Types of conjunctions + EXAMPLES

When writing a text or expressing ourselves orally in Spanish it is necessary that we use conjunctions, since these are used to establish relationships between different sentences or words. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see what types of conjunctions They exist in Spanish as well as some examples of each one of them to be able to understand them better.
The conjunctionsare used to establish a relationship between different words within a different phrase or sentences. Within the conjunctions we find two large groups that in turn will be made up of different types of conjunctions. These large groups are:
- Coordinating Conjunctions
- Subordinate Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are those that link or join words or sentences that have the same value. That is, the importance of both premises is the same. Thus, within these we can find different types of conjunctions according to the interpretation that is made of the coordinated elements that compose it.
Copulative conjunctions
Copulative conjunctions are those that are used to indicate
aggregation or addition. Thus, we can find the following conjunctions:- Y
- Neither
- Neither… nor…
- As much as…
- So much... how much ...
- As well as…
- Like…
- The same as…
- Not only…
- But also…
Some examples:
- Maria has three children Y A grandson.
- Not only he was tired of the situation but he couldn't take it anymore.
- Neither I wanted to be there neither he liked the city.
Adverse conjunctions
The adversative conjunctions are those that are used when we want to oppose two ideas or establish a nuance or correction on some element of the sentence. The adversative conjunctions are:
- But
- More
- But)
Some examples:
- I would love to go to the beach with you on Saturday but I have too much accumulated work.
- The man was tired more I didn't know if I should call him on the phone.
- We did not give him what he liked, otherwise what he needed.
Disjunctive and distributive conjunctions
Disjunctive conjunctions are those that serve to set a choice or alternation between different options that arise in the same sentence. O is always used, unless it is prepended to a word that begins with the same letter. In that case it will be changed to U.
- You have to decide between the blue car or the green one, we don't have all day.
Distributive conjunctions
Distributive conjunctions are used for the same purpose to also establish a choice between different elements and it always goes in pairs. Thus, the distributive conjunctions are the following:
- Or... or ...
- Well well…
- Now... now ...
- Ora Ora…
- Be..., be ...
- Out... out ...
Let's see some examples
- OR you ride in the bumper cars or on the Ferris wheel. You can't ride both.
- Well you accompany your sister to the library, well you stay home doing your homework.
- Pray she was running, now he sat down to rest.
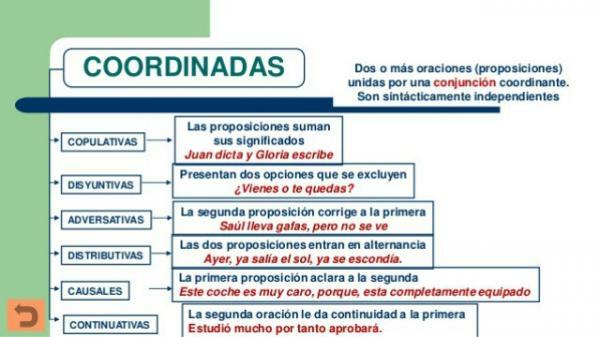
Image: QueHowTo
Next we are going to see what are the subordinating conjunctions, these are used to introduce subordinate clauses they will always depend on the principal. Depending on the type of conjunction used, this subordinate clause should be placed before or after the main clause. In the same way as in the coordinates, the subordinates have different types that attend to their meaning.
Causal conjunctions
The causal conjunctions are those that introduce a subordinate clause in which the reason or cause is displayed which is given in the main sentence. These conjunctions are:
- Because
- What
Some examples of this type of conjunctions are:
- She said that she would not go to Madrid because she didn't have enough time for it.
- What he was tired he decided it was best to stay home and save dinner for another day.
Conditional conjunctions
Conditional conjunctions are used when the introduced subordinate expresses a condition that is fulfilled in what has been stated in the main sentence. These are:
- Yes
- As + subjunctive
Some examples:
- Yes you want to come with us you have to be ready at seven.
- He said that he would whatever to be able to fulfill the delivery.
Comparative conjunctions
Comparative conjunctions are those that introduce a subordinate clause in which a comparison with the main sentence. These conjunctions are:
- What
- Like
Some examples of this type:
- Is higher what his brother.
- Michelangelo left What if he was offended.
Temporary conjunctions
Temporary conjunctions are those that serve to locate the action of the main sentence in a given time. Conjunctions of this type are:
- While
- After
An example:
- We will all be together While the storm passes.
Completive conjunctions
Completive conjunctions are those subordinate that are used as a subject, prepositional object or direct object. These are:
- What
- Yes
Let's see some examples:
- I think what he cannot eat cheese because he is lactose intolerant.
- Yes you want to come, you are invited.
Final conjunctions
The final conjunctions will be those in which the purpose of what has been expressed in the main sentence. The final conjunctions are:
- So that
- In order to
Some examples of them:
- I've already done what you asked me what for let me out earlier.
- He was working very hard all year, at the end that his boss would grant him the promotion.
Concessive conjunctions
Concessive conjunctions are used when you want express an objection to what is established in the main sentence. These conjunctions are:
- Even if
- Yes OK
- Examples of these conjunctions:
- I'll buy you the bag of potatoes even if you don't deserve it.
- Yes OK she was willing, she didn't show it.
Consecutive conjunctions
Concessive conjunctions are those that are used when we want to introduce a subordinate clause that expresses the consequence or effect of the topic sentence. These conjunctions are represented by:
- What
We show you an example:
- I was so happy to see her again what forgot everything else.
Ilative conjunctions
Ilative conjunctions are those that introduce a subordinate clause in which the logical consequence of the main sentence. The ilative conjunctions are:
- Later
- With what
- So
Some examples:
- On Saturday I was traveling in Alicante, soon she couldn't be the cause of the problem.
- You are too small to go alone so you will stay at home.
These are the types of conjunctions that we can find in Spanish. If you want to continue learning with our lessons, be sure to visit our section on Spanish language.
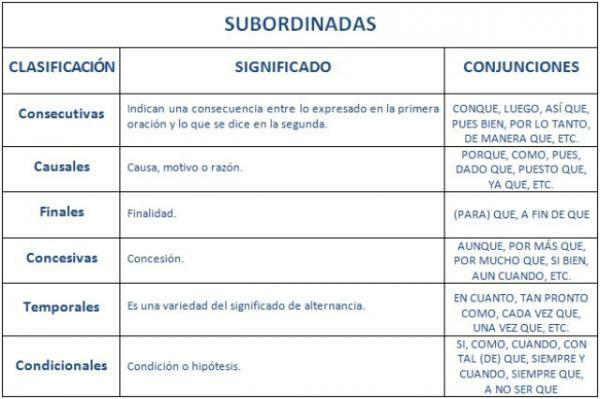
Image: QueHowTo



