SATELLITES of the Solar System

Our Solar System is a planetary system of the many that exist in the Universe. This system is characterized by having a central star, around which the planets that we all know orbit, but the thing does not end there. In the Solar System we can also find dwarf planets, satellites of different sizes and smaller bodies such as asteroids and comets.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see which are the main secondary planets or satellites of the solar system. Satellites are the celestial bodies that orbit around a planet. Satellites are usually smaller in size than the planet they accompany, although this is not always the case.
Index
- What are satellites?
- The Moon, the Earth's satellite
- Phobos and Deimos: the moons of Mars
- Jupiter and its 79 satellites
- The 82 moons of Saturn
- The 27 moons of Uranus
- Neptune and its 14 natural satellites
What are satellites?
To discover the satellites of the Solar System it is important that we know what these elements are. The satellites are
opaque celestial bodies what orbit around a celestial body, generally larger.These bodies can be both of natural origin (like the Moon that revolves around the Earth) as the artificial satellites, created by the name and put into orbit of different planets. For example, satellites that allow GPS location are bodies that rotate around the Earth, but satellites are also widely used in the study of other planets.
The satellites are opaque bodies, that is they do not generate their own light. The only light that these celestial bodies show is that they reflect from other bodies that do have their own light; in the case of the Solar System, thanks to the reflection of the light created by our only star: the Sun.
How many satellites in the Solar System are there?
At present they are known more than 219 natural satellites in our Solar system. In this lesson we will only develop the main satellites that orbit the planets primary, but keep in mind that there may be more satellites orbiting these and even the Tiny planets.
Here is a list of planets and dwarf planets of the Solar System and the number of satellites of the Solar System that are natural and known to date:
- Mercury and Venus: 0 (no satellites or moons).
- Land: 1. Remember that when we refer to the Earth's satellite, we write it with the first letter in capital letters (the Moon), while when we refer to the satellites of any planet, we write it in lowercase (moon).
- Mars: 2 satellites or moons
- Jupiter: 79 satellites or moons
- Saturn: 82 satellites or moons
- Uranus: 27 satellites or moons
- Neptune: 14 satellites or moons
- Ceres: 0 satellites or moons
- Orcus: 1 satellite
- Pluto: 5 satellites or moons
- Salacia: 1 satellite
- 2002 MS4: 0 satellites
- Haumea: 2 satellites
- Quaoar: 1 satellite
- Make-make: 1 satellite
- Varda: 1 satellite
- 2002 AW197: 0 satellites
- Gonggong: 1 satellite
- Eris: 1 satellite
- Sedna: 0 satellites

The Moon, the Earth's satellite.
The only natural satellite orbiting the Earth is the Moon. Unlike other satellites that we will see below, the Moon lacks atmosphere. For this reason, it is completely exposed to solar radiation and to meteorites, there is a large difference in temperature between a sunny area and a shaded area (between +95 ºC and -165 ºC). The absence of atmosphere also means that twilights do not occur on the Moon: the sky is always black, both day and night, just like on Mercury.
Another of the most remarkable characteristics of the Moon is that it has what is called a captured rotation. The rotation captured is called the rotation of a satellite whose rotation period coincides with that of revolution, which means that the satellite always "shows" the same face to the planet around which tour. From the Earth, we can only observe one of the faces of the Moon, since the other is always on the other side.
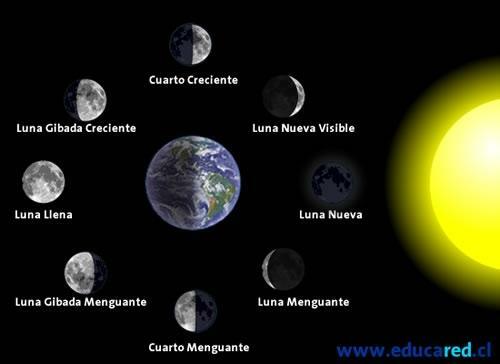
Image: Google Sites
Phobos and Deimos: the moons of Mars.
Phobos and Deimos They are another of the satellites of the Solar System; in fact, they are the two natural satellites or moons that they orbit around Mars.
Thanks to their weak atmosphere, these satellites would be easily visible from the surface of your planet, more than the Moon is from Earth. The two moons are believed to look like two very bright stars. Also, Phobos and Deimos revolve around Mars in opposite directions, creating a beautiful spectacle: two bright stars moving across the sky of Mars in the opposite direction to each other.
Phobos and Deimon are smaller than the earthly moon and not so spherical. These two moons are small in size (Phobos: 27 km x 22 km x 18 km) (Deimos: 15 km x 12 km x 10 km) and an irregular shape similar to two large cosmic “potatoes”.

Image: Astronomy for Dummies
Jupiter and its 79 satellites.
Jupiter has unique characteristics. Its composition, size, etc. They make you believe that, had it been something bigger, it could have been the second star in our Solar System. Their size and the gravitational force they possess makes them orbit around them. lots of frozen satellites: 79 known to date.
The four largest satellites orbiting Jupites are: Ganymede, Callisto, Io and Europa, the calls Galilean satellites. They are so named because they were first discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galileiand they were the first objects found to revolve around a body other than the Earth or the Sun.
Galilean satellites have been extensively studied and it is known that they don't have a real atmosphere, that its surface temperature is low (which usually varies, for example in Europe, between -160 ºC in the sunny area and below -200 ºC) and that some of them contain liquid or solid water in their inside.

Image: Trome
The 82 moons of Saturn.
Saturn, along with Jupiter, one of the most majestic planets in the Solar System. Characterized by its large size and its ring system composed of eight distinct groups of rings, Saturn possesses more than 82 satellites around it. One of them stands out for its large size and atmosphere: Titan.
- Titan is a great satellite, intermediate in size between Mars and Mercury and the only place in the Solar System, along with Earth, where rainfall occurs that gives rise to rivers and lakes. Although on Titan, meteorological phenomena are not based on water, but on liquid methane.
- Another of the most important satellites of Saturn is Enceladus, a small frozen satellite and that has geological activity due to the large amount of internal heat stored inside. This heat seems to cause phenomena similar to water geysers, or others related to cryovolcanism.
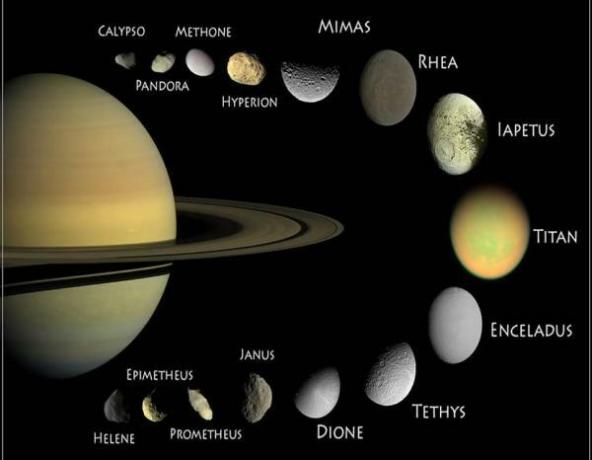
Image: Meteorology Network
The 27 moons of Uranus.
Despite having 27 natural satellites, none of them are of great importance in the study of the Solar System. The vast majority of them are made up of a rocky core surrounded by a blanket of ice or liquid water and they have a rugged surface, riddled with canyons and craters.
The four largest natural satellites of Uranus are Titania, Oberon, Ariel and Miranda. Miranda is the most active body in the Solar System to date.

Picture:
Neptune and its 14 natural satellites.
We finish this review of the satellites of the Solar System to talk about Neptune. Of the 14 satellites described so far around Neptune, Triton is undoubtedly the most important. It is the largest satellite found in the orbit of Neptune, and the only one with a spherical shape. It is somewhat smaller in size than the Moon.
- Life in Triton it is not very cozy, as it is the coldest satellite in the entire Solar System, with surface temperatures of -235ºC and is geologically very active. Both of these give rise to geysers in the polar caps, expelling nitrogen snow. In addition, Triton has a mild atmosphere, composed of nitrogen and traces of methane, mainly.
- Another important moon orbiting Neptune is Proteus. Proteus is the largest irregular body in the solar system and one of the darkest bodies in the solar system, which meant that it was not discovered until NASA brought Voyager 2 closer.
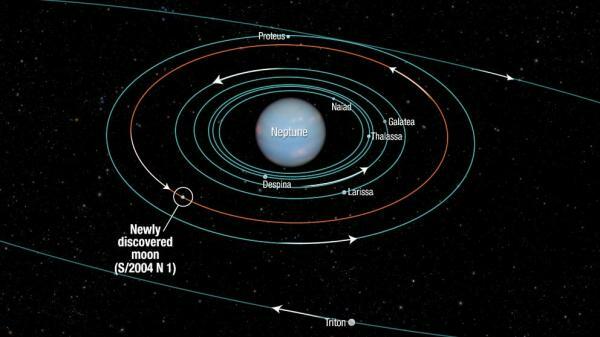
Image: OK Diary
If you want to read more articles similar to Satellites of the Solar System, we recommend that you enter our category of Astronomy.
Bibliography
- García Julio, S. (2015). The Heavens of the Planets and Satellites of the Solar System. ACTA Digital Magazine.
- Wikipedia (April 26, 2020) List of natural satellites Recovered from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_natural_satellites
- Wikipedia (May 2, 2020) Solar System. Recovered from: https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sistema_solar
- Wikipedia (February 17, 2020) Proteus (satellite) Retrieved from: https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proteo_(sat%C3%A9lite)


