Function of the isthmus of the fauces

The mouth gives entrance to the digestive system of mammals, including humans. In it there are different important anatomical structures that serve to crush the food and direct it to the along the entire digestive tract, for which structures such as the fauces and the isthmus of the jaws. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will talk about this structure and about the function of the isthmus of the fauces. If you are interested, join us to find out more!
Index
- What is the isthmus of the fauces?
- What is the function of the isthmus of the fauces?
- Anatomy of the isthmus of the fauces
- Diseases of the isthmus of the fauces
- Limits of the isthmus of the fauces
What is the isthmus of the fauces?
The oropharyngeal isthmus, also know as isthmus of the fauces or rear opening of the mouth, is the posterior limit of the oral cavity and is found communicating the oral cavity with the oropharynx.
The shape of this isthmus is irregular, It has a shape similar to an M and has the root of the tongue below, on the sides are the palatoglossal arches and the free edge of the soft palate and the uvula above.
This area is characterized by having a series of lymphatic tissue structures responsible for the defense of the respiratory and digestive tracts with the activation of the immune response to the detection of pathogens present in the area. These structures constitute the so-called Waldeyer's ring. Among them, the ones that are most related to the isthmus of the fauces are the palatine tonsils.
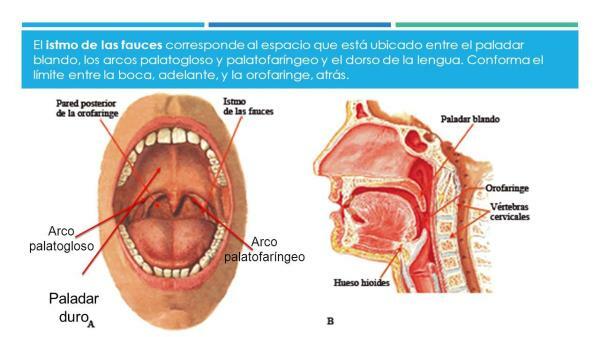
Image: Slideplayer
What is the function of the isthmus of the fauces.
We are going to know the function of the isthmus of the fauces. And the main thing is act as a regulator of various actions of the oropharynx. Here we discover the main functions:
- With its opening during the swallowing process, the isthmus of the fauces prevents the food bolus from going up to the nasopharynx
- When the isthmus closes, allows chewing, sucking and pushing bolus through the pharynx and into the esophagus during the last stage of the swallowing process.
- Another function of the isthmus of the fauces is the air pressure regulation between the nasopharynx and the middle ear. This occurs when there is an opening of the isthmus due to the contraction of the levator and tensor muscles of the palate and the circulation of air between the nasopharynx and the middle ear is favored.
- This is why the movements that occur in the oral cavity during swallowing help balance disturbances that may occur in the tympanic cavity.
A example of the function of the isthmus of the fauces occurs, for example, when our ears are plugged when going up or down great heights due to pressure variations and through the action of swallowing and the consequent opening of the isthmus of the fauces balances the pressures between the nasopharynx and the middle ear, uncovering the hearing.

Anatomy of the isthmus of the fauces.
Now that you know the function of the isthmus of the fauces, we are going to know what its anatomy is. It is made up of important parts that allow its function and movements. Among these are:
- The tensor Palate Muscle, whose function is to laterally tense the soft palate, causing the isthmus to open for swallowing and creating a septum between the oropharynx and nasopharynx that prevents the food bolus from passing into the nasopharynx.
- The levator palatini muscle helps the tensioner to fulfill this function.
- The palatoglossus muscle allows the root of the tongue to rise and lower the soft palate, allowing chewing and sucking.
- Other important muscles are the palatopharyngeal and the uvula muscle.
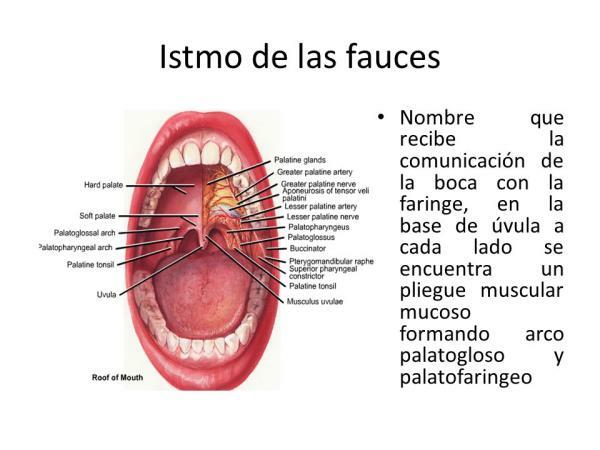
Image: Slideplayer
Diseases of the isthmus of the fauces.
There are multiple pathologies that affect the main structures that form the isthmus of the fauces, especially the palatine tonsils. However, many of these pathologies are not officially described. Thus, in some mammals such as felines, the inflammation of the posterior gingival mucosa is called faucitis.
The pathology more frequent in the isthmus of the fauces is the palatine tonsil hyperplasia. This disease generates important problems for the patient's life, since it generates dysphagia, decreased velopalatine mobility, swallowing problems and nocturnal snoring disorders.
There is also a benign tumor pathology known as fibroma due to chronic irritation of the oropharynx caused by rubbing and that is treated by surgical removal. Another important tumor pathology is the papilloma produced by the infection of the human papilloma virus and its treatment is also surgical. It is benign, although it can also become malignant infrequently.
Limits of the isthmus of the fauces.
The isthmus of the fauces is located in the oropharynx. and has the soft palate on top and the upper border of the epiglottis below.
Forward, it communicates with the oral cavity through the oropharyngeal isthmus. It is limited, therefore, by the muscular formations that constitute the muscular apparatus of the soft palate (soft palate) and that allow its movement. There are four even muscles and one odd muscle.
If you want to read more articles similar to Function of the isthmus of the fauces, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Montanez, N. TO. T., & Manotas, W. P. (2012). Face. Anatomical aspects III–oral cavity and nasal cavity. Morfolia, 4(2), 46-59.
- Farfan, D. R. MOUTH AND CONTENT.
- Sánchez Ruiz, D., Sánchez Martínez, I., & Angulo Sierra, N. AND. SWALLOWING ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. OROPHARYNGEAL DYSPHAGIA, 9.