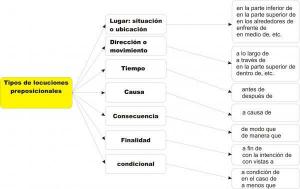
Differences between NOMINAL and VERBAL Phrase

A syntagma is a word or group of words that play a syntactic function within a sentence. These words are articulated around a term called the syntagm core, which determines the type of phrase. For example, if the nucleus of a phrase is a noun, that phrase will be a noun phrase (SN) while if the nucleus is a verb, it will be a verb phrase (SV). There are several other types of phrases, but in this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to study the Difference between a noun phrase and a verb phrase with examples.
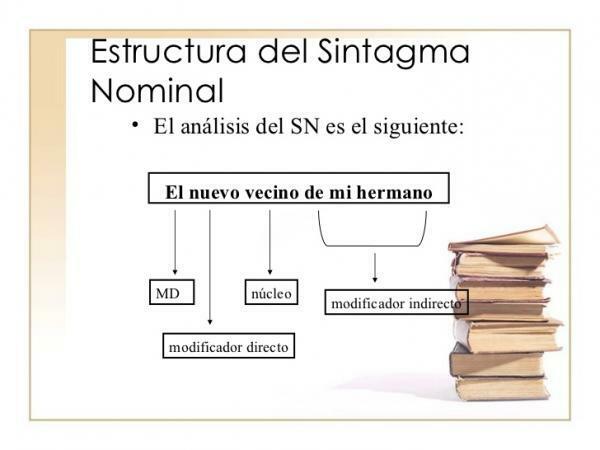
The noun phrase (abbreviated SN in syntactic analysis) is one that is constituted around a noun or pronoun, which act as the core of the phrase. Thus, for a noun phrase to exist, the nucleus must be a noun. This nucleus is the only constituent element of the phrase that must always be present, with a mandatory nature, since without a nucleus the phrase would not exist. In addition to the nucleus, in the phrase we can find various complements that accompany and modify the nucleus. They are called modifiers. Let's see an example:
One winter morning
"A winter morning" is a noun phrase (SN) whose nucleus is the singular feminine noun "tomorrow", which is preceded by an indeterminate article "one", which agrees in gender and number with the core. In addition, next to the nucleus "tomorrow" appears a prepositional phrase "winter" that works as a complement to the noun of the noun "tomorrow". In this example, we can see how the complements that accompany the kernel can be eliminated and the noun phrase will continue to exist, so that we can say One morning.
Examples of Nominal Phrases
Others noun phrase examples or SN are the following:
- Maria won the first prize in the contest.
- This Friday will be Pablo's birthday party.
- My friend came to the restaurant very late.
If you remove all the complements of the verb you will check again that the noun phrase still exists, since the kernel is preserved.
In front of the previous one, the verb phrase (SV) is one whose nucleus is composed of a verb form. In the same way, it can carry complements that modify the meaning of the verbal nucleus, but they are not strictly necessary.
The verb phrase constitutes the predicate of the sentence, since depending on the type of verb, the typology of the predicate varies. For example, if the verb nucleus of the verb phrase is formed by a copulative verb (to be to be to look like) we speak of a nominal predicate (PN) and therefore requires an attribute (Attr.), while if the verb form is any other, the predicate will be a verbal predicate (PV).
Examples of Verbal Syntagma
Let's see the following examples with predicative verbs:
- The table is very big
- The dress is torn
- The pants look dirty
"It seems dirty" is a noun predicate (PN) because the core of the verb phrase (SV) is the verb seem. This predicate is formed by the copulative verb seem plus the "dirty" attribute.
Examples with other verb forms:
- My sister reads a borrowed book
- The girl runs across the yard
- The child eats a snack
"Eat a sandwich" is the verb predicate (PV) of the previous sentence, the core of which is the verb form "eat". Within the predicate, we find complements such as "a sandwich", which in this case is a noun phrase (SN) that works as a direct object (CD).
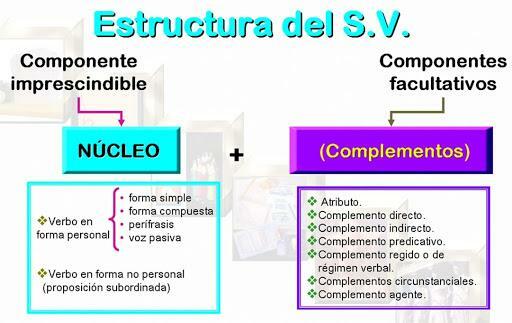
Image: XTEC
So that you finish knowing the differences between noun and verbal phrase, we leave you here some examples of sentences that will help you to clarify the concepts. Here you have 10 examples of sentences with noun and verbal phrase so that the lesson is clearer:
- The girl (Nominal Syntagma) bought a blue dress (Verbal Syntagma).
- The neighbor in the room (SN) has four newborn dogs (SV).
- My maternal aunt (SN) helped my grandmother when she was ill (SV).
- Marta and Carlota (SN) play basketball on weekends (SV).
- Mireia's mother (SN) went on a cruise last week (SV).
- The beach apartment (SN) was sold to a newly married couple (SV).
- The language teacher (SN) forgave Carlos for his insults (SV).
- My parents' friends (SN) are meeting my parents to see each other tomorrow night (SV).
- My cousin Joaquín (SN) won the chess contest last year (SV).
- My sister (SN) sold her jewelry because she needed money (SV).