MAIN characteristics of positivism in philosophy
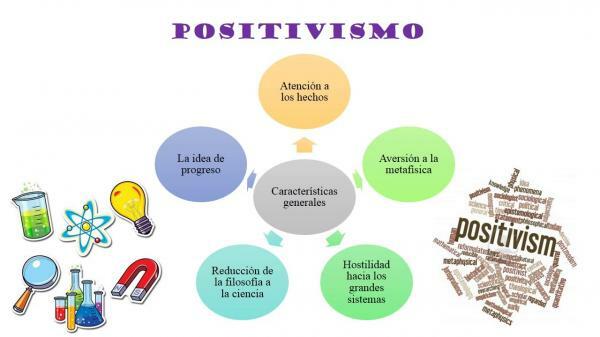
Image: YouTube
This lesson from a TEACHER is dedicated to characteristics of positivism in philosophy. Positivism is a philosophical current that begins at the beginning of the XIX century and that defends the idea that the only knowledge that exists is the scientific one. This means that a conclusion can only be reached from hypotheses. Its main representatives are Saint-Simon, by Auguste Comte and John Stuart Milly, it spread and developed throughout the rest of Europe in the second half of the 19th century. It is considered to Francis Bacon (16th-17th century) a forerunner of this theory. If you want to know more, keep reading this lesson.
The philosophical positivism states that there is only one method of knowledge, and it is the scientific method. If a discipline aspires to be a science, it must have a scientific basis. Only exists a single method for las different sciences. This is what is known by the name of methodological monism. The scientific method is also applicable to the individual and society, which from now on are understood as objects of knowledge.
The rise of positivism is due to the revolution industrial, which completely changes the way of life of the West: advances in the field of science change the modes of production, cities grow and around them, a commercial network arises, which causes an increase in the wealth. Science has managed to improve the quality of life of human beings and cure diseases. On the other hand, this is a fairly peaceful time.
The idea of unstoppable progress it is general, and society is excited. Thanks to science, it would be possible to find the tools to give answers to all the problems that concern humanity. Science now finds applications in the field of industry and will be decisive in the birth of the free market and in changes in educational models.

Image: Slideshare
We are already beginning to speak of the characteristics of positivism in philosophy. There is great diversity within the positivist current, but there are also a number of common traits, that confer a certain homogeneity to it. The main characteristics of this current are the following:
- Claiming the mscientific model as the only method of knowledge.
- Defense of the methodological monism: there is only one method applicable to all sciences.
- The laws of nature are also applicable to the study of society.
- The sociology It is the science that studies the human being and society, insofar as they are natural phenomena.
- The exaltation of the scientific method and the often blind confidence in science made positivism a dogmatic current, less in the case of J. S. Mill.
- Faces the idealistic stream and to any metaphysical conception of reality.
- Optimism is general and this is joined by the idea of unstoppable progress.
- All Explanation it must have a scientific basis. Knowledge consists of explaining the phenomena from the laws of nature, from its causes.
- The knowledge model is the inductive one from obvious truths.
Kolakowski qualifies some of the proponents of positivism as romantics. According to authors like Geymonat, positivism is strongly influenced by the Enlightenment (idea of unstoppable progress, primacy of scientific knowledge, faith in reason ...). In order to Marx, positivism is the ideology of the bourgeois class.
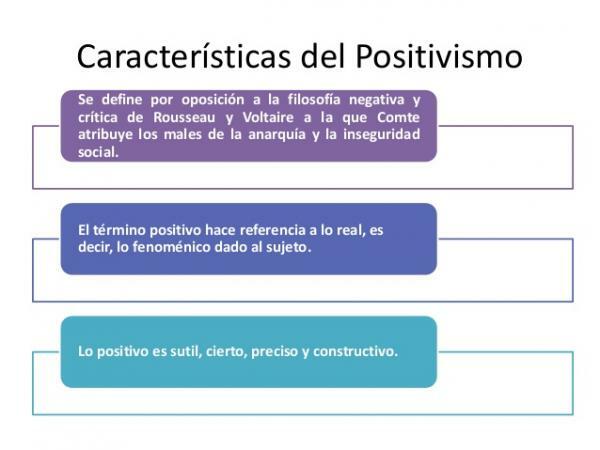
Image: SlideShare
He is considered the father of the sociology, the science that studies society, as an object of knowledge. This discipline covers all areas of society, as well as the relationships between human beings and is based on empirical data, just like the natural sciences
For Comte, the history of humanity is presented in three phases and thus, formulates lthe law of the 3 states:
- Condition theologicalor or magic: corresponds to a time when certain phenomena are considered to be caused by supernatural beings or gods. It is characterized by the search for the essences, the ultimate causes, the because of things.
- State Metaphysicalor or philosophicalor: Continues the explanation of the because of things, but in this period the explanation is more rational. It is characterized by the search for causes and supernatural beings are replaced by metaphysical concepts.
- Condition scientistor or positiveor: It is the last stage and what it is about now is to study the laws of phenomena, as natural. All knowledge, therefore, will have a scientific basis, from the observation of natural phenomena, and experimentation (mathematical model). Only science is capable of answering the great questions of humanity about the world and reality, and not philosophy.
If you liked this lesson on the characteristics of positivism in philosophy, share and keep reading more articles from our philosophy category.



