Difference between MORPHOLOGICAL and SYNTACTIC analysis

The morphological analysis consists of saying what grammatical category each of the words that make up the sentence belongs. The grammatical categories are the noun or noun, the determiner, adjective, verb, preposition. Another way to put it would be that morphological analysis consists of determining the grammatical form, class, or category of each word in a sentence.
When we do an analysis we must clearly know what is being asked of us, since we can do it in two different ways. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see what is the difference between morphological and syntactic analysis of a sentence. To understand it, we must indicate what each of them consists of and how they are carried out.
Morphological analysis is what helps us to indicate to which grammatical category belongs to each of the words that make up a specific sentence. To correctly carry out a morphological type analysis, we must point out that the classes of words are the following:
- The adverbs: they are words that serve as a complement to an adjective, another adverb, a verb or another sentence. Adverbs in Spanish have different types: mode, place, time, quantity, negation, doubt and order.
- The determinants: these are words that always accompany nouns and provide information about where they are located in space, their membership, their gender and their number. Among the determinants we can find the following: definite, indeterminate, demonstrative, possessive, indefinite, numeral, interrogative and exclamatory articles.
- The pronouns: we use them when we want to substitute a noun and thus avoid its repetition in an unnecessary way within a text. Pronouns can be of different types: personal, demonstrative, possessive, indefinite, numeral, interrogative and exclamatory.
- Nouns: they are in charge of naming people, animals or things and depending on the meaning they have, they can be different types: common, proper, concrete, abstract, countable, uncountable, individual and collectives. For their part, in addition to belonging to one or more categories of those indicated above, nouns also have: gender and number.
- The adjectives: accompany the name and complement it. That is, they serve to provide more information about it and show its characteristics. There are different types of adjectives but when we carry out a morphological analysis we only need to indicate their gender and number.
- Verbs: when we want to express an action, a state, a condition or the existence of a subject. These types of words have a root and an ending that is responsible for shaping the different conjugations and verb tenses. To carry out a morphological analysis we must indicate the following categories of the verb: conjugation, person, number, time and mode.
- The prepositions: Prepositions have the function of joining other words and establishing a relationship between them. Although there are different types of conjunctions in a morphological analysis, it will not be necessary to indicate it.
- Conjunctions: they are used when we want to join different sentences or words. These can be of different types: coordinating and subordinating.
The syntactic analysis of a sentence is the one that allows us analyze what the structure is of the same and what functions each of the words or groups of words as a whole fulfill. In a syntactic analysis we must always be clear that there are two well differentiated parts:
- The subject
- The predicate
The subject
The subject is the one who suffers the action of the verb is always formed by a noun phrase. That is, a set of words in which the name is the core of it. Within the subject we can find:
- Core
- Determinants
- Name complements
- Adjectives
The predicate
The predicate is composed of a verb phrase that expresses the action of the verb and in which this is its nucleus. Thus, within the predicate we can find the following elements:
- Core
- Direct complement
- Indirect compliment
- Circumstantial Mode Supplement
- Circumstantial Place Complement
- Circumstantial Time Supplement
- Circumstantial Company Supplement
- Circumstantial Cause Complement
- Circumstantial Complement of Purpose
- Circumstantial Instrument Supplement
- Circumstantial Quantity Supplement
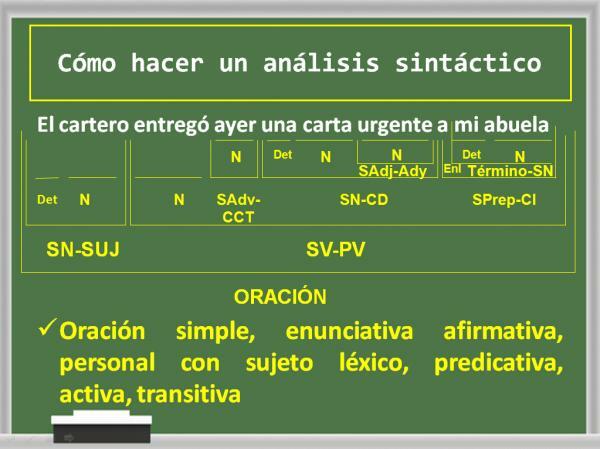
As you can see in the syntactic analysis, its own elements also appear and these must be analyzed according to the structure of the sentence and the functions that words fulfill within the same. Next, and taking the same previous sentence as an example, we will show what its syntactic analysis would be like. In this way you will clearly see the difference between the two types.
In addition, with printable exercises and their solutions that we have left on the web, you can practice what you have learned in the video by analyzing different simple sentences with the two types of analysis (morphological and syntactic)
We hope that through this lesson you have been able to understand what is the difference between the morphological and syntactic analysis of a sentence and how each of them is done. If you want to continue expanding your knowledge of the Spanish language, do not miss the rest of the content that we can offer you.