Social CLASSES in ancient ROME

Without a doubt, the most important and most important ancient culture in Antiquity was Rome, being its key influence for the existence of today's Europe. Roman society varied a lot depending on the different stages of its history and, therefore, to know its evolution in this lesson from a Professor we must talk about the social classes in Ancient Rome, analyzing its different stages.
Index
- Social classes in the Roman Monarchy
- Social classes in the Roman Republic
- Social classes in the Roman Empire
Social classes in the Roman Monarchy.
To talk about the different social classes in Ancient Rome it is important that we focus on the least known period in Roman history: that of the monarchy. And it is that here we find the origin of what, later, would be the powerful Roman empire and, therefore, being considered the founders of the region.
Already in its origin, Rome had a strong inequality between their social classes, this first stage being marked by birth and religion, dividing into two large groups known as
the free and the unfree.Free citizens of Rome
The citizens known as free were those who had greater power within society Roman in the times of the monarchy, being divided into the patricians and the underprivileged.
- The patricians were the first families of Rome and the descendants of her, being those considered as roman citizens and occupying all public positions, being the great privileged of the Roman society of this period.
- The not privileged they were the commoners who were foreign free men who had arrived in a Rome already founded, and the clients who were foreigners united to a patrician who, being under his protection, helped them in war or in numerous tasks.
Citizens not free
Then in the unfree we find the slaves or servi, being generally war servants sin any kind of right and they took care of the tasks that nobody wanted to do. They were totally dependent and they had no freedom and, to a large extent, they were the center of the economic system for performing almost all tasks.
Social classes in the Roman Republic.
The passage from Monarchy to Republic brought many changes to Rome as a civilization, one of these transformations being the ones that affected social classes of ancient culture. These changes were especially relevant because social classes were based more on aspects such as the economy or the territorial situation than on old values such as religion or birth.
The great changes in Roman society were caused, among other factors, by the society protests in his fight against huge inequality, causing large strikes that eventually caused the law to be changed and that, over the years, social classes will change.
To know the social classes in Ancient Rome within the stage of the Republic, you have to know that they were divided as follows.
Roman citizens
Could participate in political life, have civil rights such as commerce or carry out legal actions and also some military or tax obligations. Roman citizenship was earned by birth or because it was granted by the state or legally, and it was lost due to different illegalities.
In the citizen classes we find:
- The patricians that they kept many of their privileges.
- But there were also commoners as a social class with citizenship privileges
- And also the gentlemen, being a social class formed by the rich who were going to fight on horseback when they had money to buy the equipment. Over the years, they became a class focused on land exploitation and banking, forgetting their origins as gentlemen but keeping the name.
Non-citizens
In the part of non-citizens we find:
- The customers that for a considerable time they were turned into commoners, but that after some economic crises they returned to being a very common social class with little real relevance. Let us remember that the trade in Ancient Rome It was very important.
- The freedmen what were they freed slaves that they did not possess Roman citizenship, but that they were no longer required to do any work.
- The slaves that although they had numerous rebellions, they maintained the same rights, which were still almost non-existent.
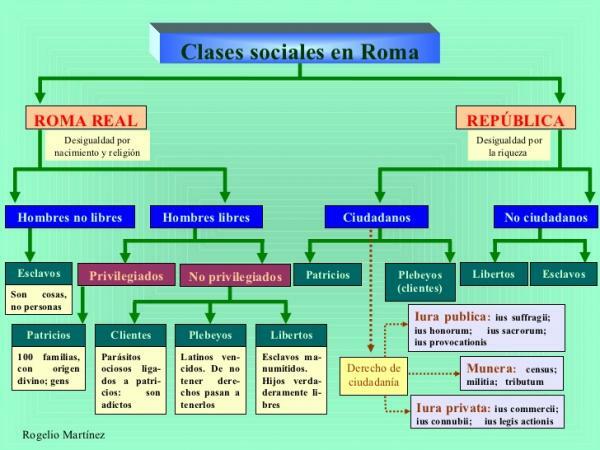
Image: Slideshare
Social classes in the Roman Empire.
To conclude this lesson on social classes in Ancient Rome we must talk about the main social classes during the last stage of Rome, being known as the Roman Empire.
- Emperors. In the highest part of Roman society the patricians were replaced by the emperors and his family, occupying the most important step in all of society for the creation of this figure as the ruler of Rome.
- Patricians and Senators. Just below them we find the most relevant figures in the republican stage, being the patricians and senators great citizens with many privileges but being under the power of the emperor.
- Equites. Behind them were the equites, formerly known as knights that, with the passage of the Empire, they occupied a greater relevance in the Roman system with greater influence and power thanks to their high economic level.
- Customers. Finally in the part of the citizens we find the customers, remaining as the plebs and generally being under the care of a great lord but achieving citizenship in many cases, although remaining in poverty.
- Colonists. People who were not slaves, but also not free, being tied to a land that had to work without possibility of escaping from it, being therefore the forerunners of the peasants of the Age Half.
- Freedmen. Freed slaves, but who had not achieved Roman citizenship.
- Slaves. On the other hand, slaves continue to have few rights, but the number is greatly diminished, since the new system makes them less necessary.

If you want to read more articles similar to Social classes in Ancient Rome, we recommend that you enter our category of Story.
Bibliography
- Mac Gaw, C. G. (2008). Debt and social classes in the early Roman republic. Circe of Classics and Modernism, (12), 243-264.
- Uriel, P. F., & Romero, I. M. (2013). Roman civilization. Editorial UNED.
- Alföldy, G., & Troncoso, V. TO. (1987). Social history of Rome (p. 214272). Madrid: Alliance.