What are the IMPERSONAL forms of the verb

Verbs have personal and impersonal forms. Personal forms are those that represent the action of a subject and that agree with it in gender and number. In addition to the personal ones, in Spanish grammar we can find others that do not agree with the subject and they do not refer to it. In this lesson from a TEACHER we want to focus on what are the impersonal forms of the verb and their examples.
The impersonal forms of the verb They are those that do not have a match in gender and number with the subject, in the same way that they do not have modality or time. These ways are three: infinitive, gerund and participle. These three forms do not combine and have their own formation and uses that we will define below.
What is the infinitive
It does not have morphemes that express the number or the time of the verb. Due to its characteristics, it can fulfill two functions within a sentence: as a noun phrase and as a verb phrase. On the other hand, they have three endings:
- Ar: speak
- Er: grow up
- To go: say
What is the gerund
The gerund is one of the impersonal forms of the verb and serves to express an action that is occurring at the same time as the nucleus of the verb phrase. In other words, the gerund is simultaneous to action which is expressing the main verb of the sentence.
The gerund is formed by adding the ending –Ando to the root of the verb when it ends in infinitive form in –Ar. In the case that this belongs to the second and third conjugations (-er, -ir), they will be formed by adding to the root the ending –In.
For example, the verb to speak has a stem (habl-) and an ending (-ar). In this case to form the gerund you must add to spoke- the termination -I walk. In this way the gerund of speaking would be talking.
In the event that the verb ends in -er or -to go as, for example, the verbs grow and feel. Therefore, to form the gerund of these verbs we must add the ending -going remaining as follows: growing up, feeling.
What is the participle
The third of the impersonal forms of the verb is the participle. In this case, unlike what happens with the participle and gerund, the participle can agree in gender and number with the subject, if necessary. It is formed by adding the ending to the stem of the verb -ado / ada / ados / adas.
The participle is used to form compound times together with the verb have. In these cases, the verb assistant, is always found in a personal way and will be the one that agrees in gender and number with the subject. So for example we would find:
- I have bought.
- Ha spoken
- Have you sung.
On the other hand, it can also function as adjective that is, agreeing in gender and number with the noun that makes up the subject of the sentence when it is preceded by the verb estar. To understand it better, let's see some examples:
- The children were tired from playing so much.
- His sister is moved With the news.
- Andres is frustrated for the result of your test.
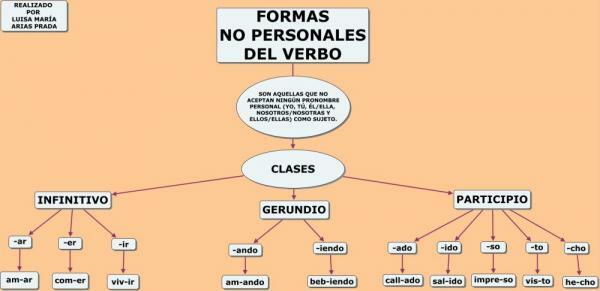
Image: Pinterest
So that you can reinforce your knowledge, we are going to see some examples of impersonal forms used in sentences.
- Alberto and I have been friends since we were little. (Participle)
- They have not yet called of the administration. (Participle)
- The baby has slept all night at a stretch. (Participle)
- The director is filming his last film on the Galician coast. (Gerund)
- They have condition many times in Madrid. (Participle)
- Sometimes you can't explain all with words. (Infinitive)
- Tonight i dreamed of who came to see me. (Participle)
- Was suffering too much with that relationship. (Gerund)
- I'm reading a very interesting book. (Gerund)
- I have noticed that you are attracting very much the idea. (Gerund)
- Play tennis is my greatest passion. (Infinitive)
- The neighbor is singing again. (Gerund)
- No one can stand him for his way to be. (Infinitive)
- Don't speak so loud, the girl is sleeping. (Gerund)
- She does not want speak about the topic. (Infinitive)
- She has been laughing for hours of the joke that his sister told him. (Gerund)
- Your goal is Approve next week's exam. (Infinitive)
- His father goes walking to work. (Gerund)
- I have you assigned some homework for Thursday. (Participle)
- I have you lying less. (Participle)
- Your grandmother has I come to see me this afternoon. (Participle)
- Your mother has already bought the wrapping paper. (Participle)
We hope that the impersonal forms of the verb have been made clear to you with examples. If you want to continue learning more about Spanish language do not hesitate to visit our sections where you will find more topics related to it. You will find summaries, examples and everything you need to continue improving day by day.




