What is the primary, secondary and tertiary sector

All economic activity is based on and divided into Economic sectors. Each sector refers to a part of the economic activity with common characteristics and in relation to the production processes that occur within them. Next, in this lesson from unPROFESOR.com we are going to carry out a study on the primary, secondary and tertiary sector with examples so you can better understand what each of these markets is.
Index
- What is the primary, secondary and tertiary sector? Definition for children
- What is the primary sector?
- What is the secondary sector?
- What is the tertiary sector - with examples
- Differences between the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors
What is the primary, secondary and tertiary sector? Definition for children.
The economic activities They are what individuals and families as well as companies and public administrations carry out in order to survive. They can be divided into three parts: production, distribution and consumption.
Depending on the division of classical economics, economic activities are classified into three groups, called sectors of the economy. They are the following: primary, secondary and tertiary sector.
- Inside of the primary or agricultural sector we would include activities through which food and raw materials are acquired from nature. For example, agriculture, livestock, fishing, forestry and mining are activities in this sector.
- The secondary or industrial sector encompasses economic activities that transform raw materials into manufactured products. Therefore, they would be all those related to the industry.
- Finally, in the tertiary or service sector activities that provide services to society take place, such as commerce, transport, education, leisure, etc.
Image: Primary Teacher - blogger
What is the primary sector?
As we have noted above, the primary sector includes the economic activities that man carries out to get resources from nature. Within it would be the following activities:
- Farming: production of plant species and different crops.
- Cattle raising: with the production and breeding of animals.
- Fishing: with the use of the various species that can be found in rivers, lakes, oceans and seas.
- Forestry: that focuses on activities aimed at the cultivation and conservation of forests or mountains.
- Mining: activity in relation to the use of soil mineral resources.
In the primary sector, the agrarian space, that arises when man modifies the natural space to be used in agricultural, forestry and livestock activities. This depends on physical factors, related to climate, relief and vegetation cover, and human, such as population, size of properties, technological conditions, etc. The elements that make up the agrarian space are the space that is cultivated Y the inhabited.
Is this a sector that has evolved with technological advances, that have caused a great impact, although they coexist with traditional practices. An example of a developed primary sector is in Spain, where in recent years the number of workers has been reduced. In addition, profitability has increased thanks to aid from the European Union, technological modernization and the use of compound feed and selected breeds in livestock.

Image: Pinterest
What is the secondary sector?
The secondary sector is a sector that includes economic activities related to the industrial transformation of food, goods and merchandise, which are used as a support for the manufacture of new products.
Two forms of industrial activity coexist: one handcrafted, with simple mechanisms of elaboration and limited productions, located mainly in underdeveloped countries, and other industrial proper, which uses mechanical energy and produces diversified items on a large scale.
The secondary sector can also be divided into other subsectors:
- Base: whose products are the raw material of other industries, highlighting the extractive, chemical and steel industries.
- Of consumer goods: that take advantage of the raw materials of the basic industry and manufacture products for consumption. Among these, food, textiles and metallurgy stand out.
- Transportation: that in addition to service is considered an industrial activity.
The evolution of the sector The secondary sector has been on the path of increasing automation, reducing the generation of waste and waste and increasing the productivity of processes.
As an example, note that the secondary sector ranks second in the Spanish economy. Although in Spain it is necessary to import raw materials and non-renewable energies, alternative energies are taking an important role in this sector.

Image: Emaze
What is the tertiary sector - with examples.
The third sectorencompasses activities that do not produce material goods directly and satisfy a need of the population. The variety is enormous since it includes any profession that is not within the agricultural or industrial framework.
Although it is considered a non-productive sector, by not producing tangible goods, it is true that it contributes to employment is created and to the formation of products and income in a society.
Within the tertiary activities we can distinguish the following:
- Commerce wholesale and retail, catering, hospitality and repairs.
- Transport, storage and communication.
- Financial services, real estate, business services and insurance.
- Social, community and personal services, which will highlight domestic and personal services, health and social services, leisure and culture, public administration and defense and private non-profit organizations.
As an example of the importance of the tertiary sector today, we can point out that it is the basis of the current Spanish economy, constituting tourism the main source of income of our country.
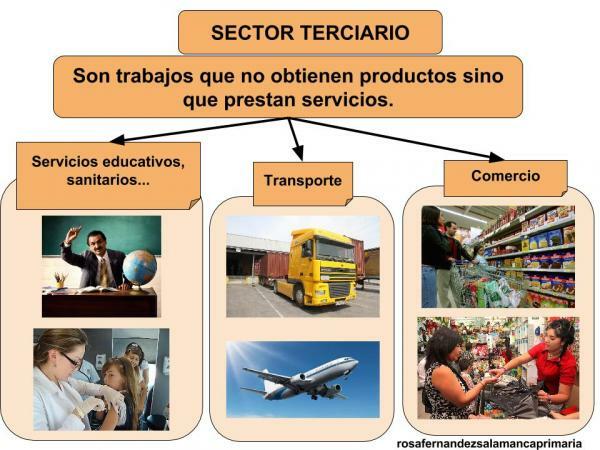
Image: Primary Teacher - blogger
Differences between the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors.
Now that you know the definition of the primary, secondary and tertiary sector, we will fully enter into their differences so that you can better understand the operation of these economic activities. In summary, it is important that you know that:
- Primary sector: it is made up of activities that focus on obtaining raw materials. Here we find activities such as agriculture or livestock
- Secondary sector: are the activities that are dedicated to transforming the raw materials obtained in the first sector and, therefore, making new products. For example, from the grapes obtained in the field, the factory makes wine.
- Third sector: these are the activities that they do is put on sale these products that have been created with the previous sectors. But, in addition to this, this sector also includes other services such as, for example, education, health, and so on.
As we see, all the sectors are correlative, that is, there could not be a secondary sector without primary, nor tertiary without secondary. Let's say that it is like an "assembly line" that allows us to take advantage of the earth's resources for human consumption.
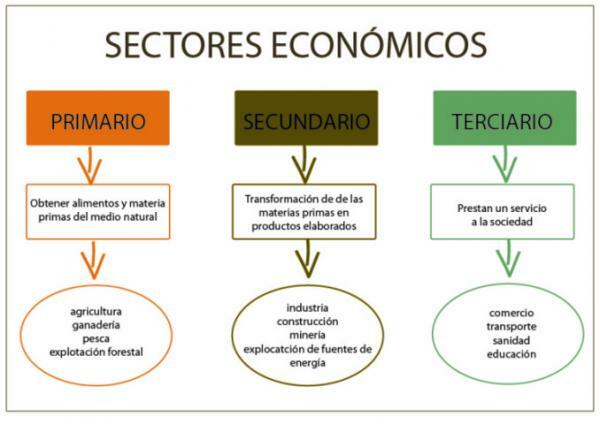
Image: Comparison Chart
If you want to read more articles similar to Primary, secondary and tertiary sector: examples, we recommend that you enter our category of Economy.
Bibliography
- Patiño Villa, M., Patiño Villa, C., & Cataño Rojas, G. (2002). Essays on technology and society. Metropolitan Technological Institute; ITM Editorial Fund.
- Muñoz, E. (1995). Genetic engineering in the primary and secondary sector: benefits and problems. Section Notebooks. Social and Economic Sciences, 2, 151-176.
- Weller, J. (2001). Processes of labor exclusion and inclusion: the expansion of employment in the tertiary sector. Cepal.



