What is the Importance of MITOSIS?
Mitosis is a very important type of cell division since it is the cell reproduction par excellence, the one carried out by the vast majority of current forms that live on Earth, from the simplest bacteria to the human being. Mitosis is the type of cell reproduction that occurs in all human cells, except for gametes (eggs and sperm) that are formed through meiosis. If you want to find out what it is, what is the importance of mitosisFor both microorganisms and multicellular organisms like us, and even know how it is related to cancer, keep reading this lesson from a TEACHER!
Index
- What is mitosis?
- Mitosis in prokaryotic organisms and its importance
- Mitosis in eukaryotic organisms and its importance
- Mitosis and cancer
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a form of reproduction o cellular division in which the starting cell, called a stem cell, generates two cells, called daughter cells. In this type of cellular reproduction, two daughter cells exactly the same as the parent cell
of departure. For this to occur, mitosis begins with the resting stem cell, which grows and copies its material. gene and its organelles and then divides leaving half of its chromosomes and organelles to each of the cells. Mitosis, unlike meiosis, is said to be a symmetric division. Discover in this other lesson What is the importance of meiosis.Mitosis occurs throughout the entire evolutionary scale, from microorganisms such as bacteria to more evolved organisms such as animals (including humans). For all organisms, mitosis is a crucial process, but it does not perform the same function in all organisms.
In this other lesson from a TEACHER you can learn more about Types of cell reproduction.

Image: Slideshare
Mitosis in prokaryotic organisms and its importance.
The prokaryotic organisms They are those whose genetic material is not organized into an enveloped nucleus, but is dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. These types of organisms are usually single-cell microorganisms.
The mitotic division or mitosis is very important for prokaryotic organisms, since allows them to reproduce. Being unicellular microorganisms, when they grow enough, they duplicate their genetic material and organelles and divide, producing two complete organisms. These two organisms will be the same as the starting organism, except for errors that may have occurred during the process (mutations).
Mitosis in eukaryotic organisms and its importance.
In organisms eukaryotes, the genetic material is highly organized, forming a core surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope. Most of these organisms are more evolved and, therefore, their body is made up of more than one cell, that is, they are multicellular. An example of this type of organisms is humans, but other mammals, plants and some fungi are also multicellular.
During the evolution, the cells of these animals they specialize to perform different functions: some cells develop to form muscles, others form neurons, reproductive cells, etc. In this case, the cells that make up the body are differentiated into two types: sex cells (with reproduction function) and somatic cells (the rest of the cells in our body). In addition to function, somatic cells differ from sexual cells by containing twice as much genetic material (23 pairs of chromosomes, one copy of each chromosome from the mother and another from the father) and by the way they divide: somatic cells undergo mitosis while sexual cells divide by meiosis. We need somatic cells to be exactly copied once specialized so that they can continue to function properly.
Somatic cells divide to make copies of themselves with two goals:
- Increase of the tissue. A clear example is the bones, which are formed during puberty, while we are growing in height.
- Replacement or renewal of the cells of the different tissues. Some cells are highly active and can "wear out", that is, they age and can even die. An example is blood cells, which are produced and function for up to four months.
Depending on the type of tissue in which we are, its activity and the age of the individual, the cells will divide by mitosis with more or less frequency; therefore, there are tissues with more renewal than others. While the cells that line our intestines are renewed every 4 days, the cells of our muscles do so every 15 years.
Therefore, mitosis is very important for multicellular organisms, since it allows them to grow and renew the tissues that are wearing out.
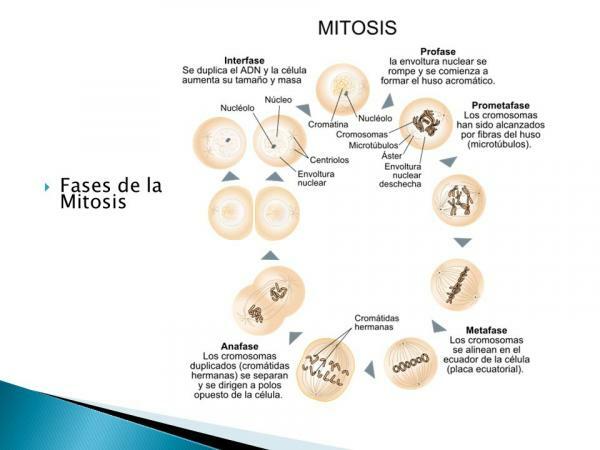
Image: Slideplayer
Mitosis and cancer.
During the cell cycle, that is, while it is still alive, the cell has different checkpoints. During division, at these points the cell checks that the division is taking place correctly and that the genetic material and the organelles of the generated cell are correct. If the cell encounters any problems, it removes the structures formed and mitosis begins again.
Sometimes cell cycle checkpoints fail and the cell begins to engage in strange behaviors. One of the most frequently occurring failures is that the division gets out of control, and the cell begins to divide by mitosis faster than it should and even ignore cells with mutations and let them continue to grow. In these cases, the cell forms a tumor. In certain cases, cells begin to divide but the body manages to stop their development and keep it stable; this is the case with a benign tumor. In other cases, the tumor keeps dividing, cells get out of control, and many mutations begin to appear; this is the case of malignant tumors or cancers. In some types of cancer, cells can become so modified that they are able to travel through the blood and begin to divide in place of other tissues (metastasis).
If you want to find out more about this topic, we invite you to watch this video from a TEACHER about a lesson about Cancer and the immune system.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the importance of mitosis?, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.


