The varieties of language

Image: Tongue notes
It is not the same language that you use when you are at work that you use when you are with your friends, is it? Nor is it the same type of language that is spoken in Andalusia as that spoken in Galicia, is it? These are just two of the many variations that the language has, an aspect that is studied within the sociolinguistics since it is related to the social use that we give to the language. In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to show you the language varieties with examples So that, thus, you know in detail what we mean when we talk about each of them.
Index
- What are the varieties of the language
- Diastratic or social variety
- Diatopic, geographic or dialect variety
- Diaphase or situation variety
- Diachronic or historical variety
What are the varieties of the language.
To understand the definition of varieties of language, it is important that we bear in mind that a language is not uniform, this means that it has certain varieties that have to do with multiple aspects such as, for example, the environment
social, record, history and geography.Within sociolinguistics, the main characteristics of the language have been studied when it is used in one context or another and, therefore, today we can talk about 4 great varieties of the language which are the ones studied in schools and universities.
We must emphasize that language is a social act and, therefore, the changes or varieties it presents with respect to standard language (the ideal language model) always they relate directly to the speaker. In other words: we are the ones who provoke the varieties of the language since, depending on our context or situation, we use it in one way or another. It is for this reason that this scientific branch is known as sociolinguistics because it combines the social fact with the linguistic one.

Image: Brainly
Diastratic or social variety.
We begin by getting to know one of the most significant varieties of the language: the diastratic or social variety. This variety appears depending on your social class since, the more you can change the linguistic register, the more you master the language and, therefore, the more you can know all its varieties. People with a low social level usually speak the same register regardless of the communicative situation.
This variety therefore takes into account the speaker's education level and is made up of 4 levels of use:
Cult level
It is the speaker who uses the language in all its planes and possibilities. You can detect this level because the speaker will use careful and elaborate forms of expression, as well as a great variety of lexicon and strong syntactic correction.
Medium level
Speakers with this linguistic level follow the linguistic norms but are less rigorous than those who dominate the educated level. This medium level is the one that is usually used in the media and is the language used by people with a medium sociocultural level.
Informal or colloquial level
All speakers use this level, regardless of their cultural level, when they speak with their close friends or trusted persons. It is the type of language that is used in familiar environments and meets some characteristics such as:
- Subjectivity when speaking
- Linguistic economics (wildcard words are used, "taglines" abound, etc.)
- Verbs with more than one meaning are used (to do, to have, etc.)
- Use of questions and exclamations to grab the listener's attention
- Use of set phrases
- Etc
Vulgar level
Speakers with little or no training low sociocultural level They usually use this linguistic level that is characterized by a lack of knowledge of the norm. The most outstanding feature is that some basic rules of the language are not respected or that there is confusion when using them when speaking. This causes vulgarisms to appear, that is, incorrect words or uses of the language that come from a lack of knowledge related to the sociocultural level of the speaker.
In this other lesson we will discover what are the language registers for you to know.
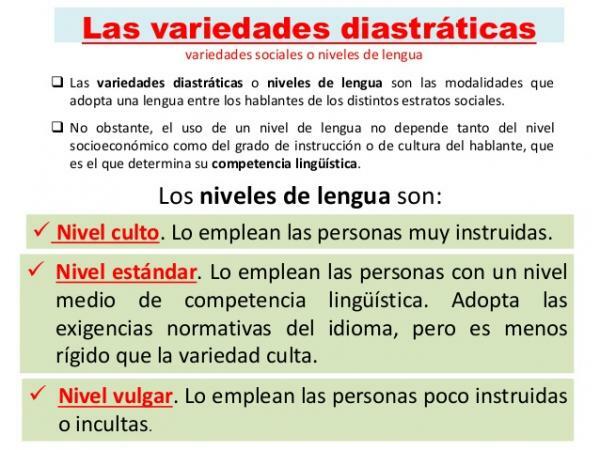
Image: Slideshare
Diatopic, geographical or dialect variety.
We continue with this lesson on the varieties of the language to speak now of the diatopic, geographical or dialectal variant. And it is that depending on where you live, where you were born or where you were raised, the language you use may have certain characteristics or others. In Spanish there are different dialects, that is, forms of the language that present certain differences with the norm but that still correspond, some of the dialects are: the Andalusian, the Extremaduran, the Canarian, the Madrilenian, etc.
A dialect is a system of signs thate is part of a common language and that it presents some varieties that are repeated throughout a territory or zone. Although it has some notable changes, the truth is that it does not have a very great differentiation in relation to the common language.
Therefore, when we speak of the diatopic variety, we are referring to the variation of the language that is used in specific regions that have created some linguistic uses that are new or typical of the region. Here we discover the differences between language and dialect so you can see what case we are facing.
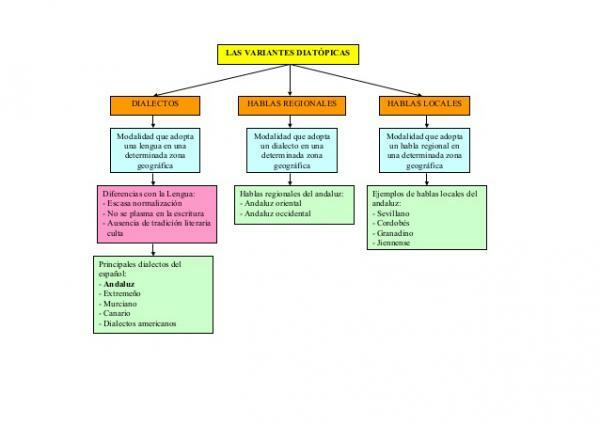
Image: Slideshare
Diaphase or situation variety.
We continue talking about the varieties of the language to now stop at the diaphasic variety or variety of situation. This occurs when a different expression modality is chosen depending on the communicative situation in which we find ourselves: the intention that the sender may have, the attitude of the receiver, etc.
For example, the diaphase variety can be perfectly understood in these two situations:
- A young girl talking about sex with her friends
- A mother talking about sex with her mother
Although the communicative planes are similar and the environment as well (familiar, close), the same language because aspects such as the sender / receiver, the intention of the message, etc. In this variety the speaker chooses how to use the language depending on the environment where you are.
Slang
Within this linguistic variation we find slang, that is, the professional languages that occur within the workplace. This occurs because a specific social group develops different linguistic habits and ends up creating a specific and specific lexicon for each field.

Image: Slideplayer
Diachronic or historical variety.
And we conclude this lesson on the varieties of the language to talk about the fourth and last level: the diachronic or historical variety. This variety takes into account the evolution that a language has undergone throughout history in order to understand some elements of the current language. With this study it is possible to verify all the linguistic variation that a language has experienced during its history.
For example, if we investigate the history of Spanish we will discover that it is a Romance language that comes from Latin. It is part of the great group of Romance languages of Europe who experienced the influence of the Roman Empire both in their culture and in their language. Since the 18th century, the Castilian romance began to be cultivated as the official language of the territory thanks to the work of Alfonso X that managed to regulate the language and standardize it.

Image: Slideplayer
If you want to read more articles similar to The varieties of the language - With examples, we recommend that you enter our category of Grammar and Linguistics.