9 characteristics of POST STRUCTURALISM
Apr 28, 2023
0

In today's lesson we are going to study the characteristics of post-structuralism, a current of thought that was born in France in the 60-70s of the 20th century and which is the heir to structuralism, a previous intellectual movement.
However, post-structuralism comes to refute and criticize many of the theses of structuralism (Claude Lévi-Strauss) such as the idea that the structure is the center of everything and that through it we can understand human culture or the thesis that defends objectivity and neutrality in the study of social sciences.
If you want to know more about the poststructuralism and its characteristics, keep reading this article by a PROFESSOR Class begins!
Before talking about the characteristics of post-structuralism, let's get to know the definition of this term better. poststructuralism takes place in France during the second half of the 20th century within the Social Sciences. Having a special incidence in sociology, anthropology, philosophy, history/archeology or the literature of Europe and the United States.
This theoretical and epistemological movement, which is contemporary with may 68 (student protests against capitalism and imperialism), was born as a current critical of the structuralism of Cluade Lévi-Strauss, but without leaving it entirely. That's why, draw the boundaries between structuralism and post-structuralism it's so complex.
However, poststructuralists are going to question the objectivity the neutrality and logic that had been inserted into the study of the social sciences with the structuralism. That is to say, structures are not something objective and may be biased by one's own interpretations, history or culture, therefore, there is subjectivity in its meaning.
Most Notable Philosophers of Poststructuralism
Finally, within this current the philosophers of the Frankfurt School already Roland Barthes, Michel Foucault, Jacques Derrida, Jurgen Habernas, Jean Baudrillard, Jacques Lacan, Judith Butler and Julia Kristeva. Although many of them refused to be labeled as post-structuralists.
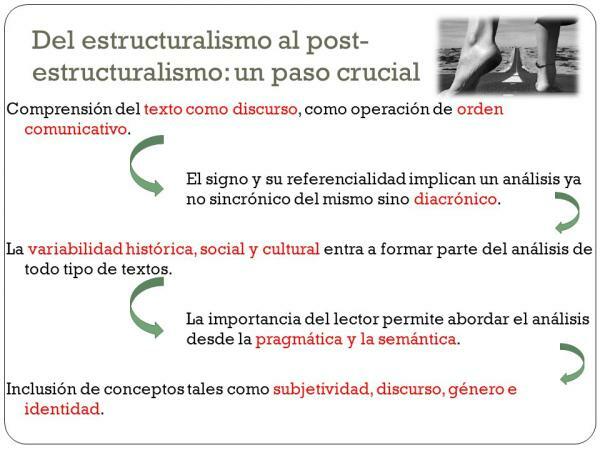
Among the characteristics of post-structuralism, the following stand out:
- The concept of the self: The self/individual is made up of a set of elements or characteristics (knowledge, gender, work, education...) that define it and that make the self a coherent entity, but in reality it is something created by one's own community.
- perception: The concept that each one has of their own self directly influences perception, that is, how each person perceives or interprets a sign, signal or symbol in a particular way. Thus, perception is key to the development of the individual's daily life, since this (the individual) gives meaning to a sign.
- The perspective: The individual has sufficient capacity to interpret a text or the reality that surrounds him from different prospects or interpretations, which do not have to coincide. What is interesting is the diversity in the interpretations and the fact that the individual is able to analyze from different perspectives.
- Reality: For post-structuralism, reality is not a neutral representation, but rather a construction carried out under the idea of objectivity. In this way, reality can be biased by language, individual interpretations, history or culture, and therefore, it will never be possible to access an objective reality.
- The individual and language: Language is what creates reality because it shapes people's thoughts, forges the self and the forms/modes of representation (ways of creating, ordering and describing reality).
- intertextuality: A text is heterogeneous, that is, it is the result of different interpretations, ideas or prejudices of the author. However, the text is not only constructed by the author, but also by the reader when he reads the text.
- The author's death: In a text an endless number of variables are intermingled (the identity of the author and the reader, the time and the culture in which it was written...). Hence, from post-structuralism it is affirmed that to analyze a text the identity of the author is left on a secondary level, since that, the text belongs to the culture and to the reader in its analysis (decomposing the structure of the language with which the text has been written up).
- The power: According to Foucaultpower goes beyond the power that a government can exercise. Power refers to all forms of power that are exercised in society, and its definition includes the notion of sub-power or different relationships of authority at different levels, which collaborate and subtly manifest themselves because they are deeply rooted (= violence symbolic).
- Gender or sexuality: According to Butler's theory, the sex-gender duality must be questioned, which is internalized in a natural in the ideology of the individual because it is a social construction (the historical, the political and the social). However, for post-structuralists, gender is built through speech because it is what shapes our self = the individual becomes a subject when he internalizes his gender.
In short, post-structuralism is characterized by being historical, by questioning the objectivity given to the social sciences, criticize universal structures by not taking into account the context that surrounds them and put aside the dualistic concept/binary relations (signified-significant) of structuralism.




