Discover ALL types of cell reproduction
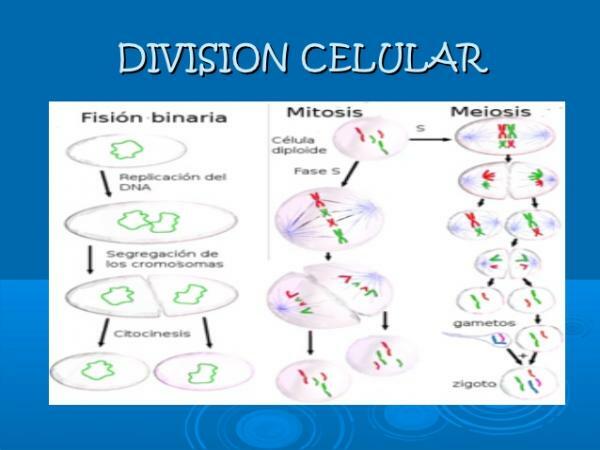
Image: Slideshare
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see the different types of cell reproduction or cell division so that you better know how this natural procedure is carried out. A cell is a smaller and minimal, morphological and functional unit of any living being. In ancient times, a class of norms or postulates were described that describe the main characteristics of cells: the cell theory. One of the main postulates of the cell theory is that all cells come from an existing cell by means of reproduction or cell division.
Index
- What is cell reproduction or division?
- Bipartition
- Budding, another type of cell division
- Sporulation or sporogenesis
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
What is cell reproduction or division?
Before getting into the different types of cell reproduction it is important that we know what cell reproduction is. It is a process whereby one cell (called a stem cell) gives rise to two or more cells (called daughter cells) is called reproduction or cell division.
This process is very important since, in organisms formed by a single cell (unicellular), they allows them to reproduce, and in organisms made up of many cells (multicellular), they allow them to replace dead cells or new ones to form to be able to grow. In the case of unicellular organisms, in certain cases
Cell division is not the same in all cases, it will be different in the case of cells that are isolated, forming complete individuals (unicellular beings) or for cells that are part of a complex organism (multicellular beings). Within this, we can find different types of cell division depending on the size of the resulting daughter cells and the amount of their genome.
In the case of single-celled organisms, we can mainly find 3 types of cell division: bipartition, budding, and sporulation. In the case of cells that are part of a multicellular organism, the cells can divide by mitosis or by meiosis. If you want to see what each of these divisions consists of and the differences between them, keep reading!
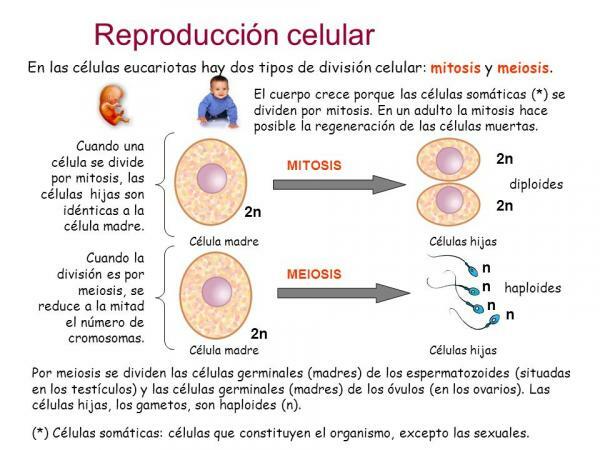
Image: SlidePlayer
The bipartition.
One of the types of cell reproduction is bipartition or binary fission is the division of the stem cell into two daughter cells of the same size and identical to the stem cell. In this type of cell division two new individuals are formed with the same structures and functions as the stem cell.
Since the two resulting daughter cells are the same, this is said to be a type of symmetric cell division. This type of reproduction is presented by organisms such as bacteria, yeasts, some protozoa and algae.
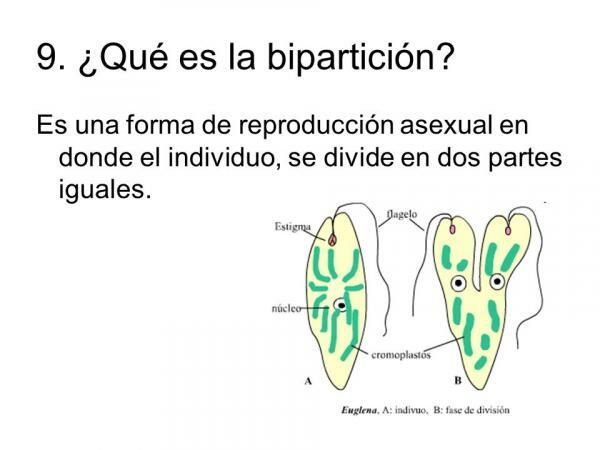
Image: SlidePlayer
Budding, another type of cell division.
The gemmationis the cell division by which the mother cell forms a lump, called buds, They grow and grow until they have the necessary structures to be able to live independently. In order to separate from the mother cell, the base of the yolk narrows more and more until the membrane that joins the two breaks and the yolk becomes an independent daughter cell.
This type of reproduction is typical of sponges (coelenterates). These buds can be of different size, so the daughter cells obtained from one cell mother may be different, so unlike division by bipartition it is a division asymmetric.
What happens if it does not separate?
Different types of organisms can have different types of reproduction by budding. In some cases, the yolk does not separate from the mother cell, so instead of forming independent daughter cells, a colony is formed. These cells live in groups, coordinated and the tasks of living beings are distributed. This type of division occurs in marine organisms called bryozoans to grow and develop, not to reproduce.
In other species, such as freshwater sponges or bryozoans, buds are produced when there are unfavorable conditions in the environment. These buds have a protective envelope that acts as a shield and protects them from environmental conditions that can threaten them.

Image: Slideshare
Sporulation or sporogenesis.
The sporulation or sporogenesis is the cellular differentiation by which the stem cell breaks or fragments its core in various parts, surrounding with an unfixed amount of cytoplasm. These new structures, called spores, surround themselves with a membrane that protects them. As they do not all have the same portion of cytoplasm, it is said that, like budding, sporulation is a asymmetric cell division.
The daughter cells that are produced are called sporesand they are cells whose main functions are to resist environmental conditions, which they are usually adverse, and spread through the middle until you reach one with the right conditions to live. Thus, the spores are said to be resistance dispersive reproductive cells.
This type of cell division occurs in fungi, bacteria, lichens, amoebas, etc. and in some plant organisms such as mosses and ferns in unfavorable situations.

Image: biology
Mitosis.
The mitosis it is another type of cell reproduction. This type is the one that occurs in most organisms eukaryotes. In this case, a stem cell grows and duplicates all its cellular structures to form two daughter cells equal to each other.
This would be a case of symmetric cell division. This type of cell division is what occurs, for example, during formation of human embryos. If you want to know more about this type of cell division, take a look at our previous post "What is mitosis?".

Image: Gtush
Meiosis.
The meiosis is a type of cell division in which a stem cell grows, duplicates all its cellular structures and divides twice in a row. In this case, the daughter cells would have half the genetic material as the mother cell. Imagine that you have a cake and you duplicate it, that is, you make another one exactly the same; now you divide what you have (the two cakes) into four equal parts: you get 4 pie halves, right? The same happens in meiosis, we obtain 4 daughter cells that are half of the original stem cell.
This type of cell division is very special and important for multicellular organisms since it allows us to create the cells in charge of reproduction (gametes). In this way, when the female gamete (ovum) and the male gamete (sperm) are rejoined through the fertilization, we will have a cell with the same amount of DNA as the starting one (joining our two halves of the cake we will have a complete cake).
Do you want to know more about this type of cell division? Take a look at our post "What is meiosis?"

Image: SlidePlayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of cell reproduction, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.