What is the BOLTZMANN constant

Although they are often confused, temperature and energy are not the same concept. Temperature, or rather heat, is a form of energy. Since energy and temperature are not the same, in order to measure the temperature of a system in units of energy, a physical constant: Boltzmann's constant. But,what is Boltzmann's constant? In this lesson from a TEACHER we will look at the definition of Boltzmann's constant, how it relates to Planck's work, and what it is currently used for in physics.
Index
- Boltzmann constant theory
- Boltzmann's constant and the ideal gas equation
- Boltzmann's constant and entropy
- Boltzmann's constant and the redefinition of the kelvin (K).
Boltzmann's constant theory.
Boltzmann's constant is value relating the mean kinetic energy of a thermodynamic system or an object cwith absolute temperature of the same. In other words: this constant is a Conversion factor to convert the temperature (degrees), to units of energy (joules, for example).
Although Boltzmann first linked entropy and probability in 1877, apparently the relationship was never expressed through a specific, numerical constant. It was Max planck who entered the value k for the first time, and who offered an exact value that, although it is not the one currently used, is quite close to it.
Boltzmann's constant corresponds to: 1,380 6488 (13) × 10−23 J / K. That is, for each kelvin degree that a system has, it is equivalent to approximately 1,380 6488 × 10−23 joules of energy.
Although few know the name of Boltzmann, today the constant that bears his name is indispensable in the application of the laws of thermodynamics, statistical mechanics and information theory. Below are some of the applications in which the Boltzmann constant is involved.

Image: Slideplayer
Boltzmann's constant and the ideal gas equation.
The ideal gas equation, which allows us know the global trend to a certain behavior of a gaseous system.
The ideal gas equation is: PV = nRT
In the ideal gas equation, shown above, we have a empirical constant (determined by experimental methods), which is called "gas constant "or R. This constant actually comes from multiplying Boltzmann's constant by Avogadro's number (which describes the number of particles in each mole of solute).
The Boltzmann constant and the gas constant are essentially the same, only the latter refers to one mole and the other does not. This transformation is only done to take into account the energy created by each of the particles within the gas, since the energy created by one mole of particles will not be the same as by ten moles of they.

Image: Slideshare
Boltzmann's constant and entropy.
The entropy is very often defined as the degree of molecular disorder of a system, but this definition is not so clear in physical practice.
Entropy can be defined from the point of view of statistical mechanics or from the point of view of thermodynamics, but both are in effect a measure of internal disorder of a system. In statistical mechanics, entropy tells us the number of microscopic states compatible with a state given macroscopic while in thermodynamics the energy of that disorder is measured in units of energy / units of temperature.
To link both concepts, and that the entropy is coherent according to thermodynamics and according to quantum mechanics, the Boltzmann constant is introduced into the equation for mechanical entropy. This allows us to introduce this conversion factor between energy and temperature and "equalize in units" to the definition of thermodynamic entropy.

Image: Slideplayer
Boltzmann's constant and the redefinition of the kelvin (K).
In recent years a new technique has been found to measure the Boltzmann constant, which allowed its value to be more accurately defined.
The new technique is based on application of laser absorption spectroscopy. The system is simple to understand: A carbon dioxide laser beam is passed through a chamber filled with gaseous ammonia. This container is kept at temperature by means of a bath during the whole experiment.
The absorption frequency of the gas molecules undergoes a doppler movement, as the thermal energy of the gas molecules increases, which is manifested in the half-width of the absorption line. It is precisely the half-width of the absorption line that is related to Boltzmann's constant.
This methodology is believed to is more accurate than the acoustic method, that was used until then to define Boltzmann's constant, which would be of great importance to take it as a method to define the kelvin degree.
What is kelvin (k)
In our days the kelvin is defined as thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water multiplied by 1 / 273.16. Putting this definition into practice has several methodical difficulties, for example: ensuring the isotopic composition of water.
That is why several authors have suggested changes in the definition of the kelvin. They believe that the Boltzmann constant should be fixed, and then re-define the kelvin as the variation of the thermodynamic temperature that results from the change of a certain amount of energy thermal. In this way, it will also be possible to relate the temperature unit with a fundamental constant, something very common in the definitions of all quantities today.
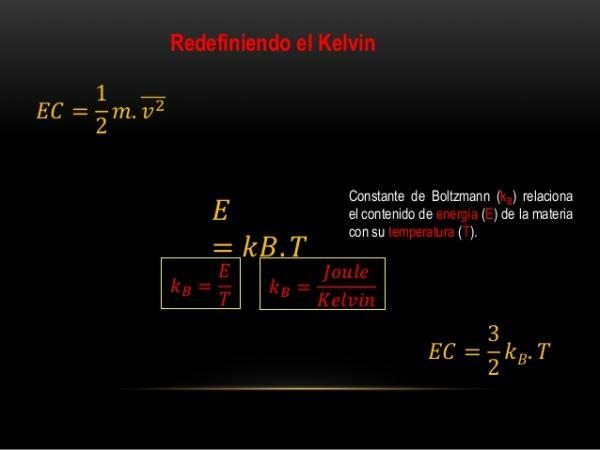
Image: Slideshare
If you want to read more articles similar to What is Boltzmann's constant, we recommend that you enter our category of Heat and temperature.
Bibliography
- Bauer, W. 2011. Physics for Engineering and Sciences. Volume 1. Mc Graw Hill.
- Giancoli, D. 2006. Physics: Principles with Applications. 6th.. Ed Prentice Hall.
- Zapata, F (s.f) Boltzmann's constant: history, equations, calculus, exercises. Recovered from: https://www.lifeder.com/constante-boltzmann/
- National Metrology Network (September 7, 2007) New technique to measure the Boltzmann constant. Recovered from: http://www.metrologia.cl/link.cgi/Noticias/81
- Quantum Tales (October 8, 2011) Boltzmann's constant and Temperature. Recovered from: https://cuentos-cuanticos.com/2011/10/08/constante-de-boltzmann-temperatura/

