DEFINITION of positive or negative IONS

As we already know, atoms they are formed by subatomic particles. Of the three types of subatomic particles, only neutrons have no electrical charge. Instead, protons have a positive electric charge while electrons have a negative charge. Only the electrons, which occupy the periphery of the atom, can be transferred from one atom to another, while the protons in the nucleus keep their number stable. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see what happens when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons. That is, we will see the definition and examples of positive or negative ions.
Index
- What are ions? Easy definition
- Ion formation: electroaffinity and electronegativity
- What are negative ions? With examples
- What are positive ions? With examples
What are ions? Easy definition.
A ion is any atom or molecule with net electric charge. That is, it is an atom or set of atoms linked together, whose electric charges are not compensated. This decompensation of charges occurs when one or more electrons join or leave an atom or set of atoms.
The ions are thus charged atoms or molecules, due to the gain or loss of electrons (subatomic particles with negative charge and negligible mass).
Ion types: monatomic and polyatomic
If we take into account the composition of the ions, two types are distinguished: monatomic ions and polyatomic ions.
- As the name suggests, monatomic ions those that are formed by a single atom.
- Ionic compounds o polyatomic ions are those in which the atoms are covalently bonded (sharing one or more pairs of electrons in the bond) presenting a number of neutrons in the molecule different from the total number of electrons.
- The polyatomic ions they usually contain oxygen and they usually have a structure with a central atom around which the remaining elements that make up the molecule are arranged.
- The charge of monatomic ions of the representative elements (families 1 and 2 of the table and families 13 to 17 of the periodic table) can be easily deduced if their location within the periodic table is known. In these cases the atoms gain or lose electrons in order to reach, in their valence shell, the configuration of the noble gas of its period (s2p6), or what is the same, fulfill the octet rule.
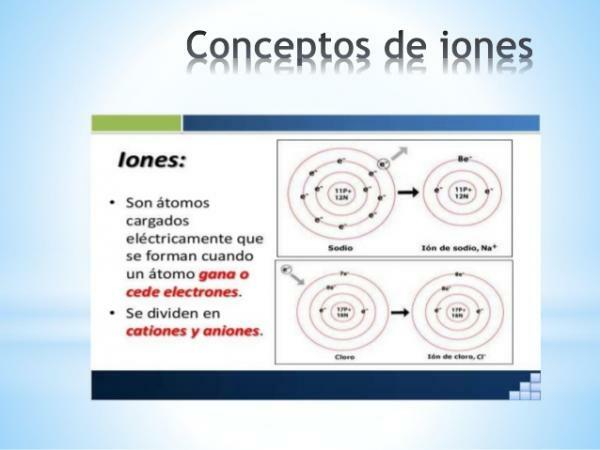
Image: Slideshare
Ion formation: electroaffinity and electronegativity.
The ability of atoms or molecules to form ions is determined by two periodic properties: electroaffinity and electronegativity. Both properties increase in value over a period and decrease as we descend through a group or family of the periodic table.
The electroaffinity, also called electron affinity, is an atomic property that is defined as the ability of an atom to attract electrons. In the case of compounds, a similar property called electronegativity which is defined as the ability of an atom to attract electrons when it forms a bond with another atom. Both properties thus define the tendency of an element to capture or lose electrons.
Ionic bonds
In their solid form, ions form compounds or ionic crystals (salts), formed by the combination of ions of different sign joined together by means of ionic bonds. The best known example of this type of compound is common salt (Sodium chloride: NaCl).
The ionic bond consists of unions of ions of different sign by means of electrostatic attractive forces (attraction between charges of opposite sign). Elements whose electronegativity or electro-affinity is very different (metallic and non-metallic elements) intervene in this type of links. In most cases, these ionic compounds are soluble in water and other polar solvents.
In aqueous solutions, ionic compounds dissociate into free ions, which are called electrolytes, since its presence in the solution makes the water behave as an electrical conductor.
What are negative ions? With examples.
The negative ions They are called anions. In all cases, they are atoms of non-metallic elements or molecules that contain non-metallic elements. These elements are characterized by having very high electro-affinity and electronegativity. That is, they are ions formed by elements with a high tendency to capture electrons.
Monatomic anions: definition and examples
They are the anions formed by atoms of non-metallic elements (groups 13 to 17 of the periodic table), which have gained one or more electrons. These anions have in common the noble gas electronic structure (s2p6) in its outermost electron shell (valence shell).
Examples:
- Chloride ion: Cl-
- Fluoride ion: F-
- Iodide ion: I-
- Sulfide ion: S-2
- Nitride ion: N-3
Polyatomic anions: definition and examples
They are negatively charged ions formed by two or more atoms of non-metallic elements linked by covalent bonds. They are the most common polyatomic ions. The most common polyatomic anions are oxoanions, which are made up of a non-metallic central atom and contain oxygen.
In general, they are considered to be chemical compounds obtained when an acidic compound loses one or more protons (H+). These polyatomic anions can retain some hydrogen in their structure, which gives them a certain acid character (ability to give up protons).
Examples:
- Nitrate ion: NO3-
- Permanganate ion: MnO4-
- Phosphate ion: PO4-3
- Hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate ion: HCO3-
- Sulfite ion: SO3-2
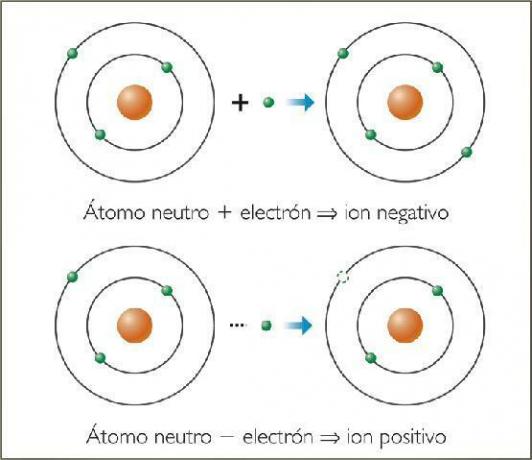
Image: Naturopathy
What are positive ions? With examples.
Positive ions are called cations. In almost all cases, they are atoms of metallic elements or molecules that contain metallic elements. These elements are characterized by having a very low electro-affinity and electronegativity, which is why they show a clear tendency to lose electrons.
Monatomic cations: definition and examples
They are ions with a positive charge (due to the loss of electrons) formed by a single atom of a metallic element. In this case, the cation is formed by the loss of electrons that allow the element to empty its outermost electronic layer and acquire a noble gas configuration (s2p6) from the lower level. They are the most common type of cation.
Examples:
- Hydrogen or hydron cation (also called proton): H+
- Sodium cation: Na+
- Iron (III) cation or ferric cation: Fe+3
- Calcium cation: Ca+2
- Copper (II) or cupric cation: Cu+2
Polyatomic cations: definition and examples
Polyatomic cations are those formed by two or more atoms. They are rare, the most abundant are the so-called homopolyatomic cations which are those that contain more than one atom of the same element, in the case of the trihydrogen ion, it is one of the most abundant molecules in the universe. Polyatomic cations formed by atoms of different elements are not common but are characterized by the presence of hydrogen and is considered to originate when a basic compound captures a proton (H+).
Examples:
- Ammonium cation: NH4+
- Oxonium cation: HO3+
- Phosphonium cation: PH3+
- Trihydrogen cation or protonated molecular hydrogen: H3+
- Dimercury cation: Hg2+2
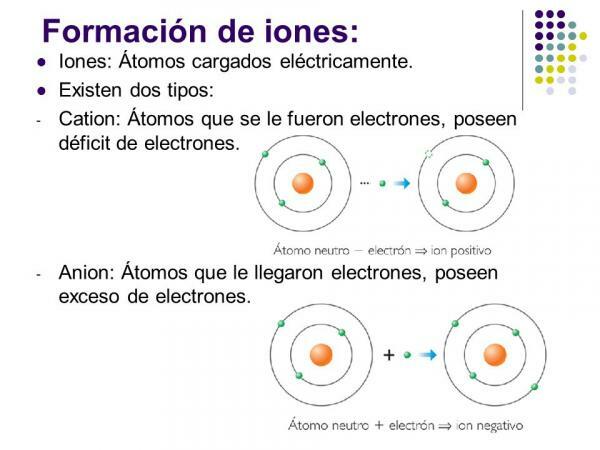
Image: Planets
If you want to read more articles similar to Negative and positive ions: definition and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of The atom.
Bibliography
Alejandrina Gallego Picó, Rosa Mª Garcinuño Martínez, Mª José Morcillo Ortega, Miguel Ángel Vázquez Segura. (2018) Basic chemistry. Madrid: Uned