POLLINATE meaning and characteristics

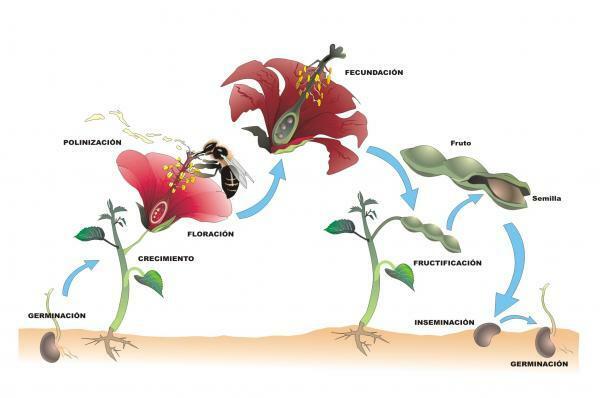
The pollination process is defined as the transport of the pollen grain or grains (male gamete) from the anther, where it is formed, to the stigma of the same flower or a different flower. East sexual reproduction mechanism it is important, since it allows plants to have descendants, since the union of pollen and ovules (oosphere) form a new individual.
Pollination is therefore a very important mechanism for the maintenance of ecosystems, since it allows reproduction and the generation of biological diversity; In addition, the pollen and the fruits generated are the food base of many other communities. If you want to know the meaning of pollinating and characteristics pollination, in this lesson from a TEACHER we will tackle this interesting topic! We invite you to continue reading!
Index
- What is pollinating? Simple meaning
- Two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination
- Pollination characteristics: pollination vectors
What is pollinating? Simple meaning.
The pollination is the act of transporting the male gamete, the pollen grain, from the anther to the stamens, where the female gamete, the oosphere, is found. Thanks to this transport, it is possible for pollen to fertilize the oosphere, producing a new individual: the seed.
Pollen can fertilize an oosphere of the same flower (self-pollination, direct pollination or autogamy) or to an oosphere found in another flower, either from the same plant or from another (cross pollination, allogamy or heterogamy). In any case, pollination allows pollen and oosphere genes to mix and form new combinations, thereby creating genetic diversity within the plant species.
Therefore, pollination is a key process for the sexual reproduction of plants, which leads to a greater diversity and the adaptation of plants to the environment and environmental conditions. This is of great importance in the study of climate and ecosystems since, a change in pollination entails an important impact on the life cycles of plants: if pollination does not occur correctly or stops, plants cannot reproduce in such a way effective. A disruption of pollination therefore affects the basic pillars of ecosystems and climate maintenance: the plants.
Due to its great importance in the natural world, the pollination process has developed, adapted and evolved throughout natural history. In addition, the study of pollination and its characteristics have made human beings capable of modifying, shaping and improving it for our benefit. It is important that we all know the meaning of pollinating and the characteristics that make it such an important process in order to maximize the yield of our crops but at the same time conserve and care for our planet, on which we depend. Therefore, as we will see in the following sections, pollination has very specific characteristics.
Two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination.
One of the most important characteristics of pollination is that there are two types of pollination fundamental: self-pollination and cross-pollination.
- The self-pollination is one in which the pollen and the oosphere it fertilizes come from the same flower, while the cross pollination pollen and oosphere are from different flowers (from the same plant or from another plant in the same species).
- The most widespread and studied pollination is the Cross pollination. This type of pollination occurs in species in which there are male plants and female plants or in species in which, the same plant, produces pollen in one part (it is male) and in another part oospheres (being female).
This is very important when planning crops since in the first case the female plants will have to be placed near the male plants and study what proportion of female plants for each male plant is more profitable to have to collect a large harvest. This is the case for example of melon plants. In other cases, such as avocado, the same plant is the one that has both sexes, so we do not have to study the proportion of female plants by male but we will observe flowering in different periods (flowering waves), totally normal.
Sometimes some plants can have both mechanisms and self-pollinate in less favorable situations, in which there are fewer individuals of its species around, and cross-pollinate when flowers are available to its around. An example of this is the handle that, in artificial crops, to improve their yield, many plants of this type are put so that there is more fertilization and more fruits are formed.

Pollination characteristics: pollination vectors.
Another important factor when studying the meaning of pollinating and the most important characteristics are vectors. For pollen transport to occur (pollination), this process can use different "helpers" or tools: vectors. Vectors can be of two types: biotic (living beings) or abiotic (lifeless forces or processes).
Biotic Pollination Vectors
The biotic vectors that make pollination possible can be different living beings, but the most important and well-known pollinators are the insects (butterflies, bees or beetles). Plants pollinated by insects are called plants entomophilous and some examples are: asparagus, sunflower, beans, almond trees and melons.
There are also plants that are pollinated thanks to the pollen transport carried out by birds such as hummingbirds. These are plants ornithophiles like geraniums or hibiscus. It is not a coincidence that the plants pollinated by the birds are relatively large and of beautiful and striking colors: it is a strategy to attract the birds and to come closer.
Vectors abiotic
On the other hand we have plants that use other forces of nature, not living, to transport their pollen: abiotic vectors. The best known case is that of plants whose pollen is carried by the wind, the plants anemophiles. These types of plants have very light pollen grains, adapted to fly and remain suspended in air currents to reach places where a long distance and sometimes they are not very good friends with humans since some species are the cause of most allergies. An example is grasses or conifers (pines).
Another example of an abiotic pollinator is water: plants hydrophilic they have pollen grains that float while their oospheres are in anthers that also float or that rise temporarily to the surface when they are mature; Thanks to this, the pollen can float downstream and pollinate very distant plants.
If you want to read more articles similar to Pollination meaning and characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Casares, M. University of Granada (s.f) Pollination. Recovered from https://www.ugr.es/~mcasares/Organografia/reproduccion/Polinizacion%20marcos.htm
- Briceño V, G. Euston69 (s.f) Pollination. Recovered from https://www.euston96.com/polinizacion/
- FAO (s.f) Bees are the diligent pollinators of fruits and crops. Recovered from http://www.fao.org/3/y5110s/y5110s03.htm