What are the UNITS of measure

From the beginning, as a consequence of life in society, man has had the need to weigh and measure. Measurements are usually expressed with a number and a unit of measure. The properties that we can subject to a measurement are called magnitudes. Examples of physical quantities are: time, mass, length, force, temperature, etc. The units of measurement have been changing over time according to the needs and technologies of the moment. In this lesson from a Teacher we will see What are the units of measure that exist?
Index
- What are units of measure with examples?
- What are the Units of the International System
- What are the SI units and equivalences
- Anglo-Saxon system of units
- Units of measures of storage in computing
- History of unit measurements
What are units of measure with examples?
Physics is the science that is responsible for studying the properties of bodies, requires measurements to be able to carry out experiments or scientific investigations of the natural world around us. In order to measure, the use of instruments and tools designed for it is required.
As mentioned before, when we measure an object or a body, we obtain a number and next to this number is placed a unit of measure that will indicate the magnitude that is being measured.
Example
Let's see an example, a tape measure is used to measure the length of a table, the result is expressed as follows: 70 cm in length.
The magnitudes are necessary to be able to study natural phenomena and reach conclusions that give rise to scientific knowledge.
What are the Units of the International System.
The International System of Units appears as such in the year 1960 in France.
Let's see what are the SI units of measurement based on the Decimal Metric System.
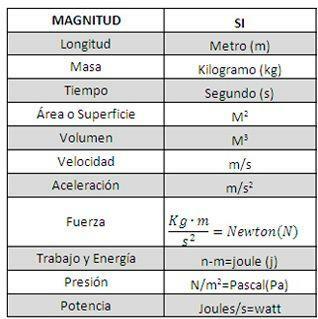
Fundamental quantities and units
Magnitude Unit of measurement Symbol
- Length meter m
- mass kilogram kg
- time second s
- Electric current intensity ampere A
- Thermodynamic temperature kelvin K
- amount of substance mol mol
- Luminous intensity candela cd
From the fundamental magnitudes arise the so-called derived magnitudes. The derived units are obtained from combinations of the fundamental units.
Quantities and derived units
Magnitude Unit of measurement Symbol
- Surface square meter m2
- Volume cubic meter or liter m3 or L
- speed meter per second m/s
- Acceleration meter per second squared m/s2
- Density kilogram per cubic meter kg/m3
- Frequency Hertz or hertz Hz
- Newton Force N.J.
- Job Julio J
- Pressure Pascal Pa
- Power Watt or Watt W
- Electric potential Volt V
- Electrical resistance Ohm Ω
- Radiation dose absorbed Sievert Sv

What are the SI units and equivalences.
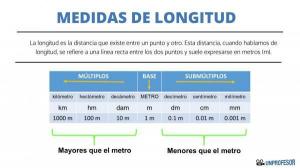
In everyday life, the various units of measurement are used in order to measure and find out different issues. If we go to the example of length, as mentioned above, the unit used is the meter, what happens if I need to measure something much smaller than that measurement or a distance much larger like that of a countryside? This happens with all measurements, volume, time, mass, area, etc. The resolution to this problem is as follows: multiples and submultiples expressed by prefixes that are accompanied by the name of the unit were established. Example with the unit of length (meter): Kilometer, it is formed with the prefix "kilo" preceding the name of the unit of length, "meter". Let's see below what are the units of measurement of the fundamental magnitudes with the prefixes and their equivalences...
Tables of equivalences of the fundamental magnitudes
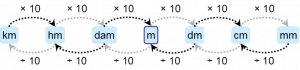
Units of length measurements in the SI with their equivalents
Current definition of the meter: The meter is the length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum during a time of 1/299 792 458 of a second.
Let's see the different lenght measures with their equivalents
unit and symbol Equivalence
- Kilometer (km) 1000m
- Hectometer (hm) 100m
- Decameter (dam) 10 m
- Meter (m) 1m
- Decimeter (dm) 0.1m
- Centimeter (cm) 0.01m
- Millimeter (mm) 0.001m
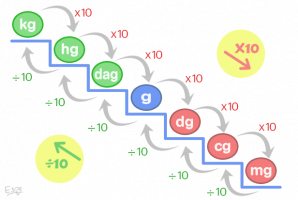
Units of mass measurement in the SI with their equivalents
Current definition of kilogram: The kilogram is the mass unit; is equal to the mass of the international prototype of the kilogram.
unit and symbol Equivalence
- Kilogram (kg) 1000g
- Hectogram (hg) 100g
- Decagram (dag) 10g
- Gram (g) 1g
- Decigram (dg) 0.1g
- Centigram (cg) 0.01g
- Milligram (mg) 0.001g
Units of time measurement in the SI with their equivalents
Definition of a second: The second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the carbon atom. caesium 133.
unit and symbol Equivalence
- Second(s) 1
- Minute (min) 60s
- Hour (hrs) 60min / 3600s
- day 24 hours
- Year 365 days
Tables of equivalences of the derived quantities
Units of surface measurement in SI and their equivalences
unit and symbol Equivalence
- square kilometer (km2) 1000000m2
- square hectometer (hm2) 10000m2
- square decameter (dam2) 100m2
- Square meter (m2) 1m2
- square decimeter (dm2) 0.01m2
- square centimeter (cm2) 0.0001m2
- square millimeter (mm2) 0.000001m2
Units of measurement of capacity in SI and their equivalences
unit and symbol Equivalence
- kiloliter (kl) 1000 l
- Hectoliter (hl) 100 l
- Decaliter (dal) 10 l
- Liter (l) 1l
- Deciliter (dl) 0.1 l
- Centiliter (cl) 0.01 l
- Milliliter (ml) 0.001 l
Units of volume measurement in SI and their equivalences
unit and symbol Equivalence
- cubic kilometer (km3) 1,000,000,000m3
- Cubic hectameter (hc3) 1,000,000m3
- cubic decameter (dam3) 1000m3
- Cubic meter (m3) 1m3
- Cubic decimeter (dm3) 0.0001m3
- Cubic centimeter (cm3) 0.000001m3
- Cubic millimeter (mm3) 0.000000001m3
Anglo-Saxon system of units.
At the moment the only country that continues to use this system of units is USA. Until recently, Burma and Liberia also used this system, but due to international trade, The governments of these states decided to adopt the metric system, thus abandoning the use of the units of the system. anglo saxon
This system is based on the yard, the pound, and the second.
The third part of the yard is the well-known measure called "foot", it is a unit of length. The pound, like the yard, are very old units, the pound is a unit of mass.
Let's see the comparison between units of the Anglo-Saxon System and the International System.
Equivalences between units of the Anglo-Saxon System and the SI
Magnitude Unit of measurement Symbol Equivalence with SI
- Length Inch ln 25.4 mm
- ft ft 0.3048 m
- Yard yd 0.9144 m
- Mile mile 1609.344 m
- Surface Square inch ln2 6.4516cm2
- square foot ft2 0.0929m2
- Acre acre 4046,856 m2
- Mass Pound lb 453.59 g
- Ounce oz 28.3495 g

Computer storage measurement units.
To measure the ability of information storage are used Bytes. In computers, information is stored and transmitted in the form of binary language through codes that use the numbers 0 and 1 as symbols. The data that contains the processes and information of a computer are found in binary code.
Below are the units used by the computer system for data storage:
Unit of measurement Equivalence Symbol
- Bit 1
- Byte b 8 bits
- Kylobyte KB 1024 bytes
- Megabyte MB 1024KB
- Gigabyte GB 1024 MB
- Terabyte TB 1024GB
- Petabyte PB 1024 TB
- Exabyte EB 1024 PB
- Zetabyte ZB 1024 EB
- Yottabyte YB 1024 ZB
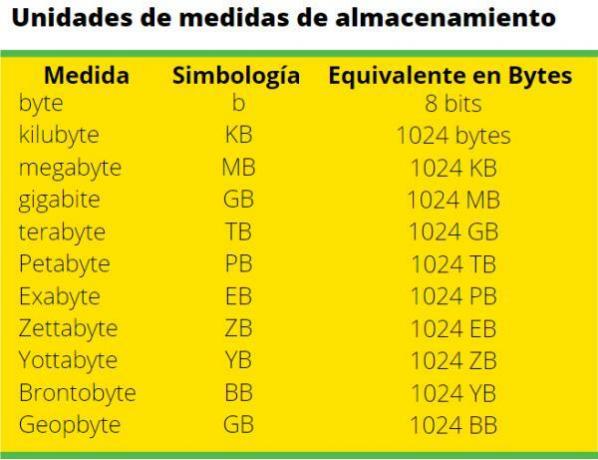
Image: Embou
History of unit measurements.
One of the first activities of man where the need to measure was seen was in the area of building. It is then said that the first units of measurement that arise are those of length. What instruments were used to measure length back then? The different parts of the body were used, for example in Egyptian they were the elbow and the arm, instead, the Sumerian peoples and the Greeks used the measurement of the foot, which was approximately half the cubit. Greeks and Romans also had the measure of the step.
Then the capacity measure would appear, since in those times they needed to know the quantity produced of the food grown on the land to exchange productions. Parts of the body were also used to measure, such as the handful: an amount that could fit by joining the two hands together, open. This was later replaced by containers for animal hides.
A curiosity that continues to occur today is that he gets confused the measure of weight with that of mass. What is your difference? The mass is the quantity of a matter, for example: to cook a cake I need 500 grams of sugar. The weight, on the other hand, is the force with which gravity attracts that amount of matter, it refers only to 500 grams without taking into account what type of matter it is.
The oldest units of mass were grains of wheat or rice (Currently it is kept in the Anglo-Saxon System of units). A balance was used to compare masses, on one side the body to be weighed was placed and on the other the number of equivalent grains. The oldest balance was found in Egypt, dating back to 3800 BC. c.
Just in the 16th and 17th centuries, in which scientific knowledge began to develop more strongly, the need was seen to adopt a precise system of units of measure. In the S. XVIII the metric system is created. In the year 1832 the scientist K. F. Gauss established a system of units based on the fundamental units of length, mass, and time. Later in time, the International System of Units and the Anglo-Saxon System of units, which are currently the most widely used.
If you want to read more articles similar to What are the units of measure, we recommend that you enter our category of Measures.
Bibliography
- Garcia I. and García C."Knowledge and conversion of units. Chap. II. Units of measurement". Final year project. DIEEC. UNED. Madrid Spain.
- International Bureau of Weights and Measures. (2008) "The International System of Units". 2nd edition in Spanish. Spanish Metrology Center.
- Prodanoff L. "Physical. Unit 1. Magnitudes. Units of measurement." University seminar. Materials for students.
- Web application for the knowledge and conversion of units