What is a NEURON and its function

The neurons They are one of the most well-known and popular cells in the human body since they are part of one of the most complicated, enigmatic and important organs of the human body: the brain. They are a type of specialized cells that mainly make up the nervous system. As we will see below, the main function of neurons is receive, process and transmit information.
Thanks to this we are able, for example, to receive a visual stimulus, process it and generate an appropriate response. But how is this function carried out? If you want to know what is a neuron and its main function inside the human body, we invite you to continue reading this lesson from a TEACHER.
Index
- Definition of neuron and main characteristics
- The main function of neurons
- Synapse and types of synapses
Definition of neuron and main characteristics.
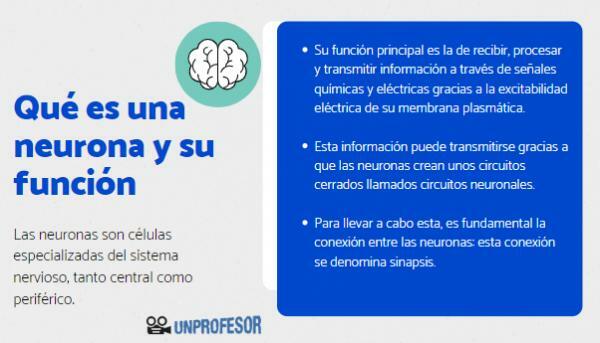
The neuronsare specialized cells of the nervous system, both central and peripheral. They are well known because these are cells in charge of memory and memories, of responding to internal and external stimuli, etc. In short: neurons make us who we are. When the function of neurons is altered or compromised, we begin to have diseases that take us away from our normal behavior.
But what characteristic makes neurons so special? The main defining characteristic of neurons, which do not have other cells is the electrical excitability of its plasma membrane. The excitability of its membrane occurs thanks to the creation of a Membrane potential, that is, there is a difference in electrical charges between the outside and the inside of the cell, which It is due to an uneven distribution of ions to one side and the other (mainly potassium, chlorine and sodium).
When the resting membrane potential changes, the neuron's membrane becomes excited. These changes in potentials or excitations is what neurons handle as information. Once the neuron has received excitation, the membrane potential is produced (which triggers the response) and the neuron returns to its initial or resting state. This is done thanks to the ion pumps inside it, which restore the existing concentrations before the alteration. In this way, the membrane is again receptive to a new stimulus.
The main function of neurons.
Now that you know what it is, let's analyze the function of the most prominent neuron. As we have already seen, neurons are specialized cells of the brain whose main function is to receive, process and transmit information through chemical and electrical signals thanks to the electrical excitability of its plasma membrane. This information can be transmitted thanks to neurons creating closed circuits called neural circuits. A neuron is seldom capable of performing its function in isolation, if not you need others to complement it.
Therefore, the main function of neurons is to create networks for the transmission and exchange of information. To carry out this, the connection between neurons is essential. This connection is called synapse, and it is not simply a place of contact between two cells, but a complex system.
In the synapse they intervene: the neuron that allows the entry of information (pre-synaptic neuron), the neuron that receives it (postsynaptic neuron) and the means by which the exchange of information takes place: the synapse. This exchange can be done in two ways: through electricity or electrical impulses (electrical synapses) or through chemicals or neurotransmitters (chemical synapses).
The synapse and the types of synapses.
The function of the neuron will be clearly influenced by the type of synapsethat occurs between the neurons that form the neuronal circuit that is involved in the transmission of information.
- The chemical synapses are responsible for the release of neurotransmitters, which can affect the neurons that are making the synapse, but can also travel across the blood and affect more distant regions of the brain or even organs that are very distant (function hormonal). For this reason, they are slower synapses, which take a little longer to respond to the arrival of information; they are said to have some synaptic lag.
- The electrical synapses are those in which, upon the arrival of an electrical impulse, they generate an energy exchange between the pre-synaptic neuron and the post-synaptic neuron. This electrical exchange is done through ion transport, which can be bidirectional. They are generally less complex and faster synapses, with a narrow synaptic gap and little or no synaptic lag. They are normally involved with the most primary defense and flight mechanisms, that is, the unconscious motor responses.
Although in this lesson we have focused on the communication between neurons through the synapse, we must take into account that neurons can make contact with other types of cells, such as muscle fibers in plaque motorboat. This is what ultimately causes muscle contraction and causes our muscles to move.
But neurons are also responsible for transmitting autonomous nerve impulses, which allow us to breathe, digest food, etc.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is a neuron and its function, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Megías M, Molist P, Pombal MA. (2019). Atlas of plant and animal histology. Cell types. Recovered from: http://mmegias.webs.uvigo.es/8-tipos-celulares/listado.php
- García-Allen, J (s.f) Types of neurons: characteristics and functions. Recovered from: https://psicologiaymente.com/
- Kardong, K. V. (1999). Vertebrates Comparative anatomy, function, evolution. McGraw-Hill.
- Paniagua, R.; Nistal, M.; Sesma, P.; Álvarez-Uría, M.; Fraile, B.; Anadón, R. and José Sáez, F. (2002). Plant and animal cytology and histology. McGraw-Hill.


