Political liberalism: EASY definition

Image: Slideshare
Throughout history, there have been many philosophical and political doctrines that have marked a before and after in humanity, being those that have managed to remain for decades, although sometimes they have been modified over the years. To talk about one of these doctrines, in this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to offer you the definition of political liberalism.
The liberalismis a philosophical and political doctrine whose main idea is the defense of individual freedom, thus seeking to limit the influence of the State in the different levels of life, such as the economy or social life.
Political liberalism can be of different kinds, because it has evolved over the years, but All these types have a series of common characteristics, being the ones that differentiate liberalism from others. doctrines.
Some of thes characteristics of political liberalism are as follows:
- Search for a Rule of law, where all people are equal before the law.
- Everyone must have a series of individual rights, over which no one can intervene.
- Right to private property, which must be defended by law.
- Division of powers, guaranteed by the constitution and civil codes.
- Separation of Church and State, existing in most cases a total freedom of worship.
- An economy based on market freedom, with hardly any State intervention in the economy.

Image: SlidePlayer
To continue with this lesson the definition of political liberalism we must talk about the main defenders of liberalism and how they helped originate this current.
The origin of liberalism can be found in the first ideas of a series of thinkers of the time modern, who wrote the first texts on this doctrine, and without whose influence its creation would not have been possible. Some of these authors are the following:
Montesquieu
It is considered as one of the precursors of liberalism, being the thinker who created the theory about the division of powers that should exist in the states. Montesquieu did not believe in the concentration of all powers in the figure of the king, and defended that the three powers should be divided for a better government.
John Locke
Lockeis considered the father of classical liberalism, being a strong defender of the theory about the social contract, and one of the greatest influences for the first constitutions in history, especially the American one. Locke believed that power should not be absolute, and that it should satisfy the individual rights of citizens.
Rousseau
Rousseau He is an enlightened thinker of the lower bourgeoisie, he supported the individual rights of citizens, and that power should reside in the people and not in the king. He was a staunch defender of Locke's social contract and the pursuit of equality in society.
Thomas Hobbes
In Hobbes's thought, several essential concepts of liberalism can be observed, such as the equality between people or the political power of the people. Hobbes was able to lay the foundations of liberalism for later thinkers, being one of the fathers of liberalism.

Image: SlidePlayer
As one of the most important doctrines in history, and having an existence of several centuries, liberalism has a wide variety of types, since it has influenced a large number of doctrines.
Some main currents that have been born of liberalism are the following:
- Neoliberalism: It was the resurgence of the ideas of the most classical liberalism, seeking greater freedom in the economic market. An example is American and British politics in the 1980s and 1990s.
- Socioliberalism: This current defends that individual freedom must be linked to social welfare. An example of this current is the philosopher John stuart mill.
- Libertarianism: This current defends a classical liberalism, with great individual freedoms and almost without State intervention.
- Minarchism: This current believes that to maintain freedom a minimal state is necessary, which never intervenes in the economy.
- Anarchism: This current defends the disappearance of the State, which it considers unnecessary to maintain freedoms. It can be divided into several streams, such as anarcho-capitalism and anarchosocialism.
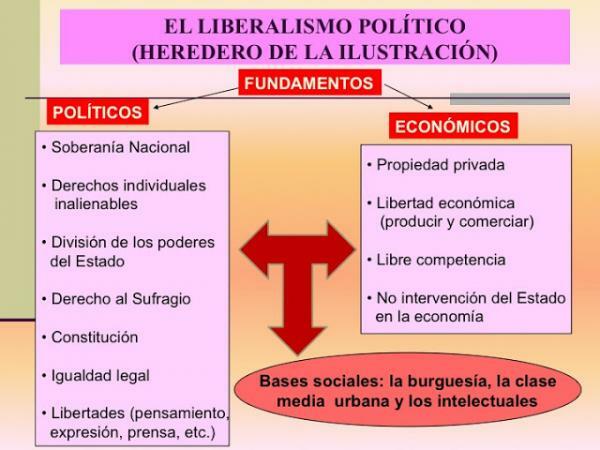
Image: contemporary world history blog



