5 sense organs and their parts
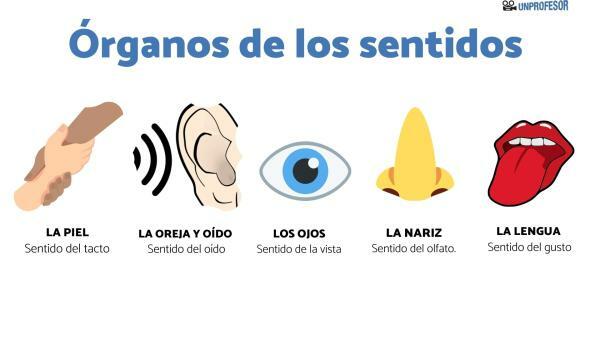
In addition to controlling their internal environment, human beings (and animals) need perceive and react to external stimuli. These stimuli are captured through the sense organs, which are five: sight, taste, smell, hearing and touch. Each of these five fulfill their function, although they are often interconnected. Subsequently, it is the nervous system that allows us to respond to these stimuli. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will learn more about the sense organs and their parts. If you are interested in delving into them, read us below!
Index
- What are the sense organs
- The ear and its parts
- sight and parts of the eye
- Smell and parts of the nose
- Taste and the parts of the tongue
- Touch and its parts
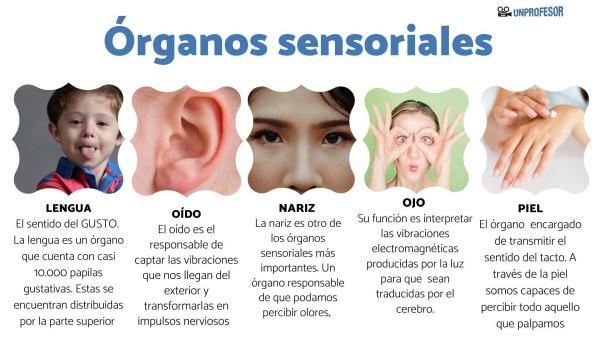
What are the sense organs?
Our five sense organs They are made up of cells that specialize in capturing external stimuli called sensory receptors and that they are the way of entry of external information to the nervous system of an organism.
A general classification of these receivers is the next:
- chemoreceptors: this type of receptor responds to chemical substances. The taste and smell are examples of chemoreceptors.
- mechanoreceptors: the information captured is mechanical. Examples of this type of receptors are those of the touch or hearing.
- photoreceptors: receptors specialized in capturing electromagnetic energy. An example is the view.
The ear and its parts.
We start with one of the sense organs: the ear. Contains specialized cells capture of sound vibrations of the external environment, but it is also in charge of balance, a function located in other specialized cells.
These vibrations are captured by the ear, directed towards specialized cells and transformed into nerve impulses that go to the brain, where they will be interpreted.
The ear is divided into three parts:
- External ear: It comprises the auditory pavilion (known as the ear) and an external auditory canal about three centimeters long that ends at the tympanic membrane. In this ear canal there are also hairs and wax-secreting glands. The function of the external ear is to channel and direct sound waves to the middle ear.
- Middle ear: It is located in the tympanic cavity or tympanic box. Externally, it is separated from the external auditory canal by the tympanic membrane. It is a narrow conduit that extends 15 millimeters in both the horizontal and vertical planes. Its function is to conduct sound waves to the inner ear, for which it consists of three small bones, the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup. Another of its functions is the balance between internal and external pressure through the Eustachian troop.
- Inner ear: is located within the temporal bone and contains the organs of hearing and balance, which are innervated by the auditory nerve. It consists of a series of membranous and bony canals that contain a liquid.
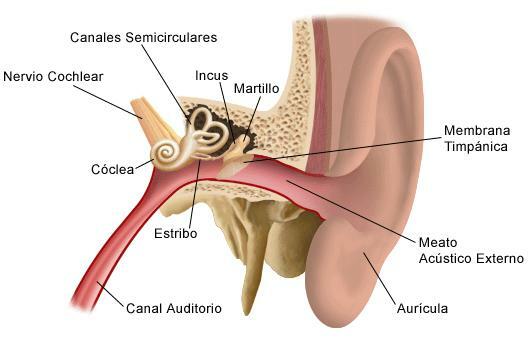
Image: Stanford Children's
The sight and the parts of the eye.
Although the eye is considered the organ of vision, the truth is that it is only in charge of translate electromagnetic signals in a certain type of impulses that pass from the optic nerve to the brain.
The eyeball is a spherical structure curved in its anterior region. It consists of three hats:
- outer layer: It is made up of the sclera, with a protective function, and the cornea, which refracts light.
- Middle layer or uveaConsists of the iris, choroid, and ciliary body.
- inner layer: is the nerve layer or retina, sensitive to light.

Smell and parts of the nose.
We continue to get to know the sense organs and their parts to talk, now, about smell. East sense serves for catch odors. It starts at the nose, which is part of the sense of smell and the respiratory system. It is divided into an external region or nasal appendage and an internal region divided into two main cavities or nostrils, divided by a vertical septum.
On the edges of the nostrils there are hairs that cross the openings and prevent the passage of foreign substances and particles. The inner part of the nose is formed by the two high and deep nasal cavities, which open through nostrils in the front part and end in an opening on both sides of the pharynx.
The olfactory region of the nose is a membrane thick, yellow-colored mucosa known as the olfactory mucosa, and this is where the receptor cells are located.
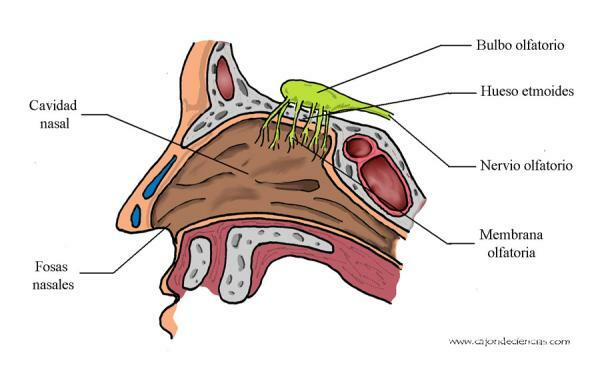
Image: EYE
Taste and the parts of the tongue.
Taste is perceived by the contact of soluble substances with the tongue. Humans can capture a large repertoire of flavors by responding to combinations of different stimuli, including taste, smell or temperature. However, if we consider it in isolation, only four flavors are perceived: sour, bitter, salty and sweet.
In the language is where approximately some 10 thousand taste buds which are unevenly distributed on the upper surface of the tongue. Contrary to popular belief, at high concentrations papillae respond to all four flavors, but at low concentrations, they are flavor specific.
Thus, the taste buds sensitive to sweet and salty are at the tip of the tongue, with those for the sour taste on the sides and the bitter taste at the back. The tongue is a muscular organ covered with a mucous membrane. Where are these papillae located?
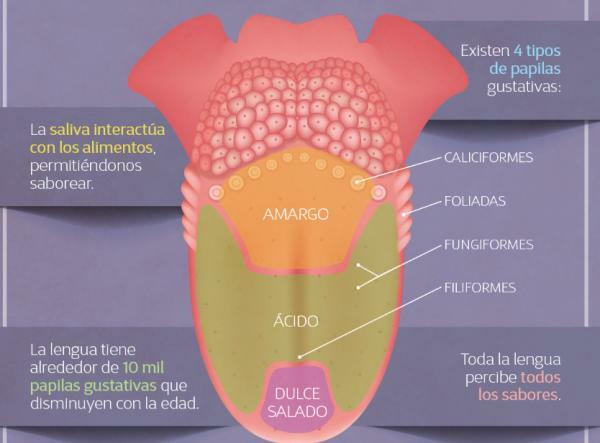
Image: Outline
Touch and its parts.
We end this review of the sense organs and their parts by talking about the sense of touch. Through this sense contact with different objects is perceived, surfaces, etc
This sense is perceived from touch receptors, which are specialized nerve endings that exist on the skin, both in the epidermis and in the dermis. Subsequently, tactile sensations are carried to the brain by nerve fibers.
exist sectors of the skin with different sensitivities, since the number and type of receptors present in the skin is not uniform throughout the body.
If you want to read more articles similar to Sense organs and their parts, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.



