The different TYPES of ENZYMES out there-SUMMARY + VIDEO!

The enzymes They are a type of proteins very important, both in our lives and in industry, medicine, etc. This is because its function is that of a chemical catalyst, that is, it facilitates different reactions to take place. Depending on the reactions they facilitate, enzymes can be classified into six main groups.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will look at the types of enzymes that we can find. If you want to know more about enzymes, keep reading!
Index
- I: oxidoreductase enzymes
- II: transferase enzymes
- III: hydrolase enzymes
- IV: lyase enzymes
- V: isomerase enzymes
- VI: ligase enzymes
I: oxidoreductase enzymes.
The oxidoreductase enzymes they are one of the types of enzymes that we are going to know. They are those that are responsible for catalyzing or facilitating redox or redox reactions. I mean, these enzymes they take care of the hydrogen (H) or electron (e-) transfer from one substrate to another.
Some examples of oxidoreductase enzymes are succinate dehydrogenase, peroxidase, or cytochrome c oxidase. Oxidoreductase enzymes have a
great importance for living beings, since they intervene among others in the glycolysis processes. Glycolysis reactions are reactions by which energy is extracted from sugar molecules, which are a very widespread way of obtaining energy among living beings.II: transferase enzymes.
Transferase-type enzymes catalyze or facilitate the transfer of a chemical group (other than hydrogen) from one substrate to another. Normally these are enzymes in charge of transferring one molecule or groups of molecules to another certain functional chemical groups.
In this way, transferases allow the formation of large and complex biological molecules, which could not under conditions compatible with the maintenance of life, either because of its speed or because of other conditions such as concentration of other groups necessary for the reaction.
There are many examples of types of transferase enzymes, but an especially important one in the case of mammals is acetate-CoA transferase, a key enzyme in the proper functioning of the krebs cycle, a set of biochemical reactions that gives us a lot of energy quickly and efficient. Other examples of enzyme transferases are glucokinases, hexokinases, kinases, phosphotransferases, or transminases.
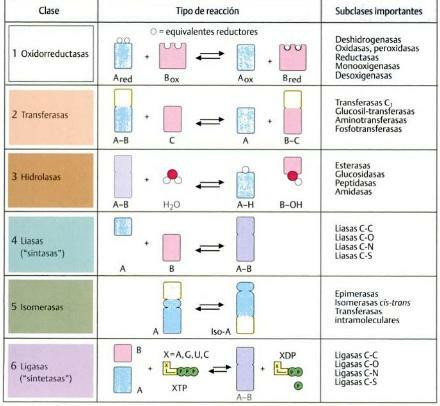
Image: Google Sites
III: hydrolase enzymes.
The enzymes hydrolase type are those responsible for breaking links. To break the bonds between molecules, hydrolase performs a reaction called hydrolyzation, that is, it uses water molecules to facilitate the breaking of a chemical bond. Hydrolyzation usually results in the production of two smaller and simpler molecules from a larger, chemically complex molecule.
Within the types of hydrolases enzymes we can find different subgroups, according to the molecules on which they act and separate. For example, there are lipases, which act on lipids; peptidases, which affect amino acids; nucleotidases, which act on nucleotides; esterases, which hydrolyze esters.
Hydrolase enzymes are especially important during digestion. The absence or lower amount of lactase, an enzyme responsible for separating the sugar molecules that make up milk, causes intolerances or allergies to lactose.
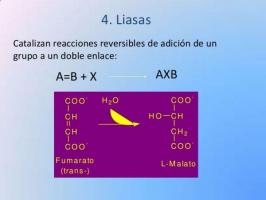
IV: lyase enzymes.
We continue to know the different types of enzymes to speak of the lyase type are, like the previous ones, they are the responsible for breaking links. The difference between lyases and hydrolases is very simple: lyases they do not need water molecules to perform their function, while hydrolases do. Furthermore, under the right conditions, lyases can reverse-react and form bonds instead of breaking them.
The link breaking function is very important for survival. One of the most present examples in all living beings is the use of the energy stored in chemical bonds, as in the case of the ATP molecule. ATP is a molecule with several bonds that are very rich in energy, which when separated in a controlled way, provide energy that can be used by the living being within which it is produced.
Another example of lyase enzymes are synthases, dehydratases, aldolases, acetacetate decarboxylase, etc. Lyases are often used in clinical laboratory practice to diagnose diseases: levels too high or low levels of a certain enzyme can give us clues about failures of certain organs or biochemical processes that do not function normally.

Image: Slideshare
V: isomerase enzymes.
Isomerases are those enzymes whose function is to change the shape of the same molecule. That is, in this case the atoms that make up the molecule are the same, there is no need to eliminate or add parts to the molecule, but they are rearranged in another way to form another molecule.
These molecules, which have the same composition but a different three-dimensional arrangement of their atoms, are known as isomers. Isomers are permutations or structural variations of the same molecule. Let's imagine a protein made up of 3 different blocks: A, B and C. If an isomerase were to act, it could generate another molecule, C-B-A, which would be an isomer of the A-B-C molecule.
Examples of isomerase enzymes are phosphotriose isomerase, phosphoglucose isomerase, cis-trans isomerases, epimerases, or mutases.
VI: ligase enzymes.
The last type of enzyme is that of ligases. Ligaases are the enzymes responsible for join or link molecules by covalent bonds. Its utility is enormous, for example, in the copying and repair of DNA. In a normal way, DNA can suffer breaks that can cause serious damage to the functioning of the cell.
DNA ligases, a type of ligase that is responsible for bind DNA molecules; this enzyme is capable of repair the breaks that have occurred between these strings. But this is not the only one, in nature there are many different types and subtypes of ligases: carboxylases, pyruvate carboxylases, synthetases, DNA-synthetases, etc.

If you want to read more articles similar to Types of enzymes, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- University of the Basque Country (s.f) Classification of enzymes. Recovered from: http://www.ehu.eus/biomoleculas/enzimas/enz13.htm
- Jaeger KE, Eggert T (August 2004). "Enantioselective biocatalysis optimized by directed evolution". Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 15 (4): 305–13. doi: 10.1016 / j.copbio.2004.06.007. PMID 15358000.
- Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., Stryer, L. (2002). Enzymes: Basic concepts and kinetics.