Polar Bodies: Definition and Function
One of the most important processes during the life of animals is reproduction. For this to occur, animals have to generate two types of gametes, depending on our sex: eggs and sperm. During the formation of the ovules (oogenesis), in addition to the ovules, cells called polar bodies or corpuscles are generated, which apparently do not have a specific function. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see what polar bodies: definition and function.
Index
- What is a polar corpuscle
- When are polar corpuscles produced?
- Function of polar corpuscles
- Can the polar body be fertilized?
What is a polar corpuscle.
The body or polar corpuscle is defined as a remnant or by-product of meiosis that occurs during the oogenesis. For some researchers, this remnant is not a full-fledged cell since, in mammals, it has chromosomes that are not have been selected to go to the ovule but little cytoplasm and also lacks enough organelles to become a Ovum.
In some species of plants or insects, the polar bodies are fertilized in a normal way while in other cases, it can be divided by parthenogenesis. In these species, more than one fertilization occurs in each oogenesis, so more offspring can be produced in each reproductive cycle.
When are polar corpuscles produced?
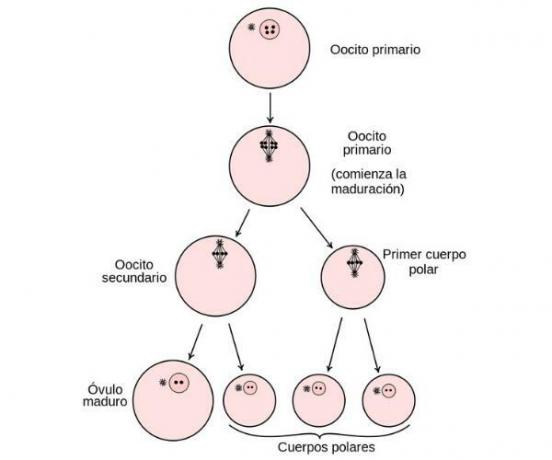
The polar bodies are produced during oogenesis, in the two cycles of meiosis that occur. The first meiosis is complete just before the woman ovulates and as a result, in addition to oocyte II, the first polar body is generated. These two cells are released during ovulation and undergo a second meiotic division. In it, the secondary oocyte forms two other cells: a large one, which contains most of the original cytoplasm (and will give rise to the mature ovum), and a small or second polar body.
Therefore, as a result of oogenesis, three polar bodies are produced, which disintegrate rapidly since under normal conditions they cannot be fertilized.
Function of the polar corpuscles.
What is the function of the polar corpuscle? The only function of the polar bodies during meiosis is reduce the genetic material that the mature oocyte has, that is, it contains the genetic material that allows the oocyte to be a cell with a single set of chromosomes (haploid). Before the first meiosis, the genetic material of the oogonia is duplicated, so we have two copies of the two chromosomes; During meiosis I, the two copies of a chromosome go to the secondary oocyte while the other half go to the polar body. Then, during meiosis II, the secondary oocyte (also the polar body) separates the chromosomes again and one of the copies goes to the mature oocyte and the other to the secondary polar body. In this way we have reduced the genetic material of two copies of two chromosomes, in the primary oocyte, to one copy of a chromosome in the Ovum mature.
Secondarily, polar body analysis can be used in an assisted reproductive technique called polar corpuscle biopsy. Thanks to this technique, embryologists are able to extract the polar bodies of a woman to analyze her genetic information and indirectly know the state of her eggs. It would be like looking at the discarded pieces of the puzzle, allowing us to know that the mature ovum has the correct chromosomes in the correct number. This allows them to discard the eggs that contain chromosomal abnormalities when doing reproductive treatments. assisted and allows specialists to choose the best eggs from women who are older or have few eggs (low reserve ovarian).
Can the polar body be fertilized?
Under normal conditions, the polar bodies degenerate upon completion of meiosis II. Without being fertilized and without performing any function other than that of allowing the chromosomes they are not chosen to form the mature ovum.
In some exceptional occasions, the polar bodies are fertilized. Being cells of such small size, with little reserve substance and few organelles, normally, the resulting embryo dies and an abortion occurs. In some exceptional cases, this embryo manages to survive and a double pregnancy occurs, in which the mature ovum and the polar body have been fertilized. In this case, the babies that are born are the product of two different sperm and the oocyte and the polar body, so they are not identical. These babies are called semi-identical twins or polar-bodied twins. These siblings, despite being born in the same birth, are just as similar to siblings who were born in two different births, the product of two eggs and two sperm different. Semi-identical gems are very exceptional cases (around 1% of twins), especially in cases of natural pregnancy in which assisted reproductive techniques are not used.
If you want to read more articles similar to Polar bodies: definition and function, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.