The functions of the skull

The skull is one of the most important bones of the body. What we commonly call the skull is actually made up of twenty-two bones, grouped into two parts: the neurocranium and the viscerocranium. These two parts are quite different and they also have different functions. What we commonly call the skull or cranial box is the neurocranium, while the viscerocranium is the so-called facial skeleton, which is normally relegated to the background. If you want to know what are the functions of the skullWe invite you to continue reading this lesson from a TEACHER!
Despite what we commonly think, the skullIt is composed of both the bones that make up the cranial box and those that make up the facial skeleton or bones of the face. In anatomy, the skull is said to be made up of two parts: neurocranium and viscerocranium.
- The neurocranium It is the bony box that covers the brain and the membranous covers that are inside. In adults, the neurocranium is made up of eight bones: four in the middle of the box, unique (frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid and occipital) and two other pairs of bilateral bones (temporal and parietal).
- The viscerocranium or facial skeleton, is part of the anterior fraction of the skull, that is, the part most in front of it. The viscerocranium is made up of fourteen irregular bones, ranging from the bones surrounding the mouth (maxillary and mandible), which make up the nose and most of the orbital cavities.

Image: Google Sites
To know the functions of the skull it is important that we analyze each of the parts. The neurocranium They are the eight bones that make up the cranial vault. The skull is also called a cranial vault because it looks like a box with rounded edges. The frontal, parietal and occipital bones form a roof structure similar to the dome of a church, called the calvaria or cranial vault; the sphenoid and temporal bones are part of the base of the construction and their function is to support the skull.
All the bones of the neurocranium have a common function, the brain protection. But, in addition, each of them can have some added function:
- Frontal bone. It is located on the forehead. In addition to protecting the brain, protects the organs of hearing.
- Parietal bones. They are found on the sides of the head. In addition to protecting the brain itself, they serve as a structure for bra for the meninges and also for the hair adhesion.
- Temporal bones. Located on the sides of the head, like the frontal bone they deal with to protect to the brain and organs in charge of hearing.
- Occipital bone. It forms the posterior limit of the head and part of the base of the cranial vault. It is one of the main protective bones of the brain but, in addition, due to its position and large size it is also insertion point of many muscles of support and stability of the head and movement of this on the neck.
- Sphenoid bone. This odd bone is part of the base of the skull and has very particular functions: it is part of the internal structure of the face, is part of the nostrils and it is the place where the turkish saddle; the pituitary gland is located in the sella turcica.
- Ethmoid bone. The ethmoid is a T-shaped bone located in the upper part of the nose. Its sides are covered with small holes through which the roots of the olfactory nerve pass. It is part of the paranasal sinuses and its main function is heat the air that reaches our lungs from the outside. In addition, it also lightens the weight of the skull as it is part of the sinus cavity.
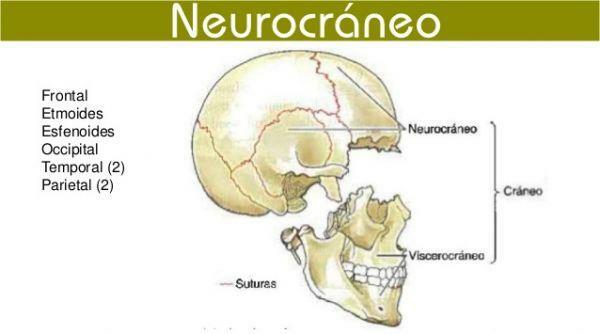
Image: Aulafacil.com
We continue to know the functions of the skull to talk about the other part: the viscerocranium. It is the part that makes up the facial skeleton and is made up of fourteen irregular bones: two centered odd bones (mandible and vomer) and six bilateral paired bones (maxilla, inferior turbinate, zygomatic, palatine, nasal and tear).
The viscerocranium has two main functions: protect the brain for its anterior part and serve areas of insertion for the muscles of the face, which allow us, among other things, to have facial expressions or to vocalize. But, in addition, each of these bones can have specialized functions:
- The maxilla and mandible they house the teeth. Between the two bones they give rise to the cavities of the mouth and the lower part of the nostrils. The maxillae form the majority of the upper facial skeleton and are attached to the base of the skull while the mandible forms the lower facial skeleton. Both have the function of chewing but they also intervene in functions as important as the swallowing, breathing, or vocalization.
- The bones vomer, inferior turbinate, palatine and nasal form the nostrils. The nostrils house the organ of smell but are also responsible for creating a barrier against entry of foreign substances into the lungs, to heat the air that enters our lungs, etc.
- The zygomatic bone or malar forms the cheekbone of the face and part of the eye socket, which contain the eyeballs.
- The tear bones It contains a tear hole, through which the tear duct passes. These are the ones in charge of channel tears outward or into the nasal cavity.
The skull is therefore an important protective structure, not only of the brain but also of many organs of the senses (ears, eyes or organ of smell). In addition, they also serve as an insertion site for the muscles of the face, neck, etc.
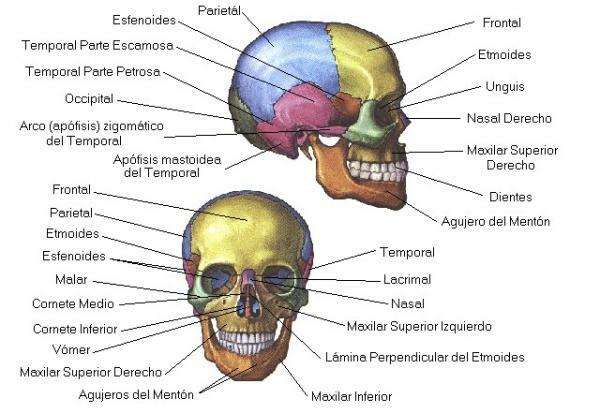
Image: UV Mural