What are the parts of neurons?

One of the most important cells of the human body are, without a doubt, the neurons. Neurons have one of the most important functions in our body, being basic for good functioning of our nervous system and so that we can react to the experiences of the day to day. In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to talk about what are the parts of neurons so that you know better what our body is like and how it also works, one of the most important parts of the human body: the brain.
Before going into explaining the parts of neurons, we have to answer an important question: what are neurons?
The neuron is the structural and functional unit of nervous system. It is an elongated cell specialized in conducting nerve impulses. That is, it is in charge of transmitting the messages that come to us through the nerves through our body, and therefore one of the most important cells in our body.
There are 27 trillion cells of different types in the human body. There are approximately between 80 and 100 billion neurons in the brain
human. Therefore we can see that the importance of neurons does not essentially lie in their number in the human body, if what makes them so important are the functions they perform.Its main task is that of nerve impulses, made through the synapse. The synapse is the approximation between two neurons, and these contacts lead to the transmission of the nerve impulse. But not all neurons are the same, the enormous amount of tasks they must perform makes them end up specializing, and dividing into different types of neurons.
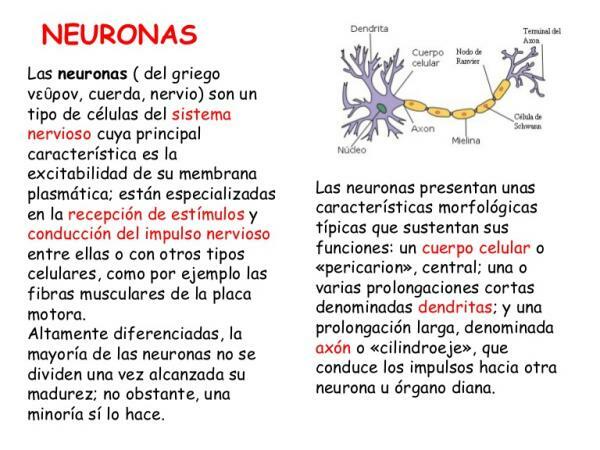
Image: Slideshare
There are several ways to classify neurons, depending on various criteria.
1- According to its function:
- Sensory neurons: They receive the information from abroad.
- Motor neurons: They conduct the nerve impulse until the response begins.
- Interneurons: Its function is to connect the sensory with the motor.
2-According to the number of extensions of the soma:
- Bipolar: Two extensions. One acts as an input and the other as an output.
- Unipolar: Just an extension. It works both as an input and an output.
- Multipolar: The most abundant in our central nervous system. They have many inlet extensions and only one outlet.
3- According to the size of the extensions:
- Polyhedral: They are shaped like polyhedra.
- Fusiforms: They are neurons that are spindle-shaped.
- Spherical: With spherical shapes.
- Starry: It is shaped like a spider.
- Pyramidal: With pyramidal shape.
In this video of a PROFESSOR we discover the different types of neurons that exist.
In this section we are going to talk about what are the parts of neurons. Although, as we have seen in the previous section, there are many types of neurons, they all have a similar structure. There are certain parts that all neurons have in common.
- Soma: It is the cell body of neurons. It is also called the pericarion. It is where the nucleus of neurons is located, from where two types of prolongations are born. Its shape is variable, and there the energy is produced for the functioning of neurons.
- Dendrites: They are extensions that come out from the soma and are shaped like branches. Its function is to receive information from other cells and transmit it to the soma. The number of dendrites can vary depending on the type of neuron it is.
- Axon: It is an elongated structure that comes out of the soma and extends in the opposite direction to the soma. Its function is to transmit information from the soma to another neuron, cell, muscle or gland in the human body. The axons can be covered with myelin, a substance that allows a faster circulation of the nerve impulse.
- Ranvier's nodules: They are periodic constrictions of the myelin sheath that surrounds the axon. Its function is that nerve impulses travel with greater speed.
- Neurolemocytes (also called Schwann Cell): These are cells that accompany neurons during their growth and development. They are the ones that make up the myelin sheath that we mentioned earlier.
- Myelin sheath: Forms a thick layer around the axons that allows nerve impulses to reach longer distances.
- Nissl's bodies: They are small structures found in the cytoplasm of the cell. They are mainly found in soma and dendrites.
- Synaptic buttons: It is the extreme part of the axon that divides to produce different terminals that produce synapses with other neurons.
- Neurites: It refers to any expansion of the soma of a neuron, be it a dendrite or an axon.

Image: La Reserva
If you want to read more articles similar to What are the parts of neurons? - Scheme with images, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.