The ABSOLUTE error and the RELATIVE error

In a PROFESSOR we explain what is absolute error and relative error, two errors that can deviate you from the result that you should obtain when making a measurement. Because even if you think you measure accurately, what you actually do is get close to a result. This may be due to a fault in the measuring instrument, from the observer's point of view or uncontrolled accidents, therefore, it is normal to make several measurements in equality of conditions and with the data obtained in each one, the arithmetic mean is calculated, and the result becomes the highest value probable. This final result is linked to the doubt in relation to that measure, and this doubt can be expressed numerically, from the calculation of the absolute error and relative error.
Index
- What is absolute error
- How the actual value is calculated
- How absolute error is calculated
- What is relative error and how is it calculated
What is the absolute error.
The absolute error (Ea)
is the difference between actual value and approximate value, that is, the result obtained when measuring. It is placed between bars to express precisely that it is an absolute value.Ea = | Actual value - Approximate value |
The absolute error is always expressed in positive, even if the approximate value is higher than the real value, and as a consequence it gives a negative result.
Absolute error example
Ea = | 2 m3 - 1.9 m³ | = | 0.1 m³ |
In this case the value is positive. But let's look at another example.
Ea = | 5 m³ - 5.2 m³ | = | - 0.2 m³ | = | 0.2 m³ |
As you can see, even though the value is negative, the result is always positive. Absolute error can never be negative.
How the real value is calculated.
First you need to know the real value. To do this, different measurements have to be made under equal conditions and calculate the arithmetic mean with the results obtained in them. As a general rule, a table is used with the results obtained after measuring a number n of times, and next to it, the number of times that each of the measurements has been obtained is placed.
Imagine that you have taken a measurement 15 times. So we have that, n = 15. Then you make the table
Xi fi
2, 50 m³ 2
2.48 m³ 3
2.51 m³ 5
2.52 m³ 5
Notice that we have put, next to each measure, the number of times each result has been obtained. Afterwards, each result must be multiplied by the number of times it has been obtained, and the final result is calculated, adding each of the results.
Xi fi
2.50 m³ 2 5.00 m³
2.48 m³ 3 7.44 m³
2, 51 m³ 5 12, 55 m³
2.52 m³ 5 12, 60 m³
Xi * fi = 37.59 m³
To calculate the real value you have to divide Xi * fi by the number n of measurements, in this case, 15 times.
X = ∑i = Xi - fi / n = 37.59 / 15 = 2.506 m³
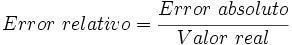
How the absolute error is calculated.
As we have commented previously, this average that we have calculated is the value that we will consider as real. Since the absolute error (εa) of each measurement is the difference between the real value and the value obtained in the measurement, we are going to add a new column in which both values are subtracted:
Xi fi Ea = X - Xi
2.50 m³ 2 5.00 m³ 0.006 m³
2.48 m³ 3 7.44 m³ 0.026 m³
2.51 m³ 5 12.55 m³ 0.004 m³
2.52 m³ 5 12, 60 m³ 0.01 m³
Xi * fi = 37.59 m³
Now it's done the arithmetic mean of all Ea and divide by n. A) Yes:
Ea = ∑ Xi * fi / n = 0.0115 / 15 = 0.0007 m³

Image: Slideplayer
What is the relative error and how is it calculated.
The relative error it is the result of multiplying the absolute error by the actual value, that is, the mean). As the absolute error can be positive or negative, but the difference is that instead of units of measurement, it is accompanied by a percentage (%).
Er = EaX * 100%
In this way, it indicates the percentage of error in the measurement.
Er = 0.0007 * 2.506 * 100 = 0.17%
Have you seen how easy it is with a few simple examples? Don't forget that math takes a lot of practice. And if you want to practice more, you will find below this video, some printable exercises with solutions for you to do.
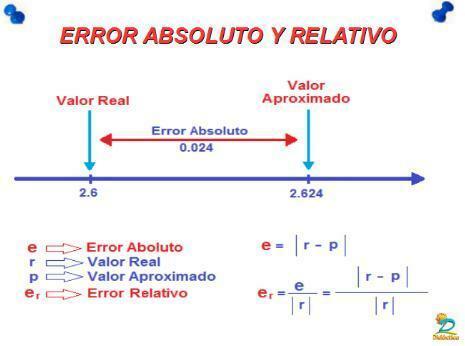
Image: Brainly
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the absolute error and the relative error, we recommend that you enter our category of Arithmetic.

