Complete LIST with neck muscles
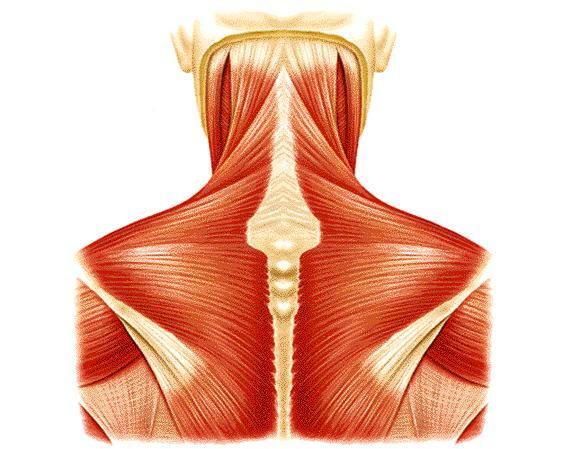
Image: Add
Of all the anatomical areas, the neck is the one with higher proportion of muscles per surface area. This is because, despite what you might think, the neck is not just the junction between the neck and the head. In addition to maintaining the weight and the correct position of the head, neck and the muscles that form it, they are in charge of performing certain movements, protect vascular and nervous structures and support the digestive tract and upper airway (pharynx, larynx, etc.). In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see what are the neck muscles, little by little in a clear way and reviewing the function of each one.
Index
- Classification of neck muscles
- Muscles of the anterior neck region
- Muscles of the lateral neck region
- Muscles of the back of the neck
Classification of the neck muscles.
The neck musculature is very complex and intricate. Neck muscles are normally long and oblique and they intertwine with each other in different planes of space. To more clearly analyze all the muscles of the neck, we are going to use a simple and intuitive first classification: muscles of the anterior region (front of the neck, in front of the shoulders), lateral muscles (join the neck with the shoulders) and muscles of the posterior region (nape, behind the shoulders).
Muscles of the anterior region of the neck.
The anterior region can also be called hyoid region since, in this is the hyoid bone. This bone is located under the tongue and above the thyroid cartilage and is shaped like a horseshoe. The muscles of the anterior region, in turn, are classified according to the position they occupy with respect to this bone: there are suprahyoid muscles (which are above the hyoid) and infrahyoid muscles (which are below this bone). The most important are:
- Suprahyoid anterior muscles: digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle, mylohyoid muscle, geniohyoid muscle
- Infrahyoid anterior muscles: sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid muscle.
One of the most important muscles in this region is the omohyoid muscle. This muscle is flattened, long and thin and runs along the sides of the neck, from the upper edge of the scapula to the hyoid bone, outside the sternocleidomastoid. Its action is very important since it depresses the hyoid bone (moves it back towards the spine) and tightens the mid cervical aponeurosis, favoring the venous circulation of the neck during inspiration.
Another important muscle in this region is the thyrohyoid muscle. This muscle, which is short and square in shape, runs close to the hyoid, from the outer surface of the thyroid cartilage lamina to the greater horn of the thyroid cartilage. Its functions are twofold: lower the hyoid bone or, if it is fixed by the previous contraction of its elevators, it acts on the larynx, which it forces to rise.
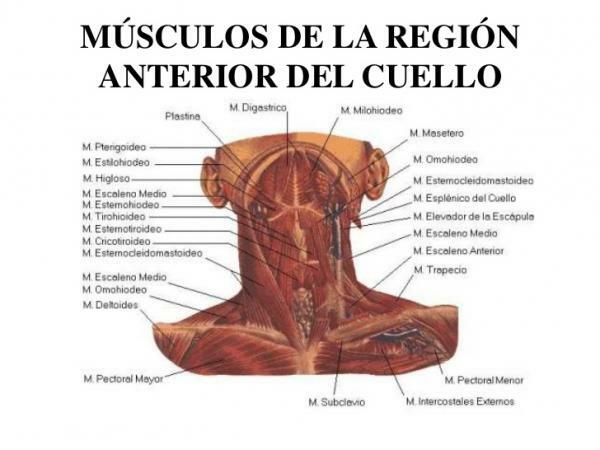
Image: Slideshare
Muscles of the lateral region of the neck.
The most important neck muscles that we find in the lateral region are the following: cutaneous muscle of the neck, sternocleidomastoid muscle, scalene muscles (anterior, middle and posterior) and lateral rectus muscle of the head.
The best known muscle in this area is the sternocleidomastoid. This muscle is even (there is one on each side of the body), long and robust and within it we can find two clearly differentiated areas or branches (sternal branch, with cylindrical shape and clavicular branch, more flattened). The sternocleidomastoid is arranged on the sides of the anterior neck, obliquely, from the upper part of the chest (inside of the clavicles) to the mastoid process (behind the ears). Its fame lies in the important functions it performs as it allows the head to rotate sideways, tilt and extend slightly. In addition, together with the scalene muscles (secondarily) it helps during breathing.
The scalene muscles. The scalene muscles is a group of three pairs of muscles on the sides of the neck, called the anterior scalene, middle scalene and posterior scalene. These muscles allow the elevation of the first two ribs taking the cervical spine as a fixed point of support, allowing us to take in air when breathing (inspirations). They have a fixed point of support on the thorax, tilt the cervical spine to its side and produce a slight rotational movement that directs the face to the opposite side. These muscles are deeper than the sternocleidomastoid and run from the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae from C2 to C7 to the first or second rib (depending on whether it is the anterior, middle or later).

Image: Human Anatomy
Muscles of the posterior region of the neck.
The back of the neck, commonly called nape, is also known anatomically as the prevertebral region. In this region we can find, among others, the following muscles: trapezius, rectus anterior superior of the head, rectus anterior inferior of the head and longus muscle of the neck.
One of the most important muscles of the posterior neck is the trapeze. The trapezius is a thin, broad, flattened, triangular muscle. It is the most superficial muscle in the posterior region of the neck and occupies practically the center of the spine on both sides. Specifically, it runs in the midline, from the external occipital protuberance (approximately where the vertebral column and skull are inserted), ligament of the nape, the medial part of the superior line, nape, and the spinous processes of the C7-T12 vertebrae (in the middle part of the thorax, where the ribs). This muscle has many functions, between them:
- When attached and attached to the trunk, it raises the shoulder and brings the scapula closer to the spine.
- Attached to the shoulder girdle, it extends the head by rotating it.
- The descending portion is a rotator of the upper part of the scapula and the ascending portion is a rotator of the lower part of the scapula.
- It is a rotator and elevator of the head and produces the rotation, recoil, elevation and abduction of the scapula.
As you can see, the trapezius is a very important muscle for the mobility of the upper part of our body, normal that it is so well known!
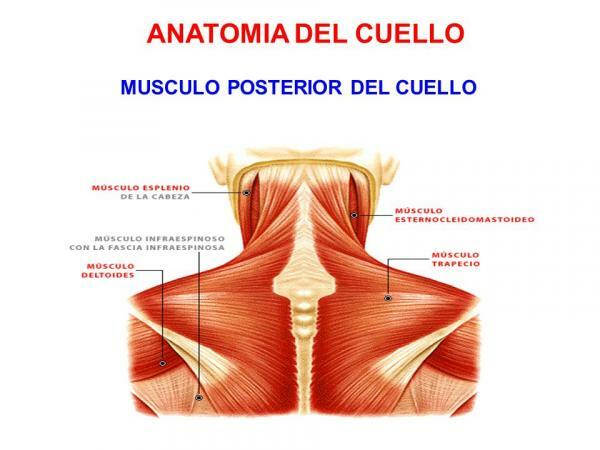
Image: SlidePlayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Neck muscles, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.