The VERBS in the present of INDICATIVE in IMPERSONAL form
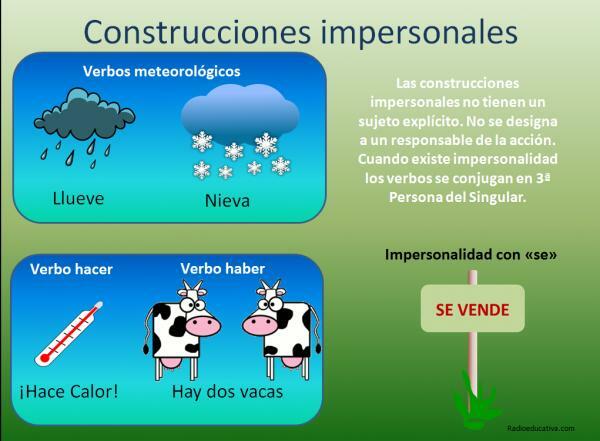
Image: Educational Radio
In this lesson from a TEACHER we want to answer a question: What are the verbs in the present indicative in the impersonal form? In the first place, and in order to answer it, it will be necessary to know which are the impersonal sentences and which verbs are the ones that form them. In this way we can indicate how they are done in the Present Indicative and establish a series of examples that help you easily understand and identify them when writing or parsing.
In Spanish we find many sentences, some of them are impersonal, for this reason and to be able to solve the question that we asked ourselves at the beginning about what are the verbs in the present indicative in an impersonal way. essential define what impersonal sentences are.
Impersonal sentences are those that do not have a syntactic subject, that is, the subject is not present in the sentence or appears explicitly and cannot be assumed to be implicit or omitted. On the other hand, it is important to know how to distinguish them from those sentences that are impersonal in terms of their meaning, that is, those in which the verb agrees with a subject, which does exist, but is unknown. Let's see an example of each of them in order to understand what the difference is between the two:
- Impersonal prayer: You sleep very well in this hotel. The subject cannot be any of those that appear in the sentence since In this hotel it is a circumstantial complement of place and very well a circumstantial complement of mode.
- Impersonal sentence with semantic character: The results will be known on Monday. The verb is found in a personal form and agrees with a subject that in this case we do not know who it is, but we can easily substitute it for them, leaving the phrase as follows "On Monday, they will know the results ”.
Within the impersonal sentences we can find several classifications, these will depend on the type of verb that is used for their training, they are divided into:
Formed by meteorological verbs
Are those impersonal sentences use impersonal verbsto talk of natural or meteorological phenomena. These always have an impersonal character and the subject does not exist in them. Some examples of these impersonal weather verbs are:
- Hail
- Sunset
- Rain
- Dawn
- to snow
- To become night
- To escape
Although these types of sentences can be presented in any verb tense, we are going to focus on the one at hand: Impersonal verbs in the Present Indicative. Thus, and taking into account their formation characteristics, we can show the following examples:
- It rains a lot.
- It dawns at 8 in the morning.
- It snows in the mountains.
Formed by the verb have
Even if the verb to have in an impersonal sentence it can be conjugated in any of its forms, the one that interests us is that of Present Indicative (LINK ARTICLE PRESENT OF INDICATIVE). Therefore, we can conclude that these sentences are the ones that include the verb have as impersonal and we are going to illustrate it with the following examples:
- There are wolves in the forest.
- There is a lot of fog.
- There is a child in the park.
Formed by the verb do
The verb make It can also appear in different verb tenses, but, in any case, in impersonal sentences It is used to make temporary or weather-related references. These examples will help you understand it better:
- It's too hot here.
- It is unbearably cold.
- We haven't seen each other in a century.
Sentences formed with the verbs ser and estar
As with the verb to have Y make, verbs to be Y to be They are also one of the most common in impersonal phrases in the Present Indicative, although they can appear in all verb tenses:
- It is night.
- It is early to go.
- It's snowing.
Sentences that contain se
The verbal morpheme I knowindicates impersonality in this type of sentences and therefore does not reflect any syntactic functionality in it. The verb, after this appears always in the third person and is undefined. So that you can understand it better, here are some examples:
- You live very well here.
- This is an important matter.
- What time is dinner in this house?
He always serves to replace the subject in this type of sentence and establishes the syntactic impersonality of the sentence thereby creating a generic statement.
On the other hand, copulative verbs when they appear attached to the verbal morpheme I knowYou can also create impersonal sentences as they refer to unspecified human properties. For example:
- You can't be that stupid.
Image: Slideplayer
Therefore, after having defined the different types of impersonal sentences, we are ready to answer the question that we asked ourselves at the beginning. Therefore, the verbs in present indicative impersonally are those who express actions that are occurring in the moment in which the speaker transmits the message and that they conform to meteorological verbs, with the verb have, with the verb to be, with the verb to be, with the verb to have and that include the verb phrase I know.
- Here you cannot be at peace.
- Good to Know.
- There is a lot of humidity.
- It is expected to give good results.
These are just some examples of verbs in the Present Indicative in an impersonal way, if you want to continue learning about Grammar and Linguistics and discover articles like this, be sure to visit our section dedicated exclusively to her.



![What is an INDICATIVE verb in Spanish- [Easy SUMMARY with +50 examples]](/f/44ea247c28a1e8f3df46b712923d3cce.jpg?width=300&height=200)