ROMAN mythology: gods and characteristics

The Ancient Rome It is one of the most important civilizations in the history of humanity, being one of the cradles of Western civilization and all Europeans being cultural descendants of them. To talk about one of the most important sections of Rome in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we are going to offer a summary of Roman mythology: gods and characteristics.
When talking about Roman mythology we must bear in mind that it underwent a great evolution from its origin to its end, since at the beginning they were a series of beliefs related to the rituals performed by the Etruscans and trying to create myths about more mundane things.
It was not until later times that the most recognized gods of Roman mythology appeared and that it was more like what we usually understand as mythology, being a consequence of the influence of the Greek mythology and the need to explain the origin of the great city of Rome.
How late many of the Roman beliefs arrived can be seen in ancient Roman texts, as many of the historians of the first ages did not speak about creation or about many of the more ancient gods. important. They focused more on other aspects, demonstrating that it was later and due to the influence of other civilizations, especially the Greek, that Roman mythology managed to evolve into what we know at the moment.
It should be noted that, although the origin of the gods of Rome happened with the culture already advanced, all of them were included in the history of the origins of the city, so it is normal to see their appearance in myths based on situations in which the Romans still did not believe in these deities, being a kind of a posteriori change of their beliefs
The great Greek influence, both in this aspect and in many other Roman ones, made the vast majority of Roman gods were taken from Greek mythology, although in most cases with a name change and sometimes with certain differences on its attributes, losing or gaining relevance depending on many factors.
To continue with this lesson we must talk about the main elements that define these beliefs, in order to better understand what were these myths, that is, we must list the main characteristics that make the beliefs of Ancient Rome so important.
The main characteristics of roman mythology are as follows:
- Is a polytheistic mythology, that is to say, there are a large number of different gods. Being very common that there were gods for all aspects of life.
- The gods generally came from other cultures, whether it was the Greek or other peoples conquered by the Romans.
- The roman gods and goddesses they personify every aspect of life and also the many natural phenomena.
- Roman mythology fuses the pcultural borrowings like the Greek with original ideas of the Romans as their rituals or cults.
- You mix the mythological elements with the foundation of your city to give it greater importance and make it seem that Rome was a unique city. It is the history of Romulus and Remus, so well known today.
- They changed names of other beliefs so that they did not look like the same deities, although they maintained most of the attributes.
- It was intended that all the conquered peoples believe in the roman beliefs, being so until the arrival of Christianity.
- Were carried out parties to honor the gods Romans and ask for their help in things like crops or war.

To continue this lesson on Roman mythology: summary and characteristics, we must talk about one of the main themes of any classical belief, its gods. For this reason, throughout this lesson we are going to list those that we consider to be the most important of the Roman pantheon. The main gods of Roman mythology are the following:
- Jupiter: Supreme God, father of gods and men, god of the sky and lightning. Her counterpart in Greek beliefs was Zeus.
- Minerva: Goddess of intelligence, just war, justice and patron of artisans. Her counterpart in Greek mythology was Athena.
- Juno: Queen of the gods and goddess of the family and marriage, being she along with Jupiter and Minerva members of the trinity of the gods. In Greece her role was in the hands of Hera.
- Neptune: God of the seas, horses and earthquakes. His Greek counterpart was Poseidon.
- Mars: God of war, being one of the main Roman gods, much more than his counterpart Ares for the Greeks.
- Venus: Goddess of love and beauty, she being one of the most represented goddesses in history. His Greek counterpart was Aphrodite.
- Phoebus: God of light, poetry, music and medicine, being the Roman counterpart of the god Apollo.
- Diana: Artemis's counterpart was the goddess of the hunt, the moon, and peace.
- Mercury: God of messengers and travelers but also a messenger of the gods, like his counterpart Hermes.
- Bacchus: God of wine, occupying a very important role due to the relevance of this alcohol for the Romans, much more common than Dionysus in Greece.
- Vulcan: Represented with the anvil and the hammer as well as his counterpart Hephaestus was the god of volcanoes and blacksmiths.
- Pluto: God of the dead and like Hades King of the Underworld.
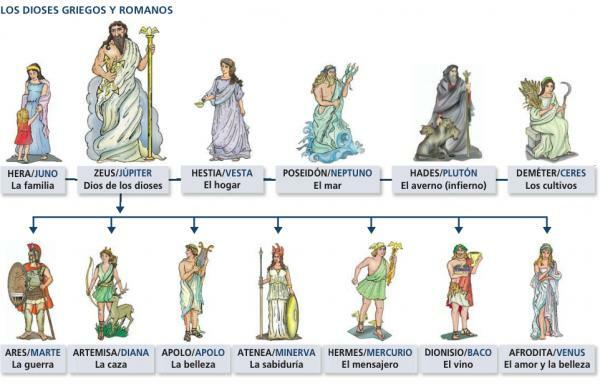
Image: Pinterest