotor system.
Short bones have cube, that is, they are approximately as wide as they are long. In the same way that long bones did not have to be large, short bones are usually small.
Within the short bones we mainly find small bones, such as those that give mobility to the fingers of the hands, and allow us to have great precision of movements. Others are found in the joints and allow the stabilization of these, such as the ankle bones.
Main examples of short bones They are:
- Carpal bones in the wrist: scaphoid, lunate, pyramidal, hamate, pisiform, large bone, trapezoid and trapezius bone.
- Tarsal bones in the ankles: calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuboid, lateral cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, and medial cuneiform.

Image: Pinterest
Irregular bones
The irregular bones They are that they have no shape that fits with the other groups. They have different shapes and characteristics, highly adapted to the function or the area of the body where they are found. Some examples of irregular bones are:
- The vertebrae: They are irregular bones that make up the spinal column and protect the spinal cord. Its shape varies according to the area of the back and, within them, we can find different faces, with different shapes and characteristics.
- The ossicles that form the inner ear: hammer, anvil and stirrup. They are three tiny bones that are inside the skull and allow the transmission of sound.

Image: Slideshare
Flat bones of the human body.
The flat bonesThey are one of the most abundant types of bones in the human body. This type of bone is characterized by being thin, thin and large. You can differentiate them because they are shaped like shield, and usually cover certain organs of the body.
In addition to protection of organs such as the brain, heart and lungs and pelvic organs, the flat bones are provide large areas for muscle insertion, which are usually quite robust.
Some examples of flat bones are:
- Skullor bone structure of the head. It is formed by the occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal and the vomer
- The rib cage. Formed by sternum and ribs.
- The pelvis. Composed of ilium, ischium and pubis.
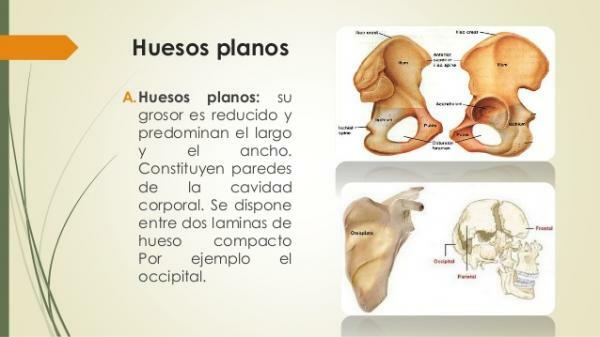
Image: Slideshare
Sesamoid bones.
Sesamoid bones are a type of bone that is normally overlooked as they are bones that are found included in tendons of many joints and are usually small, but their function is important.
Sesamoid bones are bones round, usually small, found in the tendons of the hands, knees and feet. The function of the sesamoid bones is to protect tendons from stress and joint deterioration, which is why they are a very common source of injuries (especially those of the knees).
Some examples of sesamoid bones are:
- Patela or kneecap. It is located in the front of the knee, on the tendon of the quadriceps muscle.
- Sesamoid bones of the fat fingers. They are found in the metatarsophalangeal region of the big toe and the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb.
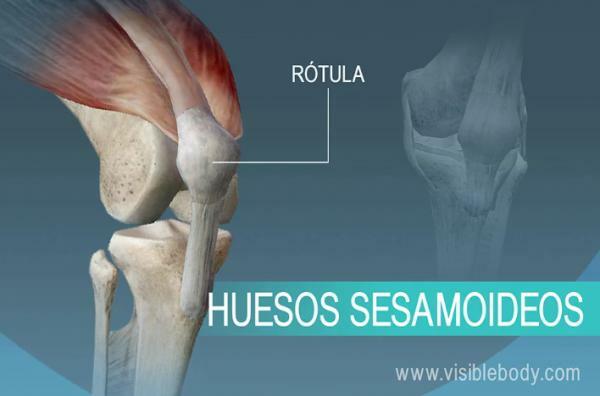
Image: Visible Body
Pneumatic bones.
Pneumatic bones are one of the types of bones in the human body more unknown. They are bones that contain spaces inside, lined with mucosa and filled with air. They are generally small, although as we will see below there are examples of larger pneumatic bones.
Are located around the nasal cavity (except the temporal bone), and its function is the protection of other organs. The appearance of air cavities (called cells if they are small in size or sinuses if they are larger large) makes these bones lighter than solid bones, thus lightening the weight of head.
They are pneumatic bones:
- Ethmoid bone
- Sphenoid bone
- Temporal bone
- Upper jaw bone
- Frontal bone
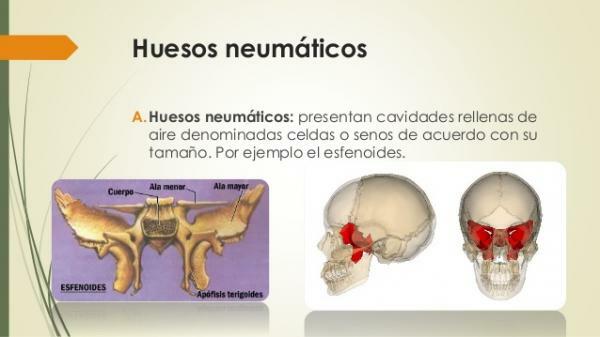
Image: Slideshare
Accessory bones.
Accessory bones are one of the most curious types of bones in the human body since are not found all over the world. These bones do not have a fundamental function for the body; they normally intervene in the movement of a joint or its stabilization.
The absence of accessory bones does not present any problem for those who do not have them, they do not cause any disease or pathology. In fact, it is very common for the individual not to know that he or she lacks said bone. Commonly, the discovery occurs when there is some type of injury in the area, after a medical examination.
The absence or appearance of these bones is usually a character inherited or genetic, so normally if someone has any of these accessory bones, one of his parents will have it.
Some examples of accessory bones in humans are: the fabela and the trine. The fabela is embedded in the tendon just behind the knee while the trigone is at the back of the ankle, and is considered an additional bone of the talus. Another example of an accessory bone in the foot is the navicular bone, which is on the inner side of the foot, just above the arch.

Image: Slideshare
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of bones in the human body, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Jens Waschke, M., & Gundula Schulze, S. (2018). Sobotta. Anatomy text.
- Elsevier (April 18, 2018) The 7 types of bones in the human body. Recovered from: https://www.elsevier.com/es-es/connect/medicina/los-7-tipos-de-huesos-del-cuerpo-humano
- Visible Body (s.f) In general: The five types of bones. Recovered from: https://www.visiblebody.com/es/learn/skeleton/types-of-bones
- Rodriguez, J (January 31, 2016). What are sesamoid bones? Recovered from: https://lafisioterapia.net/huesos-sesamoideos