Find out what SYNAPTIC BUTTONS are, where it is and its FUNCTION

In this lesson from a TEACHER you will learn what are synaptic buttons, where they are located and what are their functions. To understand what synaptic buttons are, we will start by looking at what a neuron is and how the neurons are established. synapses between them, to later delve into the role of the synaptic button in the transmission of impulse highly strung.
Index
- Neurons: excitable cells of the nervous system
- What are synaptic buttons and their function?
- How a neuron transmits information
- The synapse: transmission of information between neurons
Neurons: excitable cells of the nervous system.
Before telling you what synaptic buttons are, we are going to discover the process of which they are part. The nervous system it is, without a doubt, the most complex organized structure that has evolved on planet earth. It is made up neurons (between 1010 and 1011 in the human nervous system) and a similar number of companion cells called glial cells. While neurons are excitable cells by electrical impulse, while glial cells are not excitable.
During the development, neurons self-organize in formations where they interact with each other giving rise to the neural circuits that constitute the nervous system and through which the nerve impulse travels.
The nervous system is in charge of integrating the stimuli that the body receives, processing them and emitting an adequate response. All this process is possible thanks to the transmission of information between neurons.
What are synaptic buttons and their function?
Synaptic buttons are the terminal branches of the axon, are flared endings that contain a large amount of vesicles (small pockets bounded by a cell membrane found in the cytoplasm) where the neurotransmitters (chemical substances that allow the transmission of information between neurons).
When the electrical impulse, which travels along the emitting neuron, reaches one of the synaptic buttons at the end of the axon, the release into synaptic space of chemical messengers stored in the synaptic button vesicles.
These molecules reach their destination through the synaptic space and bind to the dendrite receptors of the receptor neuron.
This union triggers a new electrical signal in the receiving neuron, thus spreading the nerve impulse. This transmission of information is known as synaptic transmission.
Steps of Synaptic Transmission
The steps that must be taken for synaptic transmission to occur are as follows:
- The action potential (electrical impulse) travels along the axon in the presynaptic neuron, until it reaches the synaptic button at its end.
- In the membrane of the synaptic button, the arrival of the electric potential causes the opening of the voltage-gated calcium ion channels. Channels are a type of protein that crosses the cell membrane and that allow the passage of calcium ions when they acquire an open conformation.
- The opening of these channels causes the massive entrance of calcium ions to the cytoplasm of the synaptic button.
- The presence of calcium ions inside the synaptic buttons cause the fusion of the membrane of the vesicles with the cell membrane of the neuron, releasing their contents into space extracellular. This phenomenon is known as exocytosis.
- Neurotransmitters released into the synaptic space bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. The neurotransmitter-receptor binding causes the formation of an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
- The effect on the postsynaptic neuron is brief, because the released neurotransmitters disappear rapidly. The neurotransmitter can be inactivated in two ways: The neurotransmitter is degraded or the neurotransmitter is taken up again by the synaptic button of the presynaptic neuron, where it is stored again in vesicles.
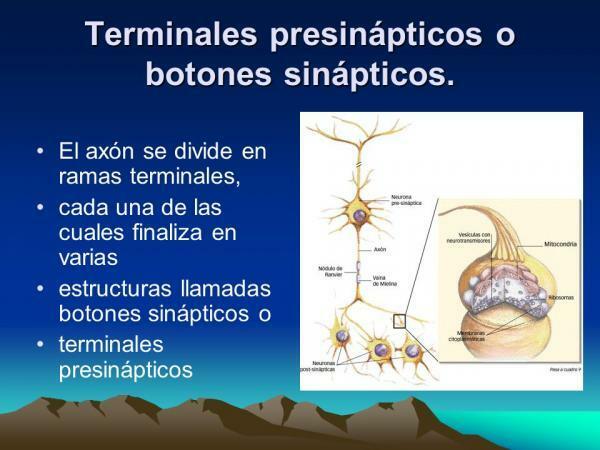
How a neuron transmits information.
The neurons transmit information in two different ways:
- Inside the neuron: The information that reaches the neuron is transmitted throughout it by electrical impulses called action potentials. These electrical impulses travel the neuron from one end to the other, from the neuronal soma to the most terminal ends of the axon: synaptic buttons.
- Between neurons: Neurons communicate with each other through specialized intercellular junctions called synapse. Information is transmitted through chemical messengers (called neurotransmitters) that are released by synaptic buttons in the small extracellular space that exists between two neurons linked by synapses (synaptic cleft).
Thus, neurons to transmit information to other neurons resort to synapses.
The synapse: transmission of information between neurons.
Synapses are generally established between the axon termination (synaptic button) of the sending neuron (presynaptic neuron) and the soma (cell body) or a dendrite of the receptor neuron (postsynaptic neuron). Synaptic junctions between neurons ensure the efficient transmission and processing of information in the nervous system.
At the synapse, the electrical signal (action potential) that travels through a neuron must be transformed transiently in a chemical signal to be able to bridge the small space of the synaptic cleft that separates the two neurons.
Thus, the synaptic button of the presynaptic neuron is responsible for converting the electrical impulse (electrical signal) that arrives through the axon, into a chemical signal.
This chemical signal consists of the release of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, where they will come into contact with the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron.
The membrane of the postsynaptic neuron presents on its surface receivers specific that bind to neurotransmitters. Receptors are proteins on the surface of the membrane that specifically bind to a certain chemical messenger, much like a key in a lock.
Neurotransmitters released in the synaptic cleft bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. This neurotransmitter-receptor binding triggers the creation of an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
In this way the information is transmitted along a neural circuit.
If you want to read more articles similar to What are synaptic buttons, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Nils Brose, Ludwig Kolb. (2013)Synapses in detail. NOTEBOOKS MYC .Barcelona: Scientific press.
- Jean-Gaël Barbara. (2020) The «bubbles» of neurotransmission. Mind and Brain. Barcelona: Scientific Press.
- Eckert D. Randall; W. Burgen; K. French; R. Fernald (Col.). (1998)Animal physiology. Mechanisms and adaptations. Madrid: McGraw-Hill / Interamericana



