Lungs and their function

The lungs are one of the most important organs of the body. The best known function of the lungs is to carry out gas exchange: in the pulmonary alveoli our body is capable of eliminating toxic gases such as carbon dioxide and taking oxygen from the atmosphere, which allows us to breathe.
In addition to respiratory function, the lungs can perform defense or metabolic functions. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see the lungs and their main function, breathing, but we will also talk in a general way about those two secondary functions that are also important.
Index
- Main function of the lungs: respiration
- Anatomy of the lungs during breathing
- The lungs as a defense barrier
- The metabolism of the lungs
Main function of the lungs: respiration.
The main function of the lungs is to carry out the breathing. During respiration, the inspired air is transported by a series of structures (mainly the trachea and bronchi) to the alveoli. The entry of air into the lungs occurs thanks to the diaphragm and a series of muscles that generate a negative pressure in the rib cage.
It is at the level of the alveoli where the gas exchange. Inspired air is found outside the alveoli, made up of a mixture of gases but mainly contains oxygen. Inside the alveoli, it meets the venous blood that comes from the different tissues of the body and that contains mainly carbon dioxide. The alveoli are small structures whose wall is quite permeable to gases, so they are produces an exchange between the oxygen in the outside air and the carbon dioxide generated by the organism.
If you want to know more about how respiration is produced, you can consult the lessons on the phases of respiration or the anatomy of the lungs.
Anatomy of the lungs during breathing.
Considering the lungs anatomy, during breathing, the lungs are able to expand and contract alternatively to carry out the respiratory cycle (inspiration or intake of air and exhalation or expulsion of air). This can be mainly due to the composition of the lungs and alveoli, the contractile parts of the respiratory system.
The interstitial connective tissue of the alveolar walls, bronchioles and capillaries is made up of elastin and collagen fibers. The elastin fibers, as their name suggests, they are elastic, so they are capable of doubling their length; the collagen fibers for their part, they limit the stretching of these structures. Once the lower airways expel the air, the elastin fibers are able to regain their original state. These fibers are arranged geometrically, forming a net, like a nylon mesh, which allows the lung to stretch in all directions and greatly increase its volume.
Once the diaphragm relaxes, the pressure inside the rib cage increases. Again, by pressure gradient, the air now leaves the lungs and the lungs contract to their original state thanks to their composition.
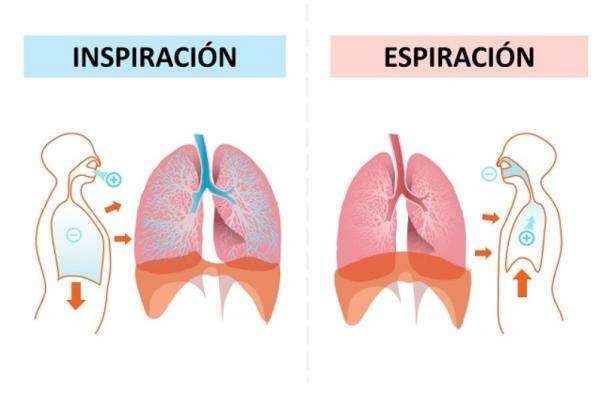
Image: Knowing is practical
The lungs as a defense barrier.
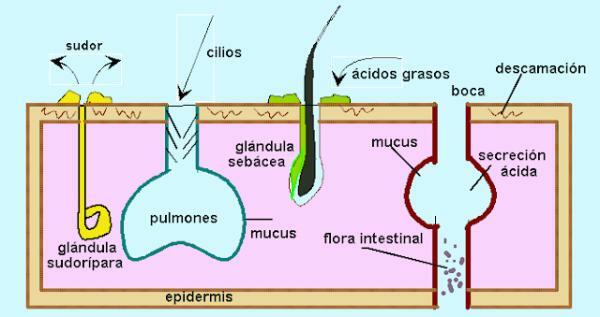
Another function of the lungs is to act as a defense for the body. The lungs are one of the great entryways for external material. The air we breathe is often a great medium of exposure to microorganisms (viruses, bacteria or even fungal spores), particles (especially dust particles) and gases (smoke, tobacco, etc.). All this reaches our respiratory tract and, if there were no immune barrier, it would enter our body.
In the upper part of our respiratory tract there are different substance removal strategies. An example is the appearance of nasal hairs and mucus in the nose create a filter that retains large amounts of particles. If these manage to reach the lower respiratory tract, they can be eliminated by mucus, cough or sneeze reflex, etc. But even so, the lung has defense mechanisms that prevent microorganisms, gases and particles that could have prevented them from reaching our bloodstream.
One of the most important is the appearance of immune cells in the alveoli: the alveolar macrophages. Alveolar macrophages are cells that are found in the alveoli, the last barrier before entering our bloodstream and are responsible for phagocytes foreign substances. In addition, different alveoli also appear enzymes that act by eliminating the particles.
The metabolism of the lungs.
Despite what it may seem, some of the cells that are part of the lung are quite active. These cells are capable of producing substances to use themselves or to travel, through the bloodstream, to other parts of the body (such as the renin-angiotensin system).
The cells of the pulmonary epithelium are capable of transforming (metabolizing) different substrates and generate energy and nutrients to support themselves. Other cells, such as pulmonary mast cells, are capable of making and releasing substances such as inflammatory mediators, responsible for inflammation and immune responses in lungs.
If you want to read more articles similar to Lungs and their function, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Sánchez, T., & Concha, I. (2018). Structure and functions of the respiratory system. Pediatric pneumology.
- University of Canrabria (May 26, 2011) Topic 2. Respiratory mechanics Recovered from https://web.archive.org/web/20161226105043/http://ocw.unican.es/ciencias-de-la-salud/fisiologia-humana-2011-g367/material-de-clase/bloque-tematico-3.-fisiologia-del-aparato/tema-2.-mecanica-respiratoria/tema-2.-mecanica-respiratoria