How the Sun was formed

The Sun, like the rest of the stars, is not an immutable object, rather, they evolve over time. Stars are born, grow old, and finally die. However, it is a process that occurs very slowly and is not observable on a human time scale.
The process of star formation lasts hundreds of thousands of years and occurs within a sufficiently dense and extensive interstellar cloud. In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we travel five million years into the past to tell you how the sun was formed.
Index
- The Sun in the solar system
- How a star is formed
- What is the Sun and how was it formed?
The Sun in the solar system.
The universe is made up of a multitude of galaxies. The galaxies they are a set of stars, planets, nebulae, cosmic dust, gas clouds and other materials that are held together by gravitational attractive forces.
The gravitational attractive forces or gravitational forces, are the attractive forces that objects with a certain mass exert on other objects of smaller mass. This force is proportional to the product of the masses of the objects divided by the distance between the two bodies, squared.
Galaxies can come in different sizes and shapes. The galaxy in which the solar system is located is the Milky Way. The Milky Way is a spiral-shaped galaxy with four arms. The Solar system orbit in the center of the galaxy located in one of these four arms, the so-called orion arm.
The Milky Way is a very old galaxy and is considered almost as old as the universe itself. It is considered to be a cannibal galaxyIn other words, an early galaxy that throughout its life has acquired its current size by "swallowing" other smaller galaxies. These collisions or mergers of galaxies cause condensation of matter that favors the star birth, like our Sun, the central star of the solar system.
How a star is formed.
The Sun is the main star in the Solar System, so if we want to know how the Sun was formed it is important that we understand how the stars were formed In the universe. Here we show you how this process is.
The formation of protostars
The birth of a star begins with a large cloud of dust and hydrogen gas relatively cold, drifting in space. Due to the gravitational irregularities of the galaxy, the cloud begins to thicken in places. In this way, the cloud of dust and gas begins to fragment in some areas, giving rise to protostars.
The protestrellas they are points of higher density within the cloud of dust and gas. As a result of gravitational forces, the protostar gains mass and contracts. This contraction of the protostar causes an increase in the temperature inside it.
Nuclear fusion reactions: the birth of stars
The more the protostar contracts, the more its temperature increases. When the temperature of the core reaches 1,000,000ºC, triggers in his interior reactions of nuclear fusion.
As we have already mentioned, the gas clouds that give rise to protostars are composed of Hydrogen. The Hydrogen (1H) It is the simplest and most abundant element in the Universe. Hydrogen atoms are composed of a nucleus made up only of a proton (a subatomic particle with mass and positive charge) and an electron (subatomic particle with negative charge and without mass) rotating around said nucleus.
There is also a isotope stable Hydrogen, called Deuterium(2H) whose nucleus, in addition to a proton, contains a neutron (subatomic particle with mass but without charge). Deuterium atoms are also part of these gas clouds.
In the nuclear fusion reactions or thermonuclear reactions, the nuclei of hydrogen atoms combine with those of deuterium, to form atoms of Helium-3 (3He), a light isotope of Helium (4He), with a nucleus made up of two protons and one neutron. This reaction releases an enormous amount of energy. The pressure of the released energy stops the collapse of the star, which stops contracting and "turns on", that is, it begins to emit radiation, including visible light.
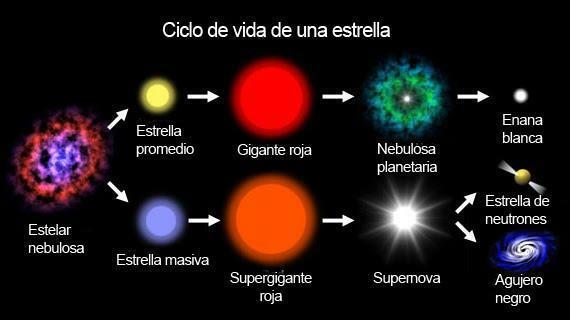
Image: Brainly
What is the Sun and how was it formed?
The sun is the star that constitutes the center of the solar system. Despite its enormous size (it is 1.3 million times larger than Earth) it is not a particularly large star and is classified as yellow dwarf.
The Sun was formed, like the rest of the stars, by the collapse of a cloud of gas and dust. The collapse of the cloud resulted in the concentration of mass in the center of the disk-shaped cloud, the so-called solar nebula. In the center of the solar nebula, more and more mass accumulated, concentrating the 99% of the mass of the entire nebula.
This central mass gave rise to the formation of a protostar that became more and more dense and increased the temperature of its core until it reached temperatures high enough to trigger thermonuclear reactions, which gave rise to the birth of the Sun, which began to emit radiation.
Although the general process of the formation of the Sun is known. It is not known with certainty how the Sun formed in detail.
Single star, star pair, or multiple star system?
The birth del Sol took place about 4.5 million years. It is an isolated star, although in many cases stars do not form in isolation, but most are part of pairs or multiple systems.
It is currently unknown whether the Sun formed as an isolated star or was part of a group of stars that eventually dispersed. As in the Orion Nebula, one of the star-forming regions closest to our solar system. In this nebula the simultaneous formation of thousands of stars takes place. Either it formed as an isolated star as in the nebula in the constellation Taurus.
A supernova from a nearby star, the origin of the Sun?
It is likely that the collapse of the cloud of dust and gas that caused the formation of the Sun was due to the blast wave from a supernova from a nearby star.
The supernovae they are the most powerful type of explosion a star can produce when it dies. When a star depletes Hydrogen, which is the fuel for nuclear fusion reactions, the core of the star begins to cool, causing the internal pressure to drop. The internal pressure exerted an outward force that maintained a balance with the forces of gravity that pushed inward, giving stability to the star. When the star "turns off" and the internal pressure disappears, the star collapses (collapses towards its center), creating huge shock waves that cause the exterior of the star to explode.

If you want to read more articles similar to How the Sun was formed, we recommend that you enter our category of Astronomy.
Bibliography
- John Gribbin. (2007). Biography of the universe. Barcelona: Editorial Crítica. Planet Group.
- National Geographic Spain. Drafting (2018). 11 things you didn't know about the Milky Way We tell you some things that will surprise you about our galactic neighborhood. Nationalgeographic.com.es
- Mario F. Lopez. (2019). Stellar Evolution: Main Sequence.astroaficion.com