RUSSIAN CIVIL WAR: causes, development and consequences

One of the most relevant events in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century was the revolution suffered in Russia that started a war that would directly affect the entire world throughout the entire century. This revolution was the origin of a power that the United States would face as the first world power for decades. To talk about this relevant war in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we offer you a summary of the russian civil war.
When talking about the antecedents of the Russian civil war, we must focus on two facts that were the keys to the beginning of the war and in which all the causes and antecedents came together: theRussian Revolution o February Revolution and also on the October Revolution.
For years, Russia had suffered numerous crises, including a serious economic crisis with great famines and poverty, a war crisis in which the Russian nation had suffered great defeats in the First World War and a political crisis in which the socialists each day had greater support and where the tsar was increasingly seen in the worst possible way.
In this situation, the people rose up against the tsar and his government and the socialists united to lead the people in a revolution that bore the name of February Revolution.
The revolution that took place between March 8 and 16, 1917 ended with the end of tsarism and with the division of power in Russia between a provisional government and the Petrograd Soviet, whose estrangement was the cause of the October Revolution.
In November 1917 the second revolution of Russia, or second part of the revolution, known as the October Revolution. This revolution started by the so-called Bolsheviks was key to the start of the war, being responsible for the end of the provisional government, the creation of so-called Soviet Russia and the beginning of the Russian civil war.
The Russian Civil War was a confrontation that took place between November 1917 and June 1923 facing the Bolsheviks and their Red Army against the military defenders of tsarism that were formed by the call White Movement.
We must understand that the war was so huge that some nations helped one or the other side, being the Bolsheviks aided by nationalist groups of workers from other regions and the White Movement by countries such as the United States or Japan.
At first it seemed that the Bolsheviks were going to end the war quickly, being able to lay waste to much of the region with almost no opposition. It was in this situation that some of the world's greatest powers, such as The United States, England or France supported the White Movement, fearful that the Bolsheviks could start a world-class socialist revolution. Foreign aid and uprisings in various parts of Russia made the supporters of tsarism they will win their first battles.
As the months passed, the White Army began to attack from numerous flanks to try to lock up the Bolsheviks who, little by little, were running out of territories to dominate, at the same time that the whites advanced towards the center.
In a situation that seemed of victory, and after some pacts signed between foreign nations and the government Bolshevik, the allied countries of the White Army withdrew much of their men and weapons causing White's advantage was decreasing. The new situation made the Bolsheviks begin the counterattack against the white troops and begin the recovery of their territories.
The power of the Bolsheviks was again superior and, for this reason, the White Army troops had to withdraw to the east, while the Reds took all the regions that their enemies were abandoning. For years, the remnants of the White Army remained in the Crimean area, while the Bolsheviks took the entire region and won the war.
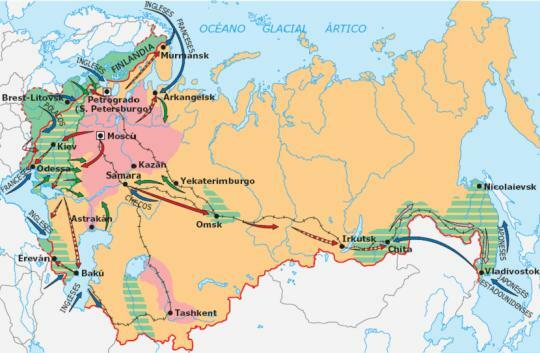
Image: Red Historia
To end this summary of the Russian civil war, we must talk about the main consequences of the Bolshevik victory and the end of such a long war. The main consequences of the russian civil war were the following:
- Defeat of the white movement ending any option of the Tsar's return and causing the departure of many Russian inhabitants who agreed with white ideas. This situation created a new Russia where the common thing was that people had ideas similar to the government.
- Defeat and expulsion of the allies that they were still helping the whites, being the beginning of a tense relationship between these nations and the USSR.
- Birth of the so-called anti-Bolshevik revolutionary groups, who fought against the existence of the new government both violently and peacefully and who formed numerous groups around the country.
- Control of the Bolsheviks in almost all of Russia, existing a few foci of distance with the ideas of these. Using a system of propaganda and education for people to defend communist ideas.
- Formation of independent republics like Finland, Lithuania, Poland, Estonia and Latvia.
- Severe economic crisis as a result of the great damage caused by the war, since the nation was in a situation of chaos.

Image: Social and language