Rules of accentuation in Spanish

Image: Pinterest
The accentuation rules They are fundamental in Spanish because they allow us to distinguish the meaning of words, as well as to facilitate their correct writing and pronunciation. The accent or diacritical tilde (´) is used to indicate the stressed syllable, that is, the syllable that sustains the greatest blow of the voice. In Spanish, the accent can only fall on one vowel and is used following a series of established stress rules.
The accent in Spanish is very important because it allows us to differentiate words from each other; for example, "public" is not the same as "public" and "published". For this reason, in this lesson from a TEACHER we will study what are the rules of accentuation in Spanish. Keep reading!
To correctly stress the words in Spanish, we carried out a division into three categories different depending on the stressed syllable; in this way, we have: acute words, which are those whose stressed syllable is the last, flat words, with the penultimate syllable stressed and, finally, the words esdrújulas, which have as their stressed syllable the syllable antepenultimate.
Well, once this division into three groups has been carried out, we are going to study what are the general rules of accentuation in Spanish:
- All sharp words (last stressed syllable) are stressed when they end in vowel, "n" or "s": english, truck, dad, paris, japan, coffee.
- The plain words (penultimate syllable) are stressed when they do not end in a vowel, "n" or "s": easy pencil nifty angel tree.
- The esdrújulas words (third to last syllable) are stressed forever: doctor, spirit, banana, camera, music
In this video of a PROFESSOR we help you to differentiate sharp, flat and esdrújulas words.
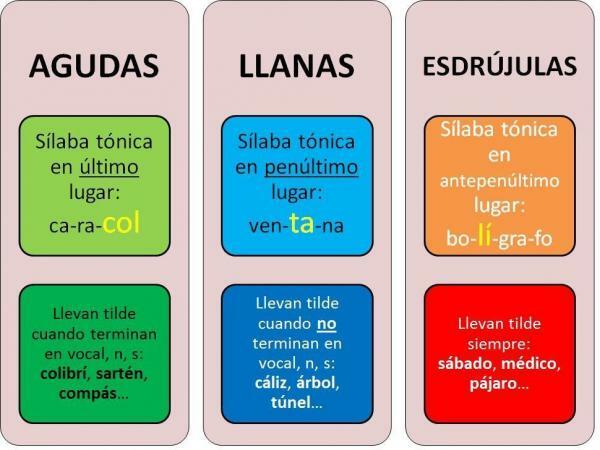
Image: Educational Pictures
In addition to the accentuation rules that we have seen in the previous section, below we are going to briefly name some important aspects related to graphic accentuation which is very important to keep in mind when we want to write without making spelling mistakes.
For example, words like adverbs ending in "-mente" They must be accentuated if, when applying the accentuation rules on the base word, it has an accent. Thus, an adjective such as "easy" that has an accent, gives rise to the adverb of "manner"easily", which must be accentuated because it is formed from a word with an accent. However, "happy" does not have an accent because it is a high-pitched word that does not end in a vowel or in "n" or in "s" and therefore it does not have an accent, it gives rise to the adverb "happily" which, for the reasons previously stated, is not accentuates.
On the other hand, verb forms that carry enclitic pronouns They must be accentuated whenever the accentuation rules so establish, regardless of whether the word on which they are formed has an accent mark or not. Thus, the verb form "coge" does not have an accent because it is a plain word ending in a vowel, however, the imperative form with the pronoun, "take it"Yes, it does have an accent because the accent shifts, becoming, in this case, an esdrújula word that, as we have seen at the beginning of this lesson, must always be accentuated. Following this idea, we can state that all imperative forms with pronouns are always stressed, since they respect the basic rules of accentuation in Spanish.
In addition, compound words whose first element has a tilde, it loses this in the first element, as is the case, for example, of the adverb "thus" which is accentuated because it is a sharp word ending in a vowel, but which nevertheless loses the accent when it becomes "in addition". However, in this regard it is important to bear in mind that if the two words that make up a compound word go separated by a dash in the middle of the two, both the first element and the second element of the same will retain their accent graphic: physiochemical.


