Main CONSEQUENCES of the FRENCH REVOLUTION

Image: Napoleon Bonaparte
The French Revolution marked a before and after in the future of Europe since it ended what would be called the Old Regime, that is, a form of government in which it was the absolute monarchs who decided how the things. In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will dwell on the causes of the French Revolution, very important to understand what would happen during the entire revolutionary period and later in the consequences of the French Revolution, in which we will see what progress was made.
Index
- The main causes of the French Revolution
- Political consequences of the French Revolution
- Social consequences of the French Revolution
- Economic consequences of the French Revolution
- Conclusion on the consequences of the French Revolution
The main causes of the French Revolution.
The antecedents to the revolution are quite clear: let's place ourselves in the France of Louis XVI (the last absolute French monarch). The king's court and the royal family themselves lived in a spiral of waste of money and incredible food, while the people of France went through moments of great misery. The monarchy, in order to keep up with the pace of life that had taken place up to that moment, had to introduce new taxes, which made the unrest among the population ever greater. We can
divide the causes into 4 four sections important:Political causes of the French Revolution
The people or plain state (commonly known) was not satisfied with the class society that existed for centuries and that made the nobles and the Church divide the wealth of the country while the people suffered in the purest misery.
Economic causes
A series of droughts and frosts before the year 1789 had ruined the crops, causing the farmers did not have sufficient income to be able to pay the taxes that were demanded by the government. Thus, death due to lack of food became more and more frequent in France in 1780.
Philosophical causes
We will find a series of philosophical movements that were introducing ideas, in addition to creating theoretical bases of the formation of a new form of government, in which the leading role would be had by the bourgeoisie instead of the ruling classes (nobility and church).
Social causes of the French Revolution
At this point, what we must take into account will be the cluster of elements defined above which would take the common people to a point of no return, in which the last step would be the revolution.
In this video of a PROFESSOR we discover the causes of the French Revolution deeper and we will dwell on all the details.

Image: Summarizes
Political consequences of the French Revolution.
In order to better understand what the consequences of the French Revolution were, it is important that we analyze them at different levels. We will start by talking about the political consequences since this revolution completely changed the landscape in France and, also, in much of Europe.
In general terms, you should know that most relevant political consequences these are:
- End of absolute monarchy in France
- Return of the democratic system in Europe
- End of feudalism
- Start of a new regimen
- Emergence of the current States of Europe based on national sovereignty
- Changes in France: linguistic unification
- Arrival of Napoleon to the power
There were many political consequences left by this revolution, however, one of the most prominent was that in France the absolute monarchy was abolished with the reign of Louis XVI and, failing that, a constituent assembly was created. A Constitution was created in 1791, a document in which it was reflected that the monarch did not have absolute power; the monarch Louis XVI did not accept this new legislation and, therefore, in 1793 he was executed with the guillotine. The new political landscape led to the return of classical democracy, a system that defended the liberty, equality and fraternity.
Another important point within the consequences of the French Revolution in the political plane is that the feudalism. With this change, the clergy and the nobility ceased to have the privileges that they had had until now in the French society and, therefore, had the obligation to pay taxes in the same way as the rest of the citizens. Since then, the State would be in charge of collecting all taxes and managing them, therefore, power was centralized.

Image: LorMaster blog
Social consequences of the French Revolution.
Society was also very changed after the French Revolution and, therefore, it is important to discover what were the main effects that this great revolt produced. The more important They are:
- Appearance of human rights
- Triumph of the ideas of the Enlightenment and, therefore, creation of systems that were based on reason
- Appearance of the different social classes
One of the main consequences of the French Revolution that was assimilated the ideas of the Enlightenment that defended a people based on freedom, equality and fraternity. This caused that in 1789 in France the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, a document that highlighted what were the rights of people in a society. The differences of rights by race, nationality, age, etcetera were abolished; and free expression was defended.
It is also important to note that another of the social consequences of the French Revolution was the appearance of a class society. As feudalism was abolished and the privileges of the nobility and the church were reduced, a new society appeared inspired by the capitalist model.
Economic consequences of the French Revolution.
In the economic plane There were also many consequences derived from this revolution. Below we discover a summary of the most outstanding ones:
- Triumph of the capitalist system
- Reduction of the economic privileges that the Church and the nobility had
- A class society in which there was a greater distribution of wealth
Of all of them, one of the most important was, without a doubt, the establishment of capitalism in France. This new economic model led to changes in French laws and institutions in 1789, such as the appearance of the law of free enterprise and free trade. With this, companies and factories were given more freedom to be able to trade their products and, therefore, improve the economy both nationally and internationally.
This new direction in the economy allowed merchants, farmers or manufacturers to be able to change their way of working and achieve commercial expansion both throughout the country and throughout Europe. This, added to the fact that many properties and lands were expropriated from the Church or the nobles, allowed the peasants to optimize their profits and get more economic margin and, by so much a enrichment of the popular classes.
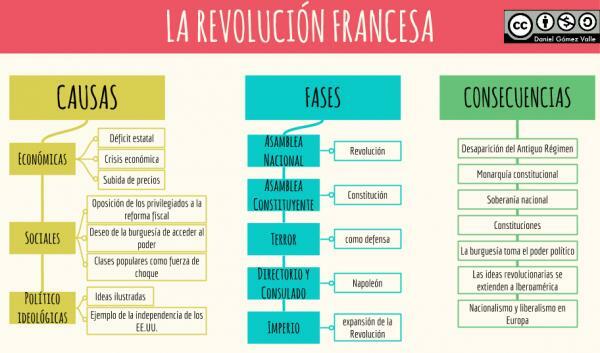
Image: Pinterest
Conclusion on the consequences of the French Revolution.
We will find a great variety of consequences after the end of the French Revolution and that also had transcendence until well past a time as we will see now.
We will describe below the most relevant consequences of the French Revolution:
- After the start of the French Revolution it is clear that there is the end of the Old Regime and with it the end of feudalism and the privileges of the Church.
- We will find on the other hand the appearance of the Declaration of Human Rightsand.
- It was the moment by which we will find the first ideas about nationalism and democracy for Europe.
- The birth of the metric system.
- The great violence unleashed during the rule of terror, would inspire other moments in European history, such as the Russian revolution of 1917.
Although these are the most outstanding elements after the end of the French Revolution, we have to say that society hardly changed in post-revolution France. Well, although a democracy was established, it was established by mostly bourgeois and therefore they would seek improvements for the people of their own group, leaving them as the old nobles.
This only changed when the most radical parties (the sons of the people) came to power, they only sought the end of every vestige of the Old Regime and violence was their greatest weapon. In this way we will find governments known as "terror" in which any person was taken to the scaffold for a mere suspicion of having a relationship with the Old Regime.
All this series of hesitations within governments would make a series of characters come to power who destabilized what was achieved by the revolution, among them the same Napoleon Bonaparte, which without being of the royalty, would get to be crowned emperor of the French thus eliminating democracy in France and returning again almost to an absolute monarchy.
Another of the moments of great destabilization came from the hand of the Bourbon restoration in 1814, by which time two sides faced each other in France, one who did not care about the return of the Bourbon monarchy (although this time of parliamentary manner) and another that did not welcome the return to the French throne of the family that had led France to the deepest misery. Thus we will find another series of confrontations and more deaths that ended with the expulsion of the Bourbons from France forever.
The only thing that is clear is that from that moment on, the Church in France would no longer be the same, since the kingdom became secular.
If you want to read more articles similar to Consequences of the French Revolution - Summary, we recommend that you enter our category of Story.



