Time zones: what they are, how they are calculated and examples
The time zones are a series of 24 sections in which the Earth is divided, using the zero meridian or Greenwich meridian as a reference. In each of these divisions a specific time governs, therefore they are a useful resource to organize time around the world.
Each time zone measures 15 degrees, which is the result of dividing the 360 degrees of the earth's sphere by 24, which is the number of hours it takes for the Earth to turn around its own axis and which is the measure of one day in the planet.
The 15 degrees measured by each time zone represent one hour, which will be calculated according to its direction (east or west) in relation to the Greenwich meridian. Therefore, the 24 spindles correspond to 24 hours a day.
How time zones are calculated
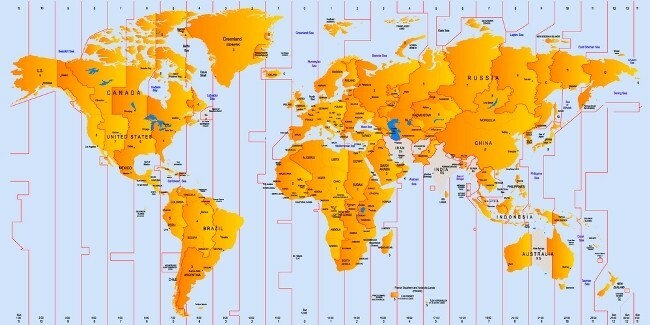
The 24 time zones are governed by a time standard called UTC (Coordinated Universal Time), which is obtained in turn from International Atomic Time, a scientific standard that measures time from atomic clocks that are found in various parts of the planet, and that so far has turned out to be the most precise.
The planet's time zones are calculated using a unique reference: the zero meridian or Greenwich meridian, located in London. From the zero meridian to the east, add one hour to each time zone as dictated by the UTC standard.
On the other hand, Time zones from the Greenwich meridian west have one hour subtracted from each.
The reason for this is that the Earth rotates in that direction (from west to east). For this reason, the hourly calculation of the zones that run through that direction is called positive deviation, while the calculation of the spindles that go in the opposite direction (towards the west) is called deviation negative.
See also Differences between parallels and meridians.
Examples of time zones
We can quickly calculate the time of a specific region or city by knowing its time zone, remembering that if the zone is negative, the hours are subtracted and if they are positive, they are added. These are some examples:
UTC ± 00:00
It is the time zone that corresponds to the zero meridian, or Greenwich Mean Time. Some countries or areas that share this zone are:
- Mali
- Gambia
- Ivory Coast
- Portugal (except the Azores islands)
- Greenland
- Ghana
- Mauritania
- United Kingdom (including Great Britain, Northern Ireland, Isle of Man, Channel Island, Guernsey and Saint Helena, Tristán de Acuña and Ascensión, located in Africa)
UTC -05: 00(five hours less)
It is the time zone of:
- Mexico
- Colombia
- Canada
- Peru
- Some regions of Brazil and the United States.
In this case, the time zone is negative, it means that 5 hours must be subtracted from the time indicated by the Greenwich meridian. Therefore, if in the localities that are located in that meridian it is 8 o'clock at night (London time, for example), in all the regions that correspond to the UTC -5 time zone it would be 3 o'clock in the afternoon.
UTC -12: 00(twelve hours less)
It is the time zone of two US islands:
- Baker Island
- Island holand
If it is 6 o'clock in the afternoon on the zero meridian, on those islands it is 6 o'clock in the morning.
UTC +06: 00(six more hours):
It is the time zone of:
- Bangladesh
- Russia
- Bhutan, among others.
If the meridian zero is 8 in the morning, in the countries mentioned it will be 4 in the afternoon
What are time zones for?
Time zones are used to organize time around the world. Previously, the hours were based on different meridians according to what the authorities of each country or locality decided, and this had a series of consequences in daily life.
With the creation of the spindle system, the time measurement of the 24 time zones is governed from the zero meridian, and having a single origin, the calculation of the time in each place.
The proposal of a world time governed by the spindles, but subordinated to the zero meridian was of the Scottish-Canadian engineer Sandford Fleming, who with his initiative helped create a coherent system of organization of time that started from a single origin at the end of the XIX century.
See also:
- Parallels and meridians
- Map types