5 differences between ANCIENT and MEDIEVAL philosophy
One of the main differences between ancient and medieval philosophy It is that Greek and Roman philosophies have the world as their center, while medieval philosophy takes divinity as the center of the world. A basic difference that also defines which is the basic branch of each of these epochs. Thus, classical philosophy had ethics as its central part, while medieval philosophy has metaphysics.
In this lesson from unPROFESOR.com we delve with you into what are the differences between ancient and medieval philosophy.
Before talking about the differences between ancient and medieval philosophy, we are going to learn more about both philosophical contexts that will help us better understand the lesson.
Theancient philosophy It is a period in the history of philosophy that spans from its beginnings in ancient greece, around the sixth century BC, until the end of the roman empire in the fifth century AD c. A period of time in which various philosophical schools arose and fundamental ideas were developed that have influenced Western thought to this day.
Between the main names of ancient philosophy stand out:
- Thales of Miletus (c. 624-546 B.C. C.)
- Pythagoras of Samos (c. 570-495 BCE C.)
- Heraclitus of Ephesus (c. 535-475 BCE C.)
- Parmenides of Elea (c. 515-450 BCE C.)
- Socrates (469-399 B.C. C.)
- Plato (427-347 B.C. C.)
- Aristotle (384-322 B.C. c.).

The medieval philosophy refers to a period in the history of philosophy spanning from the 5th century to the middle of the 15th century. A period of time during which philosophy was greatly influenced by Christian tradition and the Catholic Church, thus developing numerous debates and philosophical reflections within the context of religious faith.
Between the main currents of medieval philosophy stands out:
- The Patristic, or Christian theology of the first Christian writers, whose main representatives were Saint Augustine of Hippo or Saint Anselm of Canterbury;
- The Scholasticism or philosophical current developed in the medieval universities and that harmonized the Christian faith with the philosophical reason. Among the main figures of Saint Thomas Aquinas and William of Ockham.
- The medieval islamic philosophy greatly influenced European philosophy and contributed to philosophy, science and medicine. Prominent figures include Al-Farabi, Avicenna, and Averroes.

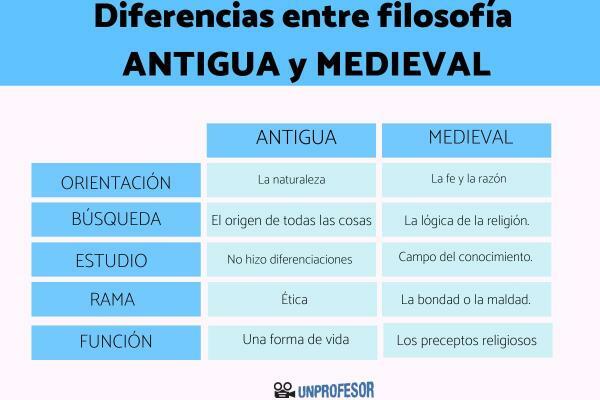
Between the main differences between ancient and medieval philosophy stand out:
- Ancient philosophy had as its center of philosophical orientation nature and all the processes that are perceived in it, while medieval philosophy had faith and reason as its main centers.
- ancient philosophy searched for the origin of all things, being interested above all in where and how life arose and what was the substance of all things of the nature, while medieval philosophy was more rational and traced the logic of the world to religion and Faith.
- ancient philosophy did not make differentiations between the different disciplines of knowledge since philosophy covered all knowledge, from art to mathematics. Within medieval philosophy, the branches included in philosophy were located within the field of knowledge.
- In ancient philosophy they had as their main branch the ethics, a branch that tries to establish what is good and bad, while in medieval philosophy ethics is applied following the dictates of religion in relation to goodness or evil.
- During ancient times, philosophy became a way of life, living the philosophers according to their philosophical thought, while in medieval times the philosophers had to stick to religious precepts.
Similarities between ancient and medieval philosophy
Be that as it may, ancient and medieval philosophy also had certain similarities as:
- Both seek the truth and happiness of the human being.
- They had a series of important representatives who left us their writings and thoughts.
- Both searched for answers to basic questions of life, looking for a meaning to it.



