What is the FUTURE INDICATIVE with examples

One of the great things of Spanish is that it is made up of multiple verb tenses. As a consequence its richness and verbal complexity, compared to other languages of the world, are unmatched. One of the most widely used verb tenses is called the future indicative. In this lesson from unPROFESOR.com we are going to delve into what is the future indicative with examples so that you know how to use it and the particularities of the conjugation of the future indicative in Spanish.
Index
- What is the future of indicative
- Future indicative examples
- The forms of the future indicative
- How to conjugate the future indicative
- Conjugation of irregular verbs in the future indicative
- Conjugate the future indicative of inflectional verbs
What is the future of indicative.
The indicative future is a verb tense of indicative mood indicating a subsequent event or action. That is, it indicates an action that has not yet occurred, but most likely will happen in the future.
In Spanish grammar, as in many Romance languages, the development of the future is increasingly displaced by other verb forms. From the first knowledge of the language we are presented with a non-existent future, in which a desire is indicated as an expression of futurity.
For example, enter "I hope to eat" Y "I'll eat" there is not much difference in the action that is thought to take in the future.
In our mother tongue, In Latin, these desiderative-futuristic forms were also almost non-existent. They used two formations for the future: depending on the conjugation to which the verb belonged, a suffix "b" derived from the stem (Amabo for I will love), and the derivative of a subjunctive with great affinity with the future, especially in a phonetic way.
Later evolutions, most of them, coming from the vulgar language, and ended up disappearing until reaching the currently known forms future indicative. Although, even these, they are losing ground in favor of periphrasis depending on the context.
"I will sing" for "I'm going to sing"
Examples of the future of indicative.
We use the future indicative with the following expressive needs:
Description of actions to be carried out in the more or less near future.
- My daughter will be arriving from London tomorrow.
- You will write the letter on the first Monday of the month.
Probability questions that occur in the present within rhetorical premises.
- Where will you put my books? for Where are you going to put my books
- Will they be on the right shelf? For It will surely be the best site.
Determination and affirmation that the action will be carried out in the future, whether it is indicated if it will be executed soon or in the distant future.
- I'll finish tomorrow at eight tells us with certainty that Tomorrow at eight I'm done.
- I will never do it again, expresses determination to I'm not going to do it anymore.
It is also used with order value, almost as if it were an imperative expression: You will go to bed now; or as an attenuation of the forcefulness of an idea:You will not have my approval for it.

The forms of the future indicative.
According to its temporality, the future indicative has two forms:
- Future simple indicative to inform what will happen in the future, without dependency and efficiently. Example: You will hear what I am about to say. It indicates that yes or yes he will listen.
- The future perfect indicative It is a time that is composed with the auxiliary verb "Haber", conjugated in the person and number of the noun, plus the participle of the verb that expresses the action to be performed. It links a previous future action to a future one, and in relation to the past. Example: I will have arrived at eight.
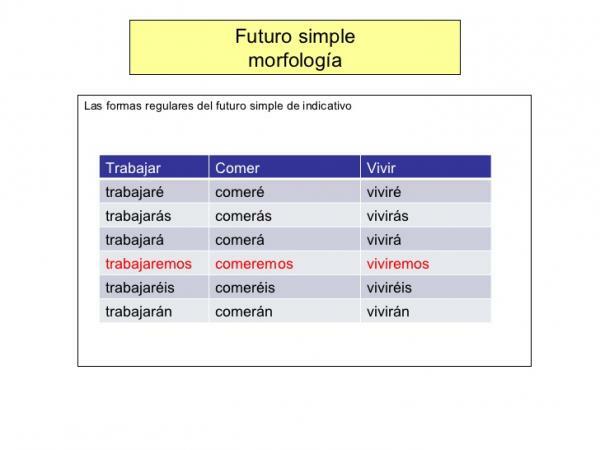
Image: Slideshare
How the future indicative is conjugated.
The conjugation of the future indicative for all regular verbs in all endings (-ar, -er, -ir) is constructed by adding a series of invariable endings to the infinitive form of the predicate that is conjugated.
Conjugation endings of the future indicative in regular verbs
- -é: to add in the first person singular. Example: I will sleep
- -ace: is added to the second person singular. Example: will you sleep
- -á: added to the third person singular. Example: will sleep
- -emos: in the first plural. Example: we will sleep
- -eis / éis: to add in the second person plural. Example: you will sleep
- -an: to form the third person plural. Example: they will sleep
The conjugation of irregular verbs in the future indicative.
In our grammar irregular verbs in their conjugation with the future indicative they can present the following cases.
The loss of the vowel "-e" of the infinitive, in verbs of the second conjugation (-er), and the endings of the regular verbs are added. They are: fit, power, have, know.
- I will fit> I will fit
- Say> will you say
- Power> may
- Have> there will be
Irregular verbsput, leave, have, hold and comereplace the vowel of the second and third endings (-er, -ir) with a “d”, and they are conjugated with the regular endings.
- Put> I will put;
- Exit> you will exit;
- Have> we will have;
- Worth> you will be worth;
- Come> they will come
In theirregular stem verbs say and have they change its root in all persons before adding the future endings.
- Say:I will say, you will say, we will say, you will say, they will say
- To have: there will be, there will be, there will be, we will, there will be, there will be.
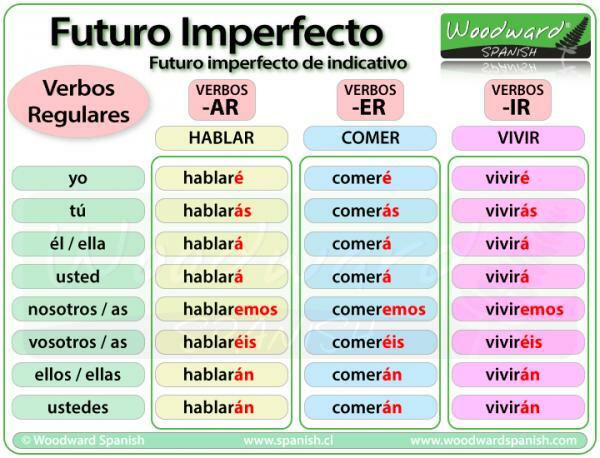
Image: Woodward Spanish
Conjugate the future indicative of inflectional verbs.
For the reflexive verbsthe reflexive pronouns are added before the verb that is conjugated I, I, I, I, I, I, I, and it is the same for the regular ones as for the irregular ones.
- Say> you will tell me;
- Put> you will put;
- To love> you will love each other.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the future indicative and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of Grammar and Linguistics.
Bibliography
BUSQUETS, L. and BONZI, L. (1993). Spanish verbs. Madrid: Ed. Verbum.



