EXTERNAL structure of a text and its parts

Identifying the order and the way in which a text is divided allows us to recognize its type, its purpose and sections. A) Yes, the structure at the hour of writing It's fundamental to achieve spinning a sense and order of what we want to communicate. In this sense, they are made up of two types of structures, one internal and one external. In this lesson from a teacher we will see what is the external structure of a text.
First, let's break down the meaning of external structure. On the one hand, we have the word structure that refers us to order and the relationships that the parts of a whole have. In this case the whole is our text. On the other hand, the word external refers precisely to those parts of the whole: the title, the subtitles, the sections, the paragraphs, among others.
The structure of a text is the way in which we arrange its parts to facilitate reading and so that the type of text that we are writing is identifiable, since it is the first thing we identify at the moment of having contact with it.
For example, visually, a song is not the same as a letter and an essay. While in the song we find a title followed by stanzas, in the letter We will see that there is a header with the date and the sender. And, unlike these two, the essay or argumentative text comprises a structure that follows the order of introduction, development and conclusion. Since we want to know the structure of a text, we will refer to examples that have to do with this third case.
Image: Literature-Blogger
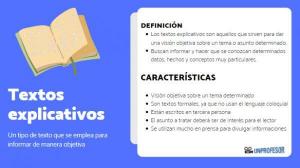
Communicating ideas always implies giving them a common thread, for this the external structure of the texts allows us to constitute our ideas through paragraphs. At the same time, these paragraphs are preceded by a title and are divided into 3 main levels: the introduction, the textual body and the conclusion. Although each type of text varies in its objective, for example, argumentative text does not have the same intention as the exhibition, its structure maintains similarities with these 3 levels mentioned. In the following, we present in a general way the parts of the external structure that are shared by most of the texts.
Title
This is the gateway to our writing. It's the first thing readers will come across. It should give a general idea of the text. The reader must be able to intuit, when reading it, what type of content he will find there. However, the title does not need to explicitly state that topic. It can be through an ironic tone, a metaphor or indirectly that the title fulfills its function.
The introduction
This is the first section of any text. Usually, the opening paragraphs that introduce the topic and objective of our text are what we call introduction. In these first paragraphs the author comments on the main idea. If the title already gave us the idea of the text, here the author fully comments on what the writing will be about. This allows readers to identify whether the content of the text is of interest to them or not.
The textual body
The development or body of the text is usually the longest section. In it we find the arguments, justifications, explanations, figures, quotes or data that support the general theme that the author proposed in the introduction. Depending on the type of text in the development we will find opinions or facts. It can be divided by subtitles.
Additionally, this is the space where the author establishes that purpose and objective that was drawn at the beginning of the text, is the point at which we find the meaning of the title and the introduction that he has presented to us in a previous.
The conclusion
This is the last section of the text and works as a collection type or summary of the path traveled by the author. Usually in a couple of paragraphs, a recap of the main ideas is made. However, the endings may vary. There are texts that use closed endings, where only a summary of the text is made; open ends, where the author brings up questions or concerns that remain open after having presented his position; or they can also be used circular ends, where the author refers to a specific idea that started the writing.
As we have said throughout this article, this is a basic structure shared by different types of texts. To know in depth the structure of different written products, we recommend you properly investigate the argumentative texts, exhibition, historical or informative.